Available starting with FlowX.AI 5.3.0: Update Process Variables allows operations teams to modify process variables on active instances to resolve production issues without developer intervention.
Overview
Update Process Variables allows you to modify process variables on active process instances. You can edit, add, or delete variables on process instances with Started or On Hold status.This feature is part of operational process instance management, allowing teams to resolve data issues without developer intervention.
- JSON syntax validation and formatting
- Edit, add, or delete operations on variables
- Automatic synchronization to Task Manager and Elasticsearch
- Audit logging with snapshots of previous values
Features
JSON editor
The JSON editor offers:- JSON syntax validation
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-formatting
- Error detection
Access points
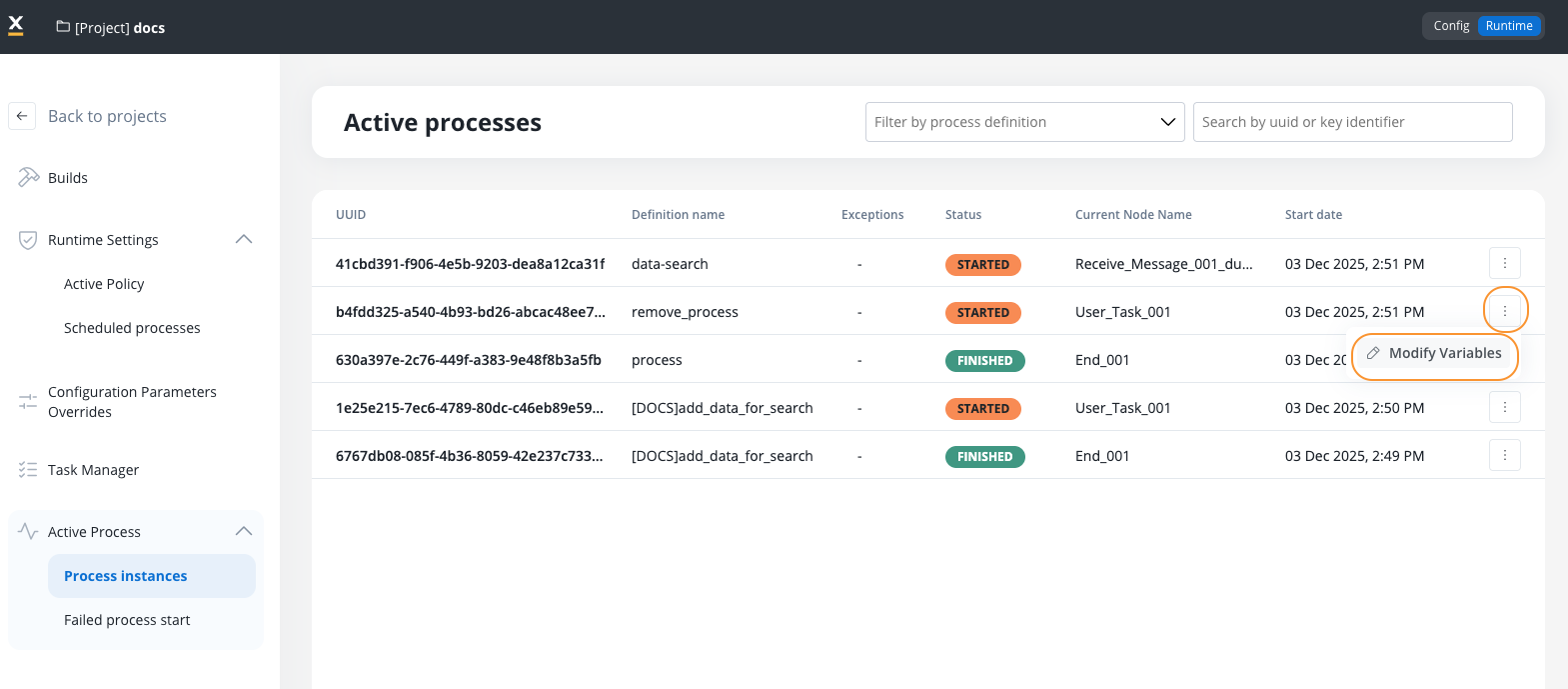
Access the editor from two locations:- From Process Instances page
- From View process instance page
- Navigate to Processes → Active Process → Process instances
- Click the contextual menu (three dots) on any process instance row
- Select Modify Variables
- The system navigates to the Process Instance page and opens the Variables tab in edit mode

Dual view modes
Switch between two viewing modes for process variables:- Tree View (existing): Hierarchical display of variables with expand/collapse
- JSON View: Raw JSON format, editable when in edit mode
Compare view
Available starting with FlowX.AI 5.5.0
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Side-by-side diff | Original values on the left, modified values on the right |
| Change highlighting | Added, removed, and modified lines are color-coded |
| Toggle views | Switch between Edit and Compare modes while editing |
- Open the variables editor in Edit mode
- Make your changes in the JSON editor
- Toggle to Compare view to see a diff of your modifications against the original values
- Switch back to Edit view to continue making changes, or click Save to apply
Operations
You can:- Edit existing attribute values
- Add new attributes or objects
- Delete existing attributes or objects
Access requirements
Check permissions
Ensure you have the
process_variables_edit permission at the workspace level.The Edit option is only visible to users with this permission.
