What is a BPMN node?
BPMN node
A BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) node is a visual representation of a point in your process. Nodes are added at specific process points to denote the entrance or transition of a record within the process. Each node type has a specific purpose and configuration requirements.
Available node types
FlowX.AI supports a rich variety of BPMN node types that you can use to model your business processes:Flow control nodes
Activity nodes
Task Node
Executes automated tasks and business rules
User Task
Creates user interfaces and handles user interactions
Send Message Task
Sends data to external systems or services
Receive Message Task
Receives data from external systems or services
Gateway nodes
Exclusive gateway
Creates decision points with mutually exclusive paths
Parallel Gateway
Splits process flow into multiple concurrent paths
Event nodes
Message event
Captures interactions between different process participants
Timer Event
Triggers actions based on time conditions or delays
Error Event
Manages error handling in processes
Subprocess nodes
Call activity
Calls and runs a subprocess within the main process
Start Embedded Subprocess
Initiates subprocesses embedded within a parent process
Boundary event nodes
Message catch boundary event
Waits for a specific message during task execution
Timer Boundary Event
Triggers based on time conditions during task execution
Error Boundary Event
Catches errors during task or subprocess execution
Boundary events can only be attached to certain node types:
- User Task
- Service Task
- Send Message/Receive Message Tasks
- Subprocess (Embedded and Call Activity)
BPMN Node Documentation
BPMN node types in FlowX.AI
Intro to BPMN
Learn fundamental BPMN concepts and standards
BPMN 101
Learn more about BPMN and how it’s used in FlowX through our Academy course
Adding a node to your process
1
Access Your Process Definition
