Overview
The FlowX Knowledge Base integration enables you to ingest static documents into contextual Knowledge Bases that AI agents can query when preparing responses. This integration provides a centralized repository for information that can be semantically searched and retrieved by AI agents during workflow execution.Knowledge Bases use vector embeddings and semantic search to find the most relevant information for AI agent queries.
Key features
- Centralized content management: Upload documents into organized Knowledge Bases
- Multiple content sources: Manage content by splitting it across different sources for better organization
- Semantic search: AI agents can find relevant information using natural language queries
- Testing capabilities: Test queries and operations in isolation before adding them to workflows
- Content versioning: Append, replace, or delete content sources with full traceability
- Relevance scoring: Understand which content chunks are most relevant for agent responses
How it works
High-level workflow
- Create Knowledge Base: Add a new Knowledge Base data source in Integration Designer
- Ingest content: Upload documents into content sources
- Automatic chunking: Content is automatically split into chunks and indexed for semantic search
- Query in workflows: AI agents query the Knowledge Base to find relevant information
- Monitor usage: Track which chunks are used and their relevance scores in console logs
Main capabilities
Content ingestion
Manual upload
Upload PDF documents directly from the Knowledge Base admin interface
Content management
Organize by sources
Manage content by organizing it into separate content sources for better control and traceability
Append or replace
Update existing content sources by appending new information or replacing it entirely
AI agent integration
AI agents can use Knowledge Bases with the ReAct (Reasoning and Acting) model to:- Find relevant information based on user queries