Navigate to process instance
Access from either:
- Process Instances list → contextual menu
- Process Instance detail page → secondary navigation
Editing process variables
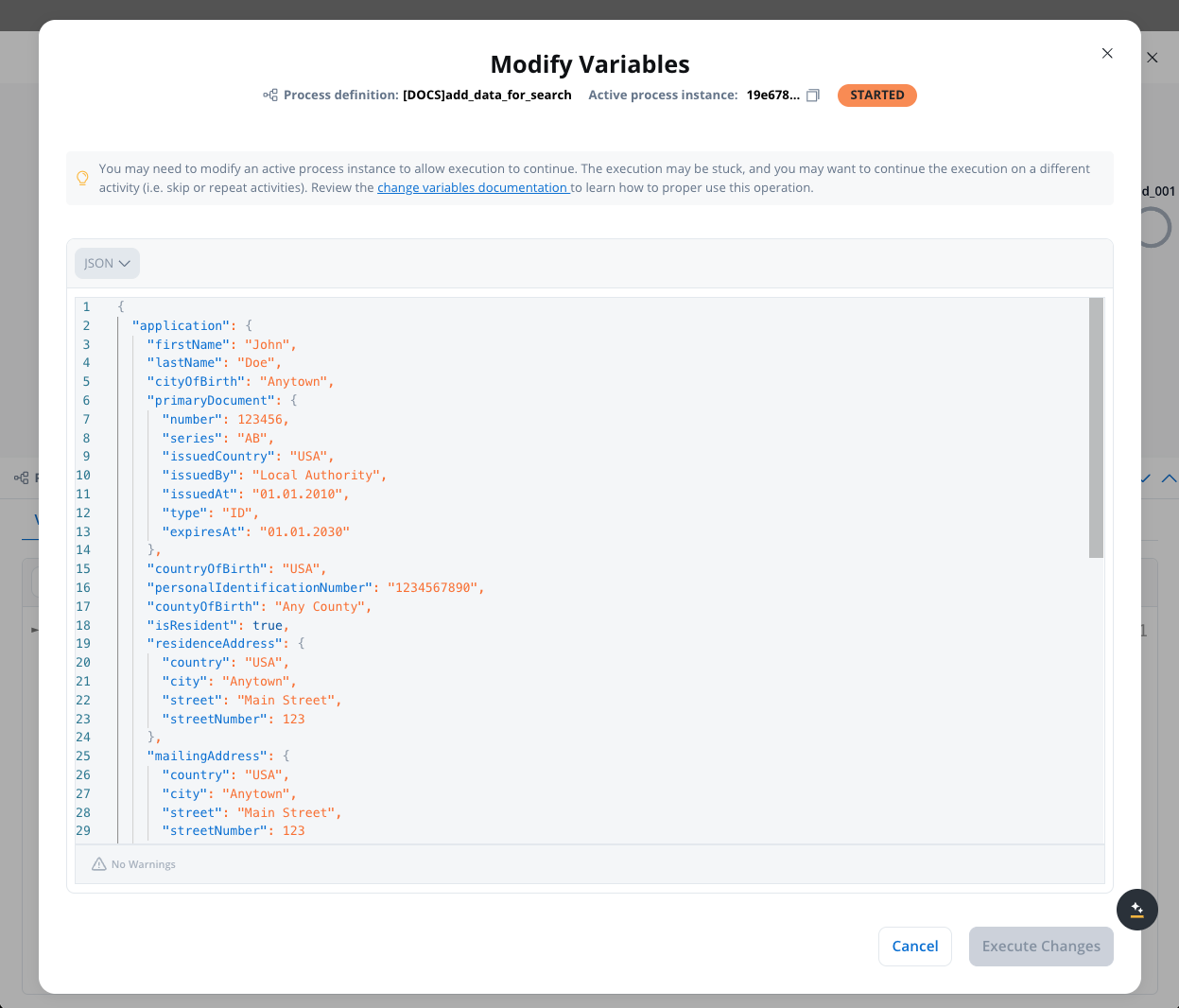
Switch to JSON View
In the Variables tab, switch from Tree View to JSON View using the view dropdown selector.
