Subprocess
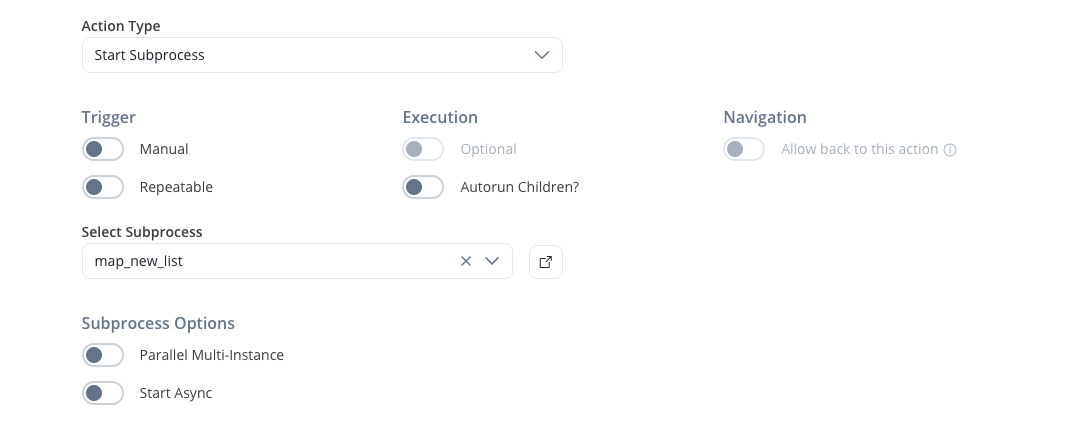
- Async mode: The parent process will continue without waiting for the subprocess to finish.
Select if this task should be invoked asynchronously. Make tasks asynchronous if they cannot be executed instantaneously, for example, a task performed by an outside service.
- Sync mode: The parent process must wait for the subprocess to finish before advancing.
Starting multiple subprocesses
Parallel multi-instance
The Call Activity node can also be used for starting a set of subprocesses that will be started and run at the same time. This is useful when there is an array of values in the parent process parameters, and a subprocess needs to be started for each element in that array.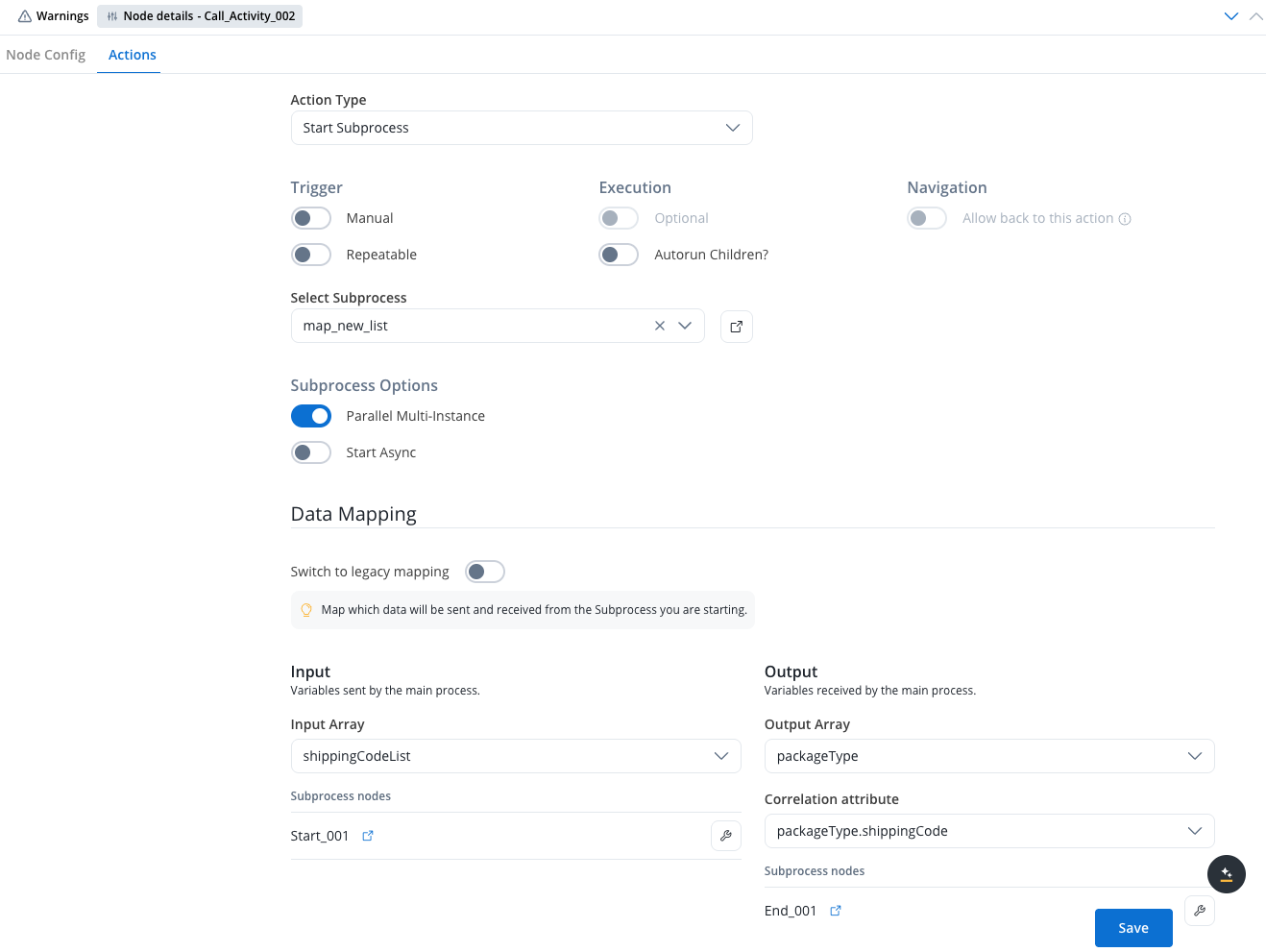
Configuration options
When configuring parallel multi-instance on a Call Activity node, you have access to the following configuration options:- Input Array: Declare the array used for subprocess input. Map the array of objects or the keys inside the array of objects to the destination object or its keys from the subprocess.