- Understand which content sources provided the information
- See relevance scores for retrieved chunks
- Make informed decisions based on contextual knowledge
Content sources
Content sources represent individual collections of information within a Knowledge Base. Each content source can be:- Manual: Files uploaded through the Knowledge Base admin interface
- Workflow: Content ingestion through workflow operations (planned for future release)
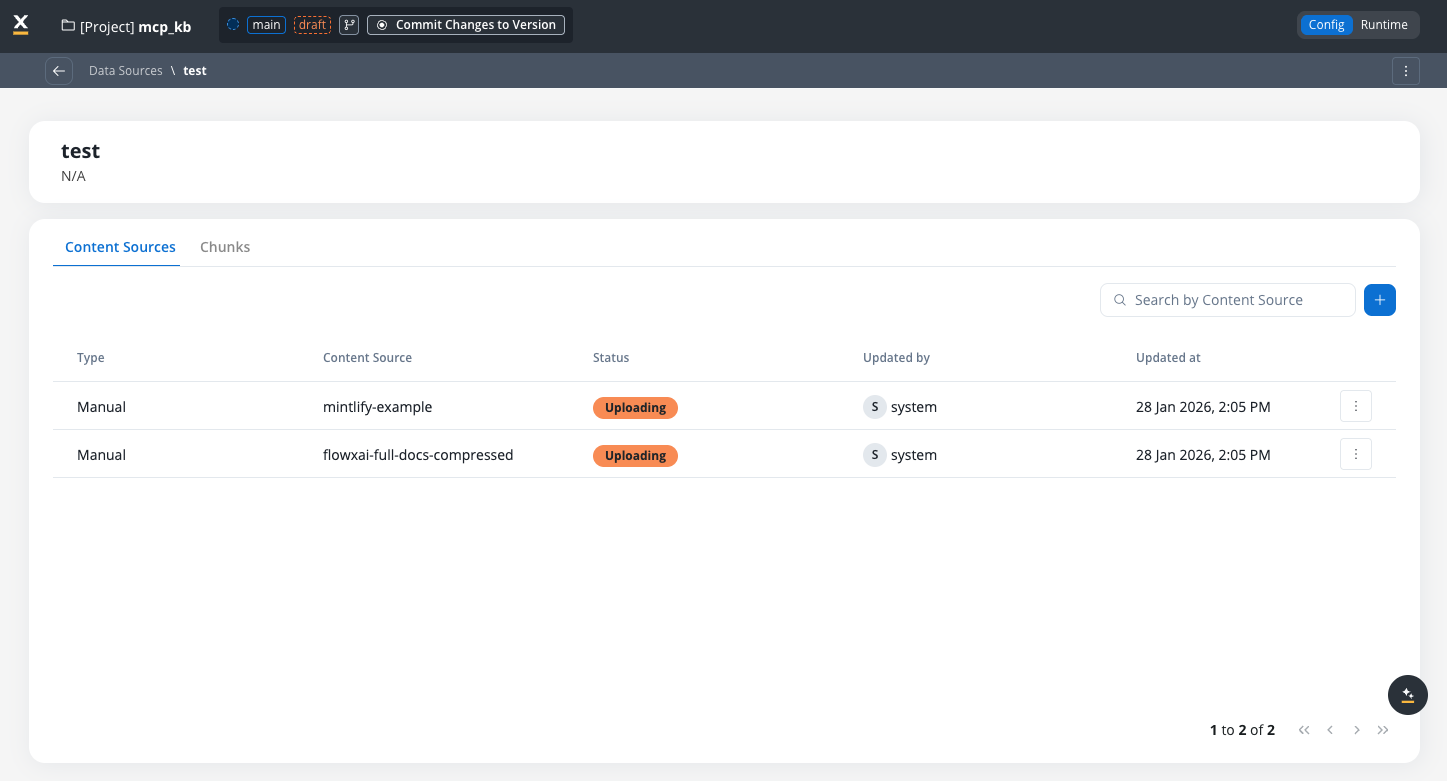
Content source lifecycle
Content sources progress through the following states:- Uploading: Content is being uploaded
- Chunking: Content is being processed and split into chunks
- Available: Content is ready and can be queried
- Failed: Processing encountered an error
Chunks and semantic search
Chunks are small snippets of content that are indexed in the vector database for semantic search. When an AI agent queries a Knowledge Base, the most relevant chunks are returned based on:- Content similarity: Semantic meaning of the query vs. chunk content
- Relevance score: Percentage indicating how relevant the chunk is (0-100%)
- Metadata filters: Optional filters based on content source and metadata
Use cases
Product documentation assistant
Create a Knowledge Base with product documentation and allow AI agents to answer customer questions based on the latest documentation.Policy compliance
Upload company policies and compliance documents. AI agents can reference these when processing requests to ensure compliance.Dynamic knowledge updates
Upload updated documents to Knowledge Bases to keep AI agent knowledge current. Workflow-based ingestion for automatic updates is planned for a future release.Multi-source information synthesis
Organize information across multiple content sources and let AI agents synthesize information from different sources to provide comprehensive answers.Limitations