Enable edit mode
Click the Modify Variables button to make the JSON editor editable.
This button is only visible if you have the necessary permissions.

Modify variables
Edit process variables in the JSON editor:Example - Editing existing values:Example - Adding new attributes:Example - Deleting attributes:Remove unwanted attributes by deleting their lines from the JSON.
Validate JSON
Ensure your JSON format is valid before saving.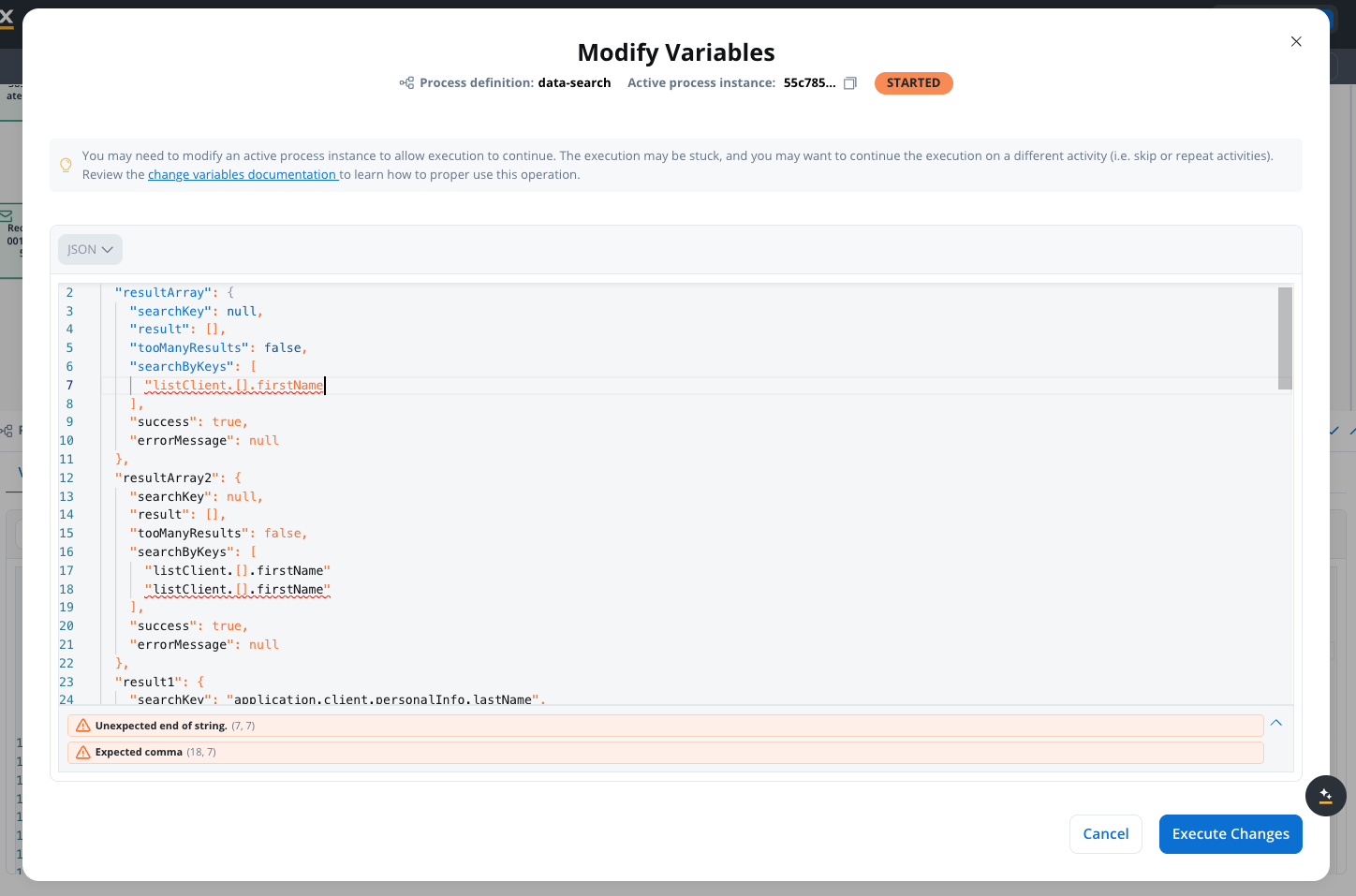 Common validation errors:
Common validation errors:

- Missing commas between properties
- Unclosed brackets or braces
- Missing quotes around strings
- Trailing commas
Save changes
Click Save to apply your changes.The system automatically:
- Creates a snapshot of previous values in a new table
- Updates the process instance variables
- Syncs to Task Manager (using existing mechanisms)
- Updates Elasticsearch (for variables configured for data search)
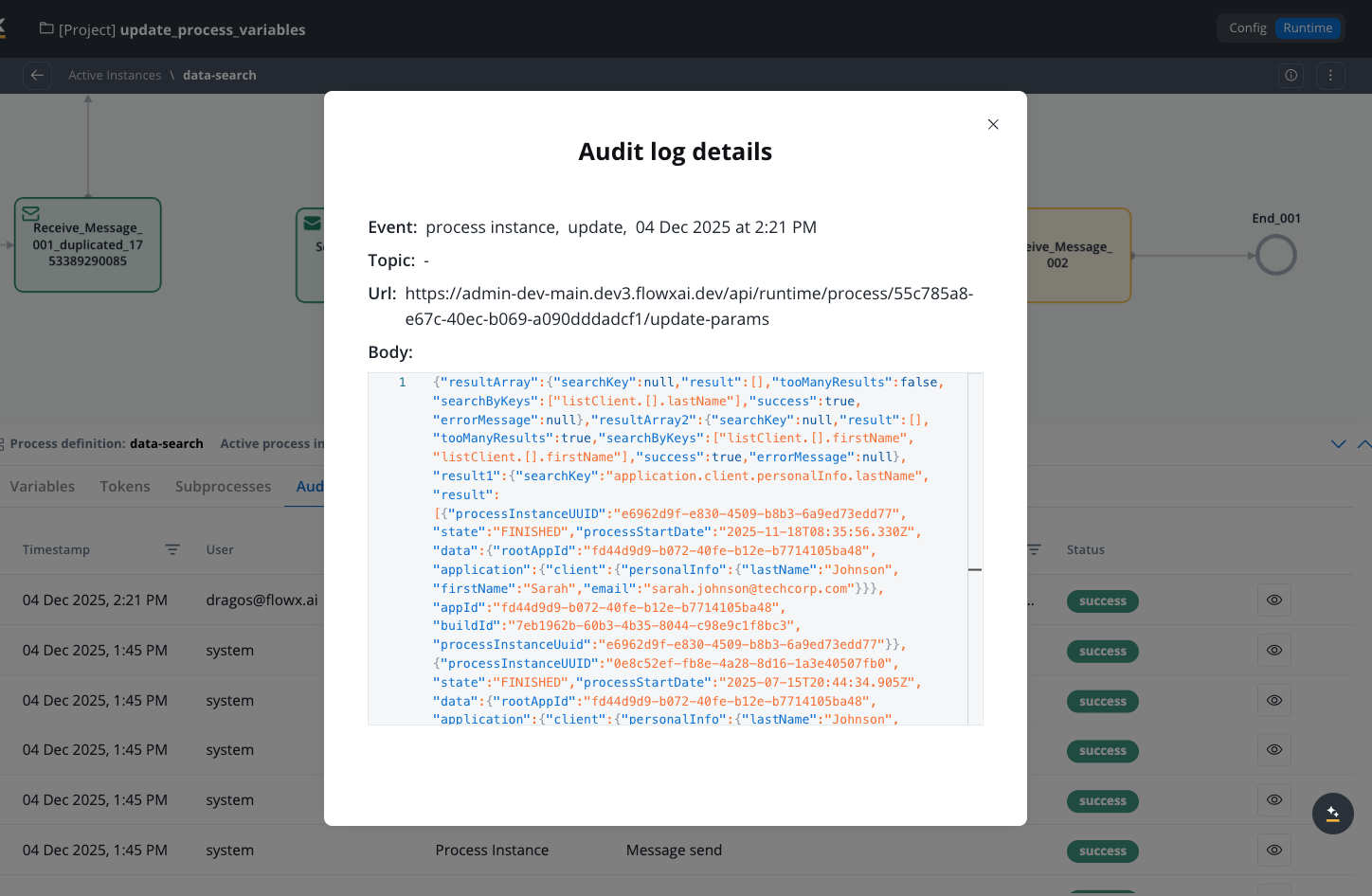
- Records the modification in the audit log
Permissions and security
Access control: This feature requires the workspace-level permission
wks_process_instance_variables_edit (permission name: process_variables_edit). Users with this permission can edit and save variables; others can only view variables in read-only mode. By default, ORG_ADMIN and WORKSPACE_ADMIN roles include this permission.Security features: All modifications are logged in the audit trail with user identity and timestamp. Previous values are preserved in snapshot history before changes are applied. JSON syntax validation prevents data corruption.For more information about permissions, roles, and access management, see Workspaces Access Rights and the Permission Reference Guide.Data synchronization
Updated automatically
When you modify process variables, the following are updated:Process instance parameters
Variables are updated immediately in the database
Task Manager
Variables sync using existing mechanisms; task keywords and data remain consistent
Elasticsearch
Variables configured for data search are updated automatically
Snapshot table
Previous values are saved in a snapshot table before changes are applied
Not updated
The following are preserved to maintain data integrity:Process snapshots