- Open FlowX.AI Designer and navigate to your project
- Go to the Processes section within your project
- Click on the process definition you want to edit
2
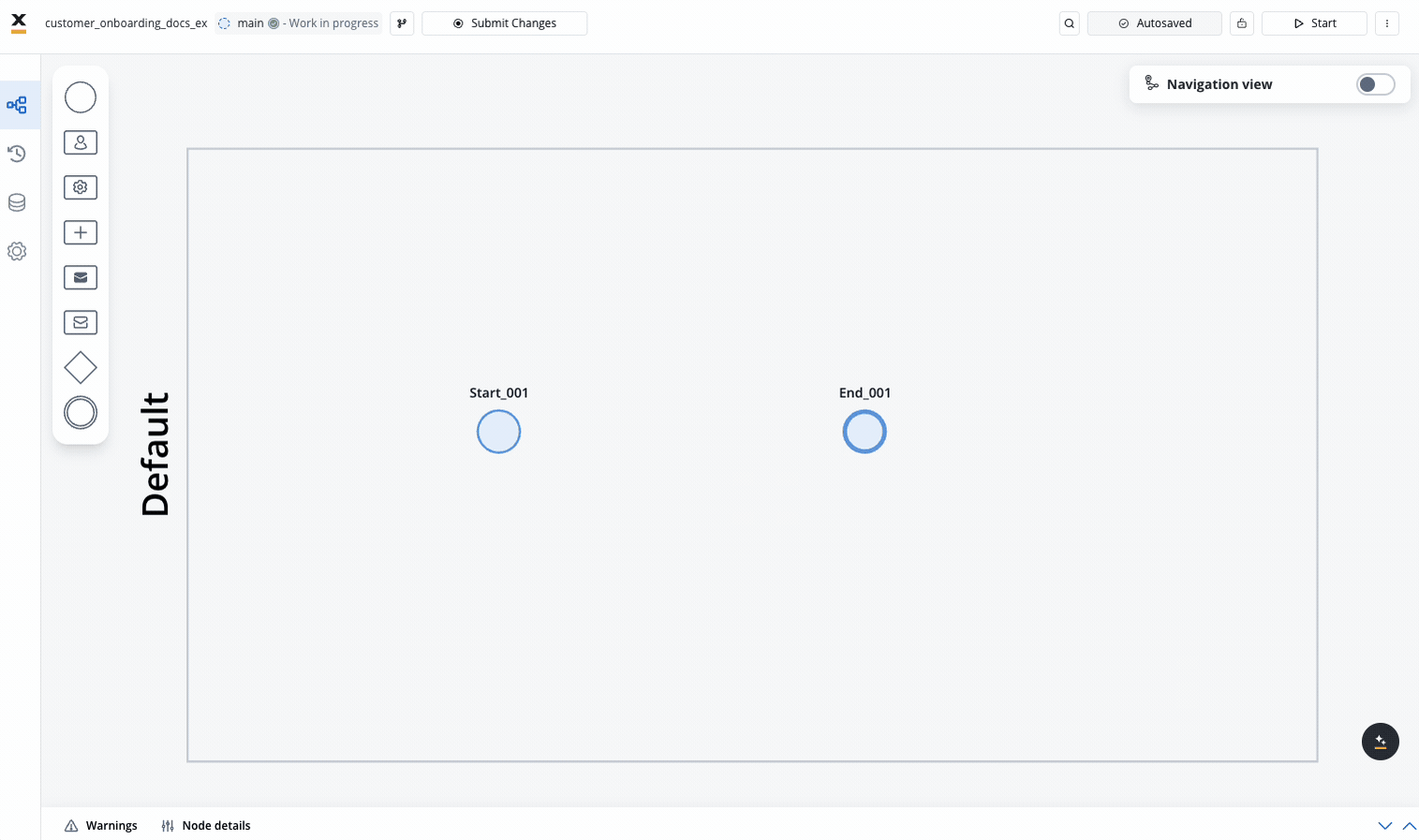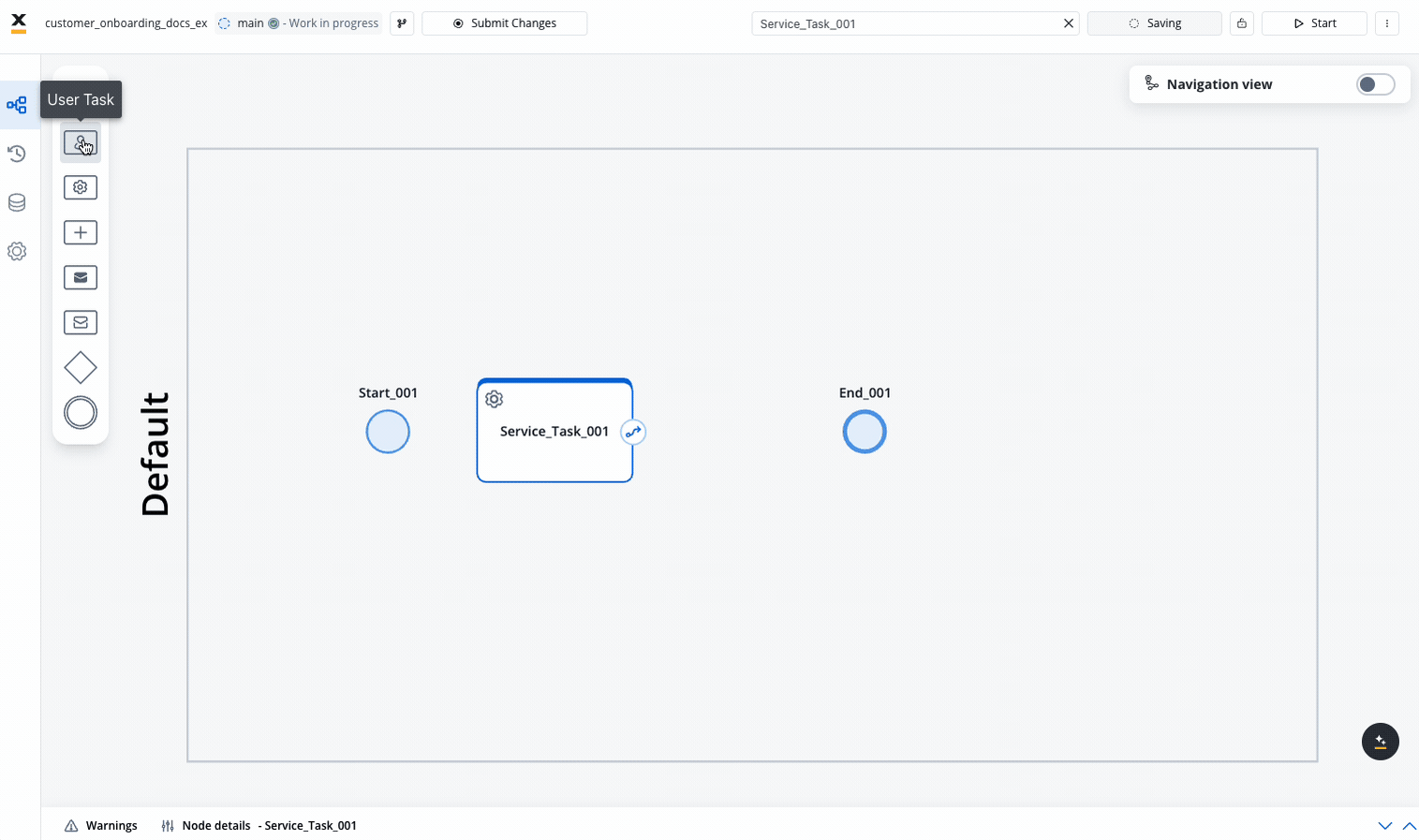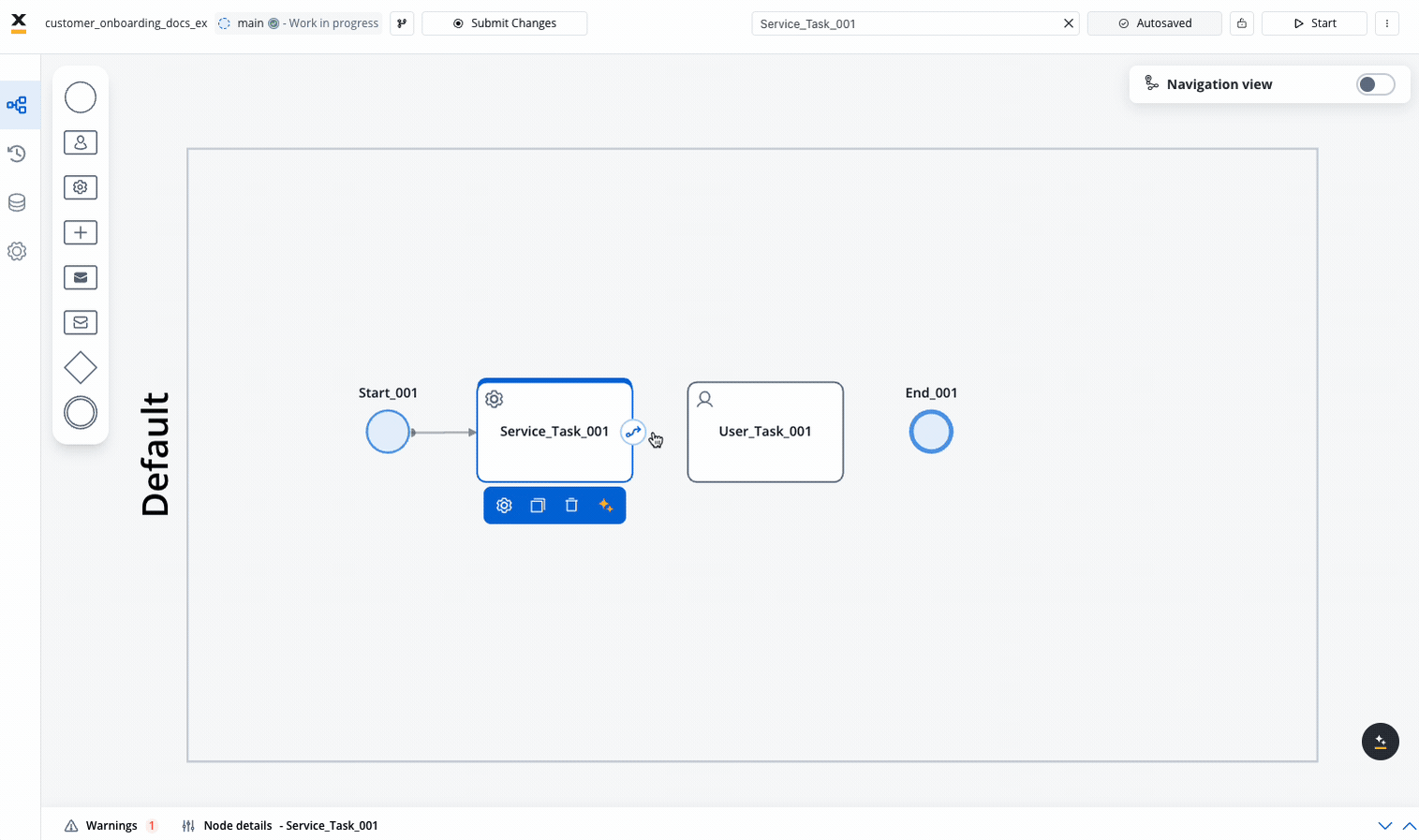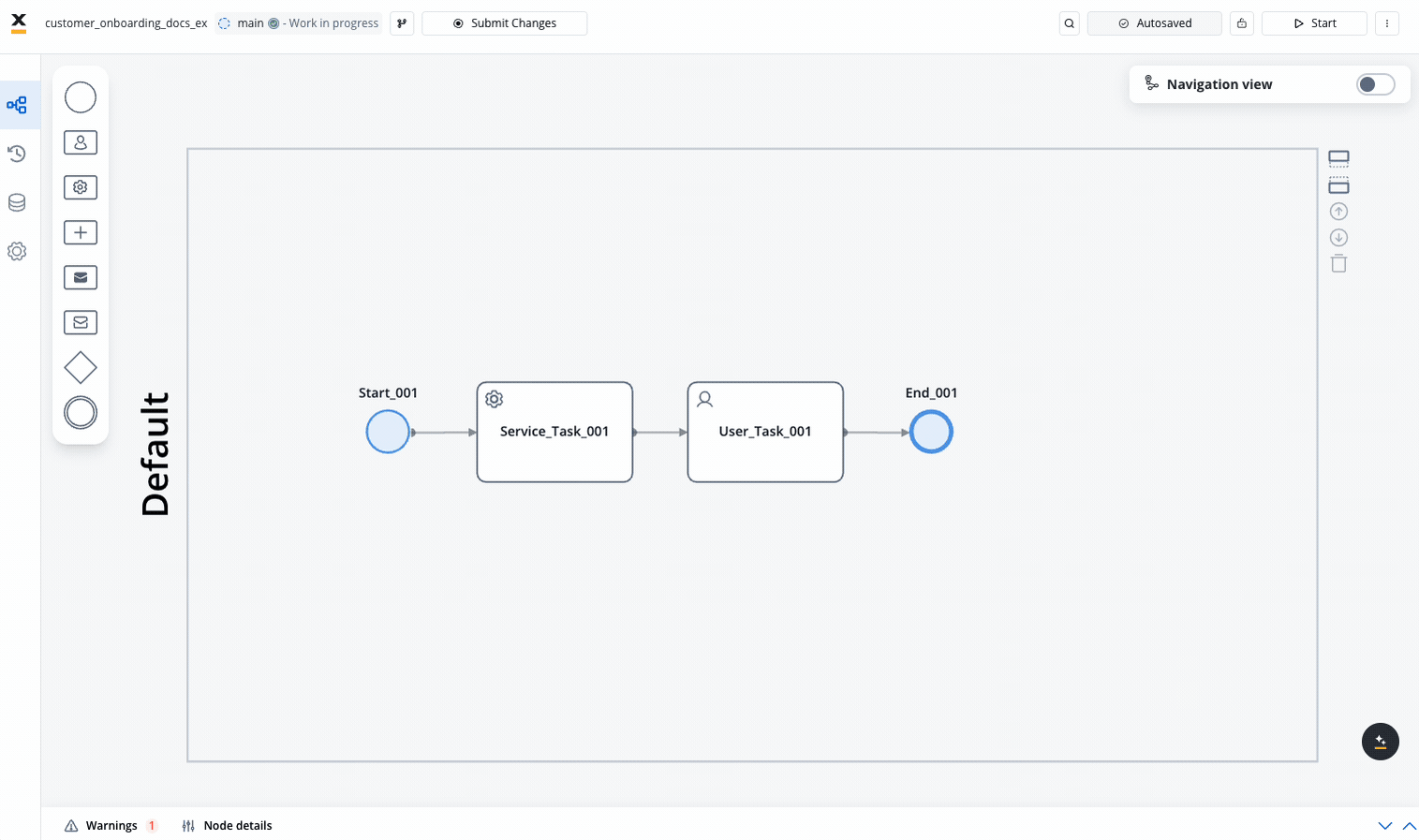
Add a Node to the Canvas
- Locate the node palette on the left side of the screen
- Drag and drop your desired node type onto the canvas
- Position the node where you want it in your process flow
3
Connect Nodes with Sequence Flows
To create a connection between nodes (called a sequence flow):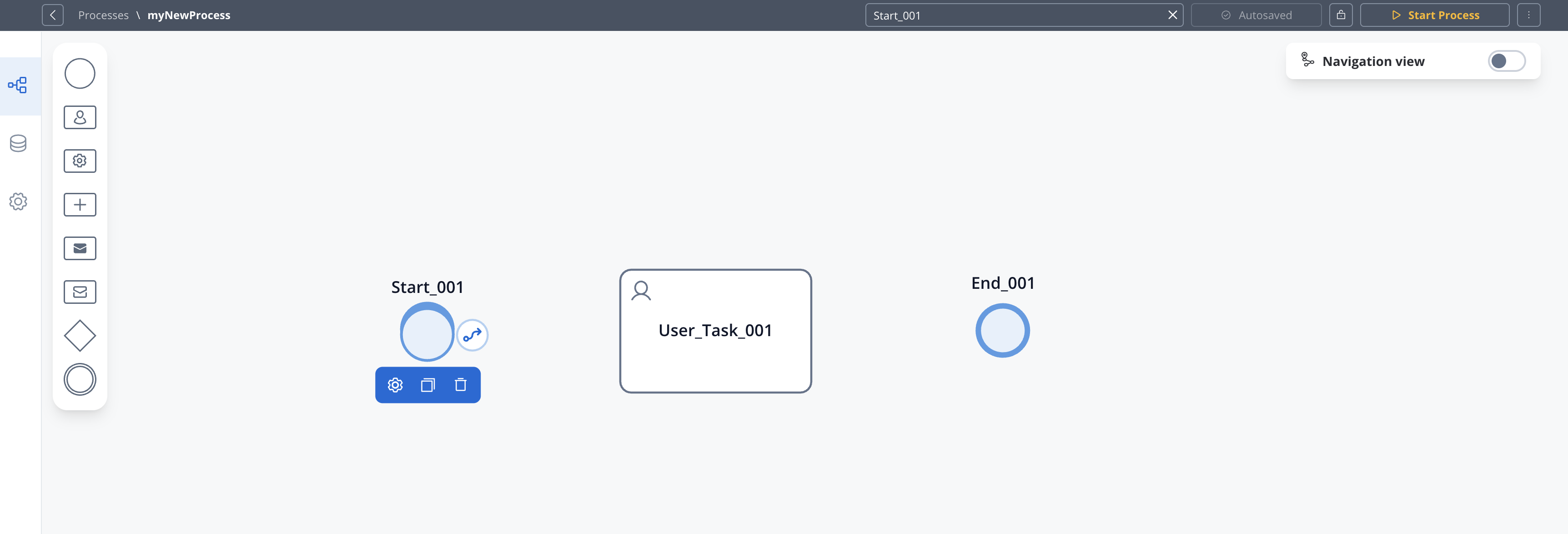