The current release has the following limitations:Creating a knowledge base
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:- Access to FlowX Designer with appropriate permissions
- A project where you want to add the Knowledge Base
- Content ready to ingest (PDF documents or JSON data)
Setup steps
To add a new Knowledge Base data source:Navigate to Integration Designer
Go to FlowX Designer → Workspaces → Your workspace → Projects → Your project → Integrations → Data Sources
Create new data source
Click Add New Data Source and select FlowX Knowledge Base as the data source type
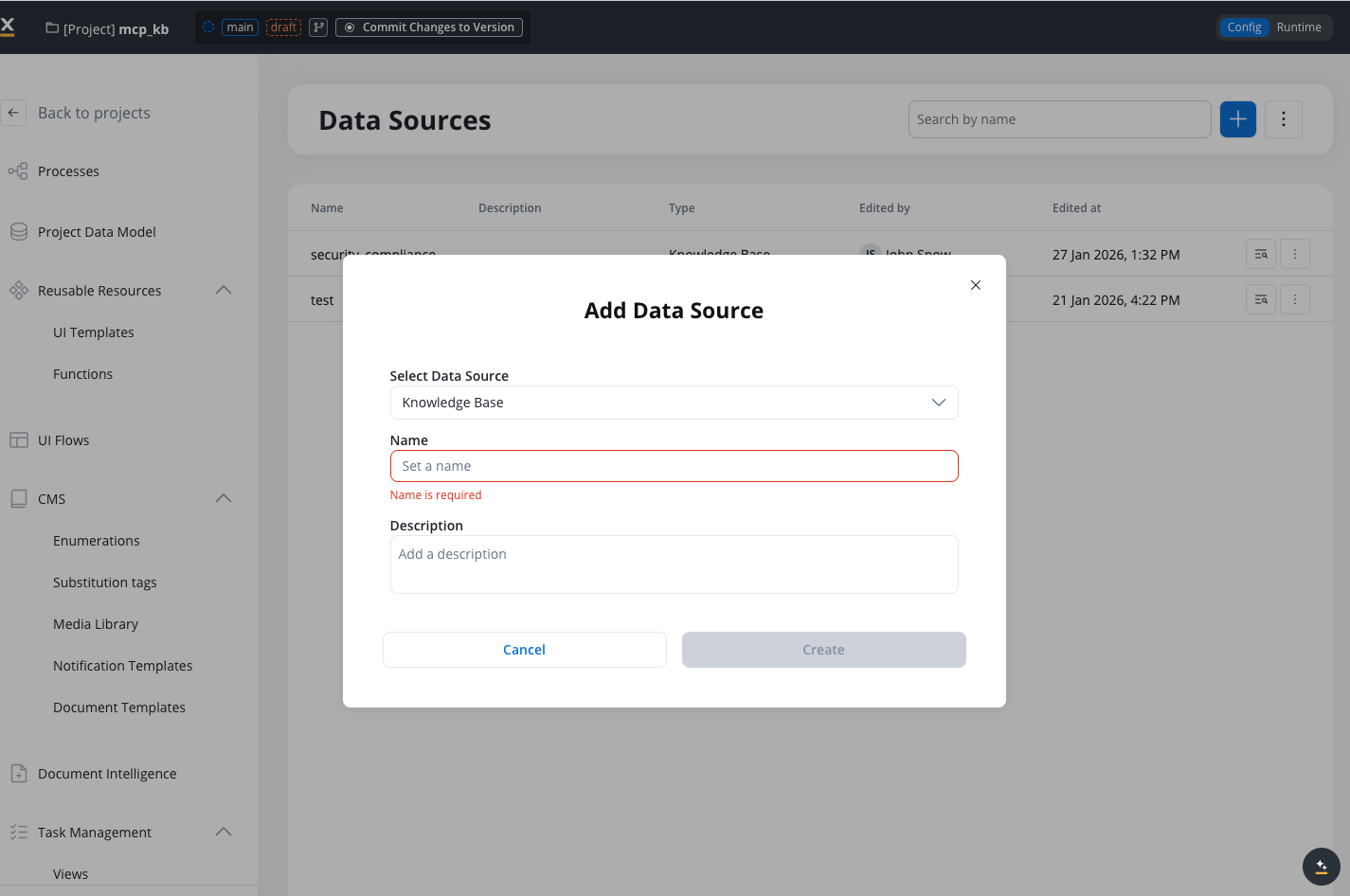
Configuration fields
Name
The unique identifier for your Knowledge Base within the project.Validation rules:
- Required: Field cannot be empty
- Uniqueness: Must be unique within the project
- Special characters: Only letters, numbers, and the following characters are allowed:
[],(),.,_,- - Length: Minimum 3 characters, maximum 50 characters
Description
An optional description explaining the purpose and contents of the Knowledge Base.Provide additional context about what information this Knowledge Base contains and how it should be used.
Example configuration
Here’s an example of a well-configured Knowledge Base:After creation
Once you’ve created a Knowledge Base, you’ll see three main sections:Content Sources
View and manage all content sources ingested into the Knowledge Base
Chunks
Search and view the individual chunks created from your content
Operations
Test Knowledge Base operations before using them in workflows

Next steps
Managing Content
Upload documents and manage content sources
Using in Workflows
Query Knowledge Bases from workflows
Testing Operations
Test queries and operations before production use
Related resources
Integration Designer
Integration Designer and data sources
Custom Agent Nodes
Using AI agents in workflows
Integrations Overview
Integration ecosystem overview