Snapshots used for back navigation (Reset process data) remain unchanged
Debug records
Process instance debug records preserve execution history as it occurred
Existing audit logs
Previously recorded audit logs (manual actions, integrations) are not modified
Subprocess variables
Child subprocess variables are not updated; parent changes don’t cascade to children
Synchronization details
Task manager sync
Elasticsearch sync
Audit logging
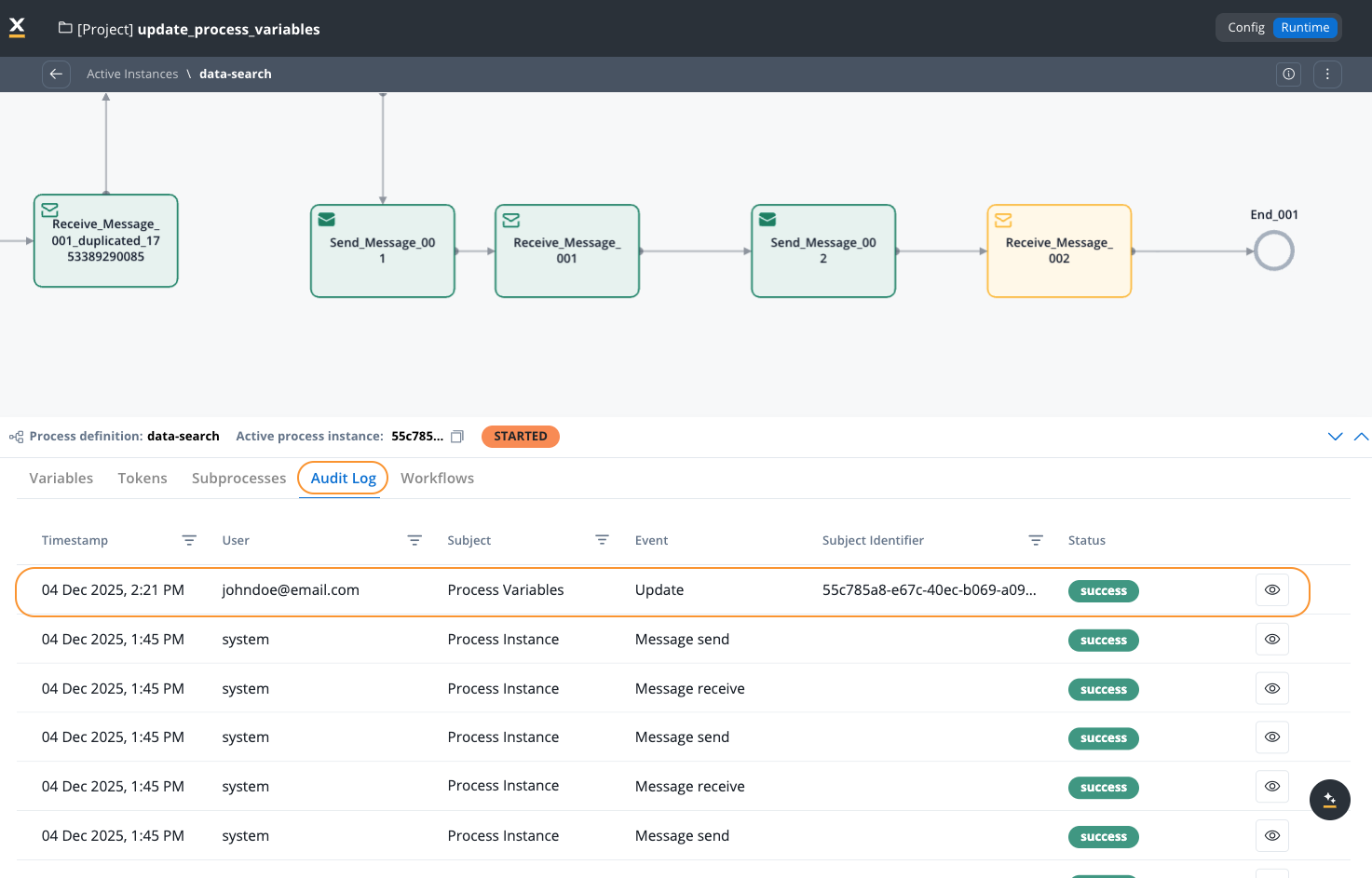
Every process variable modification creates a detailed audit log entry. Audit logs are displayed in the Audit Log tab within the process instance (in the Runtime -> Active Process -> Process Instance page).Important considerations
Subprocess impact
Back navigation
Integration messages
Process instance debug table
Not updated: the process instance debug table records remain unchanged. Reason: debug records capture execution history as it occurred. Modifying them would compromise debugging and troubleshooting capabilities.Best practices
When to use
Correct user input errors
Fix incorrect data submitted in forms
Unblock stuck instances
Resolve missing data preventing continuation
Fix integration data issues
Correct incorrect responses from external systems
Add missing attributes
Add required data not collected initially
Remove invalid data
Clean up test or incorrect data
Update search keywords
Correct Task Manager search data
Fix Elasticsearch data
Ensure accurate search results
When not to use
Regular operational updates
Design proper process flows instead
Subprocess coordination
Parent-child sync not supported
Complex back navigation flows
Snapshots won’t reflect changes
While waiting for integrations
Responses based on original values
Routine data corrections
Indicates process design issues
Automated scripts
Use process design and actions instead
Validation before saving
Verify JSON syntax
Ensure valid JSON format to prevent data corruption and save failures
Review impact
Understand which variables you’re changing and their impact on process flow
Check dependencies
Review process flow, subprocesses, and integrations before modifying critical variables
Document changes
Audit logs record changes automatically, but document why changes were made
Common use cases
1. Correct user input errors