- Click on the source node to select it
- Click the arrow icon that appears
- Click on the target node you want to connect to
- A sequence flow arrow will be created between the two nodes

4
Configure Node Properties
After adding a node, you need to configure its properties: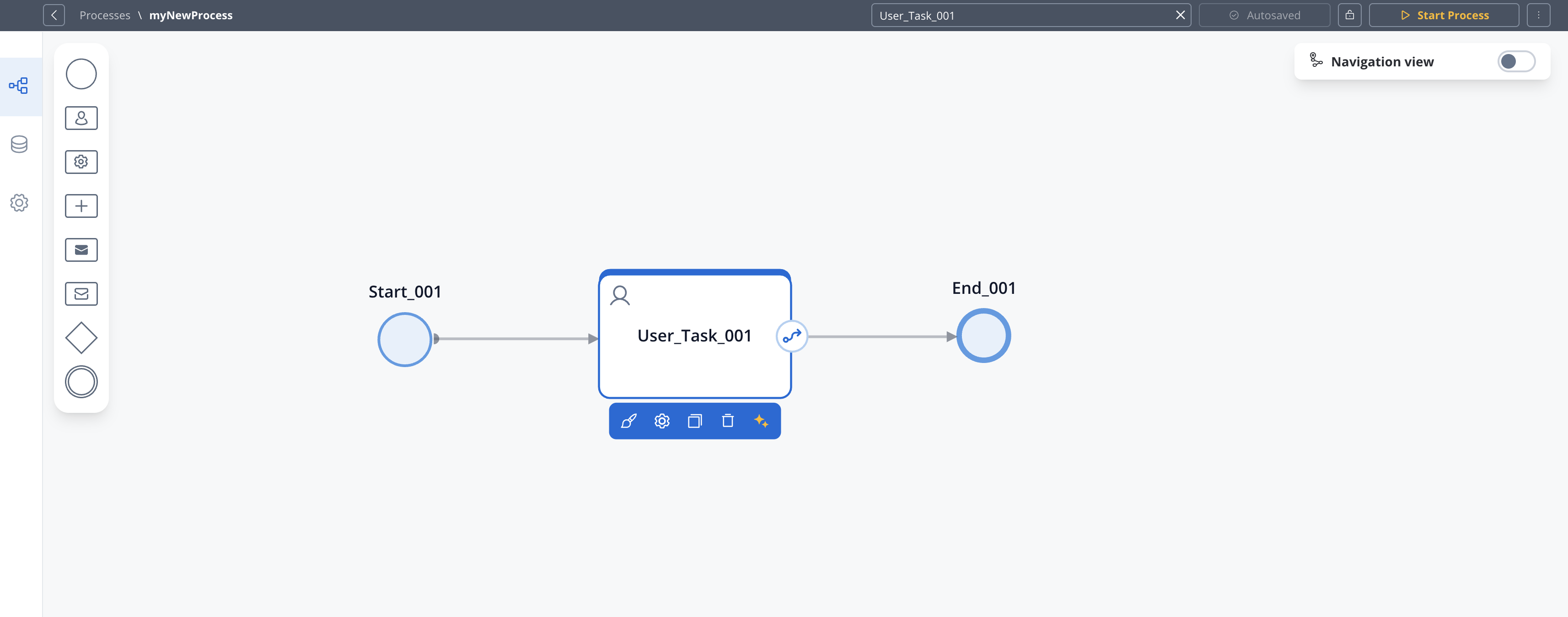
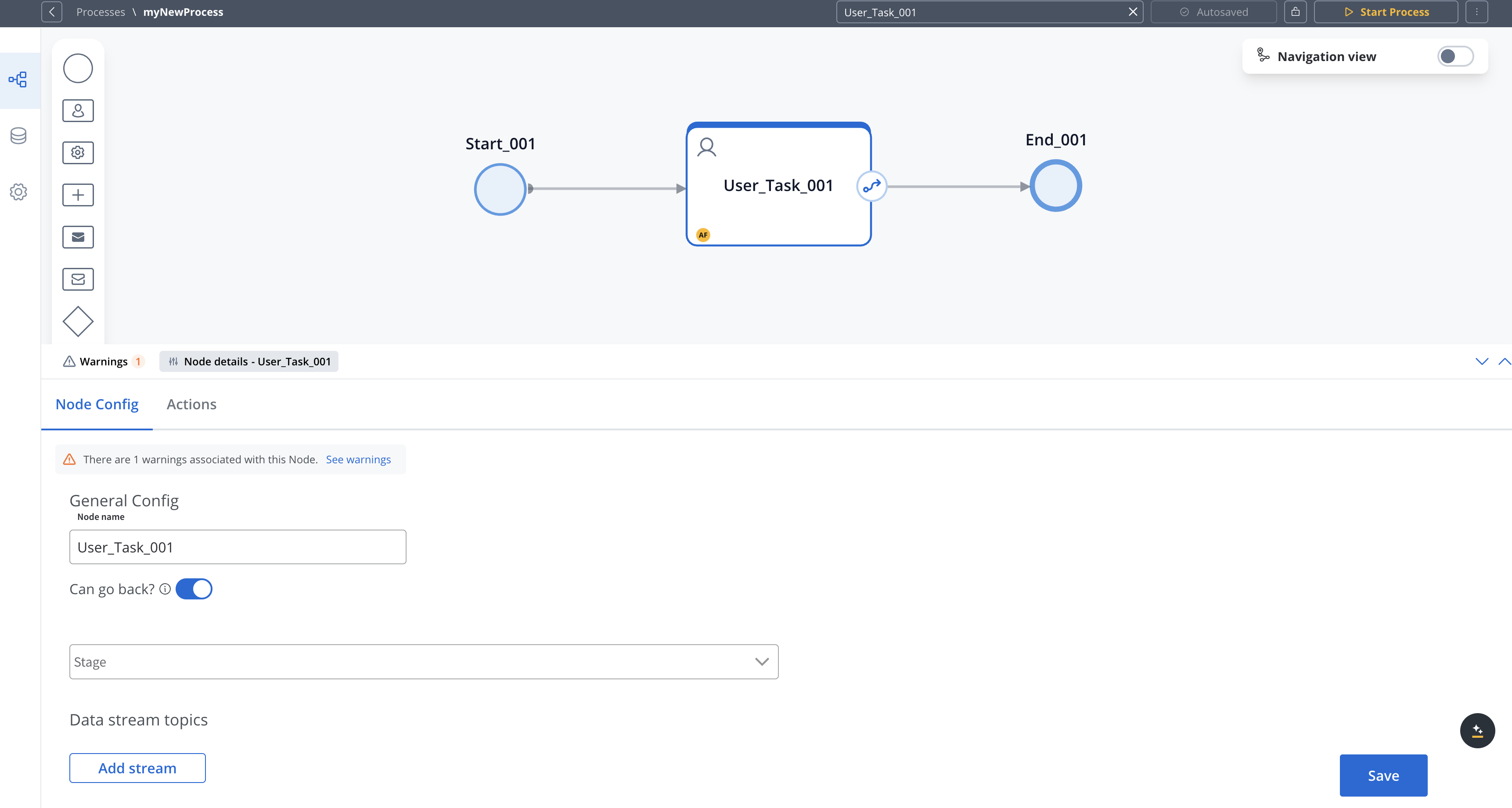
- Click on the node to select it to open the properties panel
- Click edit icon to open the properties panel
- Configure basic properties like name and description
- Set node-specific properties depending on the node type
- Configure actions for the node