Scenario:Customer submitted incorrect loan data (wrong income amount, invalid address, incorrect contact information). Solution:
- Navigate to the process instance
- Access Variables tab in edit mode
- Locate the incorrect values in JSON
- Correct the data:
- Save changes
- Process continues without requiring customer to restart the process
2. Unblock stuck process instances
Scenario:Process is waiting for external data that never arrives due to integration timeout or external system being down indefinitely. Solution:
- Identify the variable causing the blockage
- Open process variables in edit mode
- Update the variable to provide expected data or bypass condition:
- Save changes
- Instance unblocks and continues execution
3. Fix integration data issues
Scenario:External credit check system returned incorrect or incomplete data due to system error. Solution:
- Review the integration response variables
- Edit variables to correct the data:
- Save changes
- Process continues with accurate data
4. Add missing attributes
Scenario:Process needs additional data that wasn’t collected at start time, but is now required for a decision point. Solution:
- Access process variables
- Add new required attributes:
- Save changes
- Process can now access the missing data at decision points
5. Delete invalid data
Scenario:Process contains test data or incorrect objects that shouldn’t be there and are causing validation failures. Solution:
- Open process variables
- Remove problematic data:
- Save changes
- Process continues with clean, valid data only
6. Update task manager keywords
Scenario:Task search keywords need updating based on corrected customer data for better task discoverability. Solution:
- Modify variables that are configured as Task Manager keywords:
- Save changes
- System automatically syncs to Task Manager
- Tasks become searchable with correct keywords
7. Fix Elasticsearch search data
Scenario:Process data indexed for search contains errors, making instances unsearchable or showing in wrong search results. Solution:
- Identify variables configured for Elasticsearch data search
- Correct the values:
- Save changes
- Elasticsearch automatically updates
- Process instances appear in correct search results
8. Emergency business rule changes
Scenario:Regulatory change requires immediate update to pricing or terms in active applications. Solution:
- Access affected process instances
- Update variables to reflect new business rules:
- Save changes for all affected instances
- Processes continue with compliant data
Troubleshooting
Edit button not visible
Edit button not visible
Cannot save - JSON validation error
Cannot save - JSON validation error
Symptoms:Correct:Trailing comma:Unclosed brackets:Solutions:
- Save button disabled or shows error
- Red error indicators in editor
- Error message: “Invalid JSON format”
- Use JSON editor error highlights to locate issues
- Copy JSON to external validator (jsonlint.com)
- Check for common issues: commas, brackets, quotes
- Validate structure matches JSON specification
- Remove trailing commas
- Ensure all brackets and braces are closed
Changes not reflected in Task Manager
Changes not reflected in Task Manager
Symptoms:
- Task Manager still shows old values
- Task search doesn’t find with new keywords
- Task data appears outdated
- Task Manager sync delay
- Variables not configured for Task Manager keywords
- Task Manager service issues
- Cache issues
- Wait and refresh:
- Wait 10-30 seconds for sync
- Refresh Task Manager view
- Clear browser cache if needed
- Verify configuration:
- Check if variables are configured as task keywords
- Review Task Manager configuration
- Confirm variable mapping is correct
- Check system health:
- Verify Task Manager service is running
- Review sync logs for errors
- Check Kafka messages if available
- Verify save completed:
- Check audit log for successful save
- Confirm no error messages appeared
- Review process instance variables show new values
Elasticsearch search not showing updated data
Elasticsearch search not showing updated data
Symptoms:
- Search doesn’t return expected results
- Old values appear in search results
- Process instance not found with new criteria
- Elasticsearch sync delay
- Variables not configured for data search
- Index refresh delay
- Elasticsearch service issues
- Wait for index refresh:
- Elasticsearch typically refreshes within seconds
- Wait up to 1 minute for propagation
- Try search again after waiting
- Verify configuration:
- Check if variables are configured for Elasticsearch indexing