Different node types have different configuration options. For example, Gateway nodes have condition-related settings.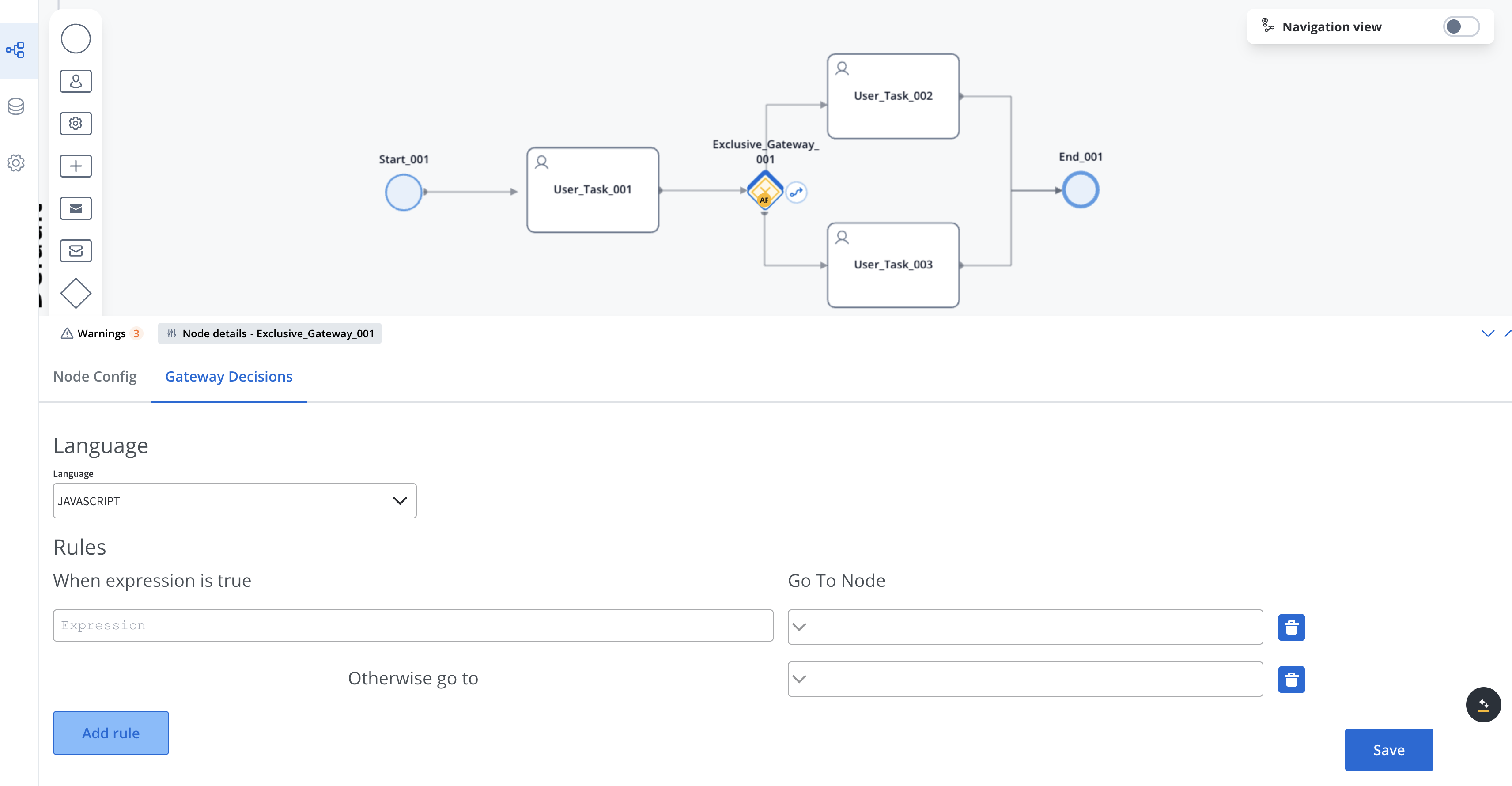

5
Add Actions to Nodes
For nodes that support actions (task nodes, user task nodes, and message nodes):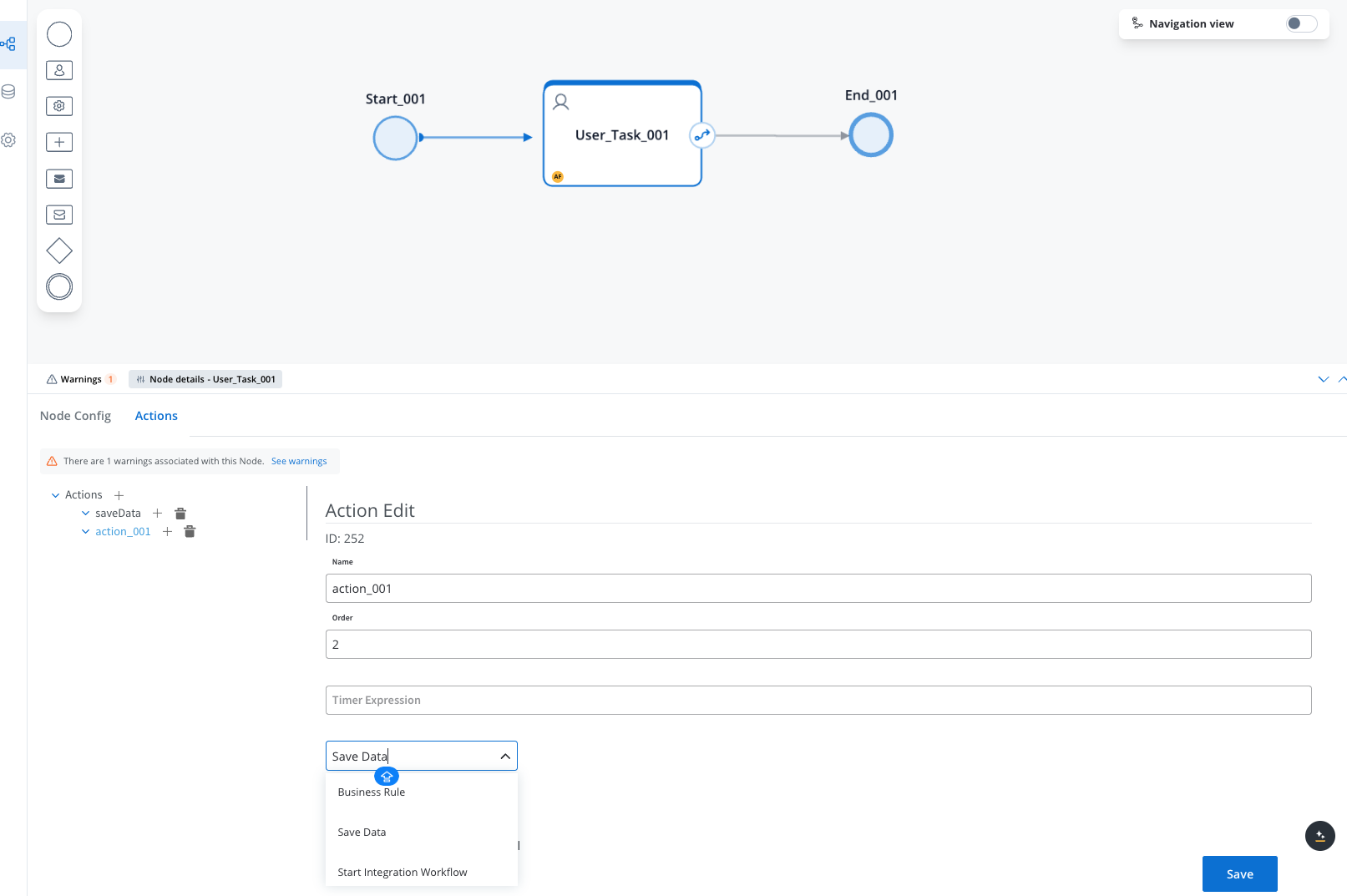
- Select the node
- In the properties panel, navigate to the Actions section
- Click + Add Action
- Select the action type and configure its parameters

Actions allow you to incorporate business rules, save data, send messages, and interact with users. Learn more about Node Actions.
Common node configuration options
While each node type has specific properties, many share these common configuration options:Basic Properties
Basic Properties
- Name: A descriptive name for the node (visible in the Process Designer).
- Can go back: Option available in various nodes that controls whether users can return to previous steps in a process. When enabled (set to true), it allows users to revisit and redo that step after completing it.
- Stage: The stage of the process the node belongs to.
Action Properties
Action Properties
For nodes that support actions:
- Action Type: Type of action to execute
- Action Parameters: Configuration for the specific action
- Execution Order: Sequence for multiple actions on a node
Node type-specific configuration
User Task Configuration
- UI Component selection
- Form configuration
- Data validation rules
- Task assignment settings
Gateway Configuration
- Condition expressions
- Default sequence flow
- Branch naming
- Gateway direction (diverging/converging)
Message Task Configuration
- Message format
- Target system
- Correlation keys
- Timeout handling
Service Task Configuration
- Service implementation
- Input/output mapping
- Error handling
- Execution parameters
Best practices
Next steps
After adding nodes to your process, you can:Add Actions to Nodes
Configure business rules and actions for your nodes