- Review process definition for data search settings
- Confirm variable paths match index mapping
- Check Elasticsearch health:
- Verify Elasticsearch service is running
- Check index status
- Review indexing logs for errors
- Manual verification:
- Query Elasticsearch directly if possible
- Check index document for process instance
- Verify field values match expected data
Modified variables lost after back navigation
Modified variables lost after back navigation
Subprocess shows different data than parent
Subprocess shows different data than parent
Symptoms:
- Parent process variables updated
- Subprocess still has old values
- Data inconsistency between parent and child
- Subprocesses have independent execution context
- Each subprocess operates on its snapshot of data
- Maintains process isolation and integrity
- Understand before modifying:
- Check if process has active subprocesses
- Review parent-child data dependencies
- Assess impact of data divergence
- Manual coordination:
- Modify subprocess variables separately if needed
- Document intentional data divergence
- Test subprocess behavior with original values
- Process design considerations:
- Design processes to minimize parent-child data coupling
- Pass critical data as subprocess parameters
- Use events for dynamic data synchronization
Integration response doesn't match modified data
Integration response doesn't match modified data
Symptoms:
- Integration called before modification
- Response based on original values
- Data mismatch between variables and integration result
- Integration already executed with original parameters
- External system processed original request
- Response is based on what was sent
- Modifying variables is local to process instance
- Avoid modifying during integration:
- Check if token is waiting for integration response
- Wait for integration to complete before modifying
- Document which variables were sent to integration
- Re-execute if needed:
- Consider re-executing the integration node
- Manually trigger integration with new values if possible
- Design retry mechanisms in process flow
- Accept response:
- Use integration response as-is
- Modify only non-integration-related variables
- Document why integration response doesn’t match