- Output Array: Declare the array used for subprocess output. Map from the subprocess object back to an array of objects in the parent process.
- Correlation attribute: The attribute that will be used to correlate subprocess results with parent process data.
Data mapping
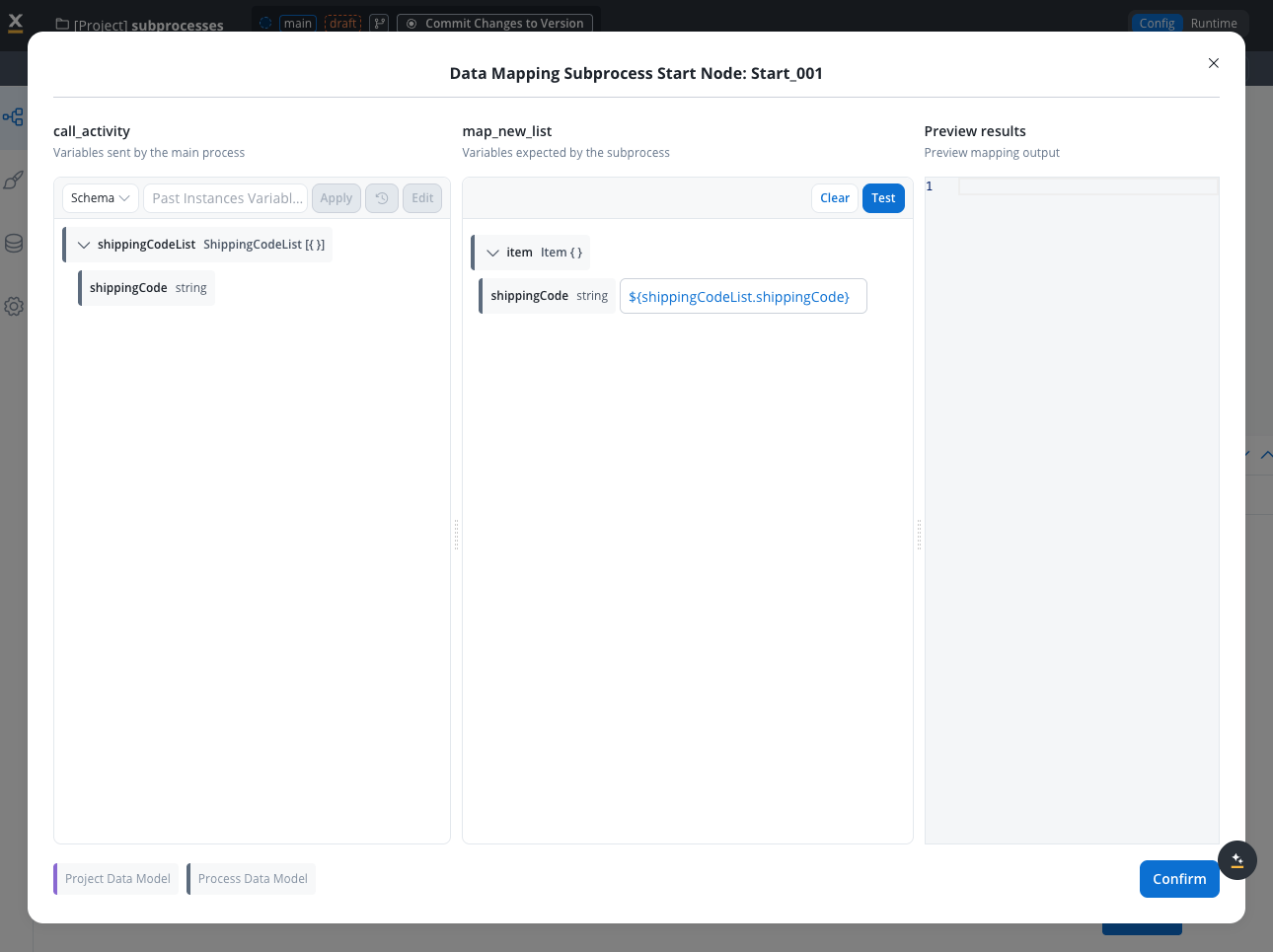
In the Data Mapping section, when Parallel Multi-instance is enabled, you can configure:New data mapping
- Declare arrays: Define the arrays used for subprocess input and subprocess output
- Input mapping: In the mapping modal, map the array of objects or the keys inside the array of objects to the destination object or its keys from the subprocess
- Output mapping: Map from the subprocess object back to an array of objects in the parent process
Legacy mapping
Legacy mapping works using current mechanics in both configuration and runtime, with no changes to existing features.Correlation attribute behavior
When results from parallel subprocesses are returned, the correlation attribute determines how the subprocess payload is handled:- Update existing element: When the correlation attribute value from the subprocess payload matches one or more elements in the parent process array, those elements are updated with the subprocess payload
- Insert new element: When the correlation attribute value from the subprocess payload doesn’t match any records in the parent process array, the payload is inserted as a new element in the array
Dismissing unfinished subprocesses
When subprocesses are started in Sync mode:- If the token is advanced due to another action being performed in the process
- Then the subprocesses that haven’t finished are automatically dismissed
Business rule example
Below is an example of an MVEL business rule used to generate a list of shipping codes: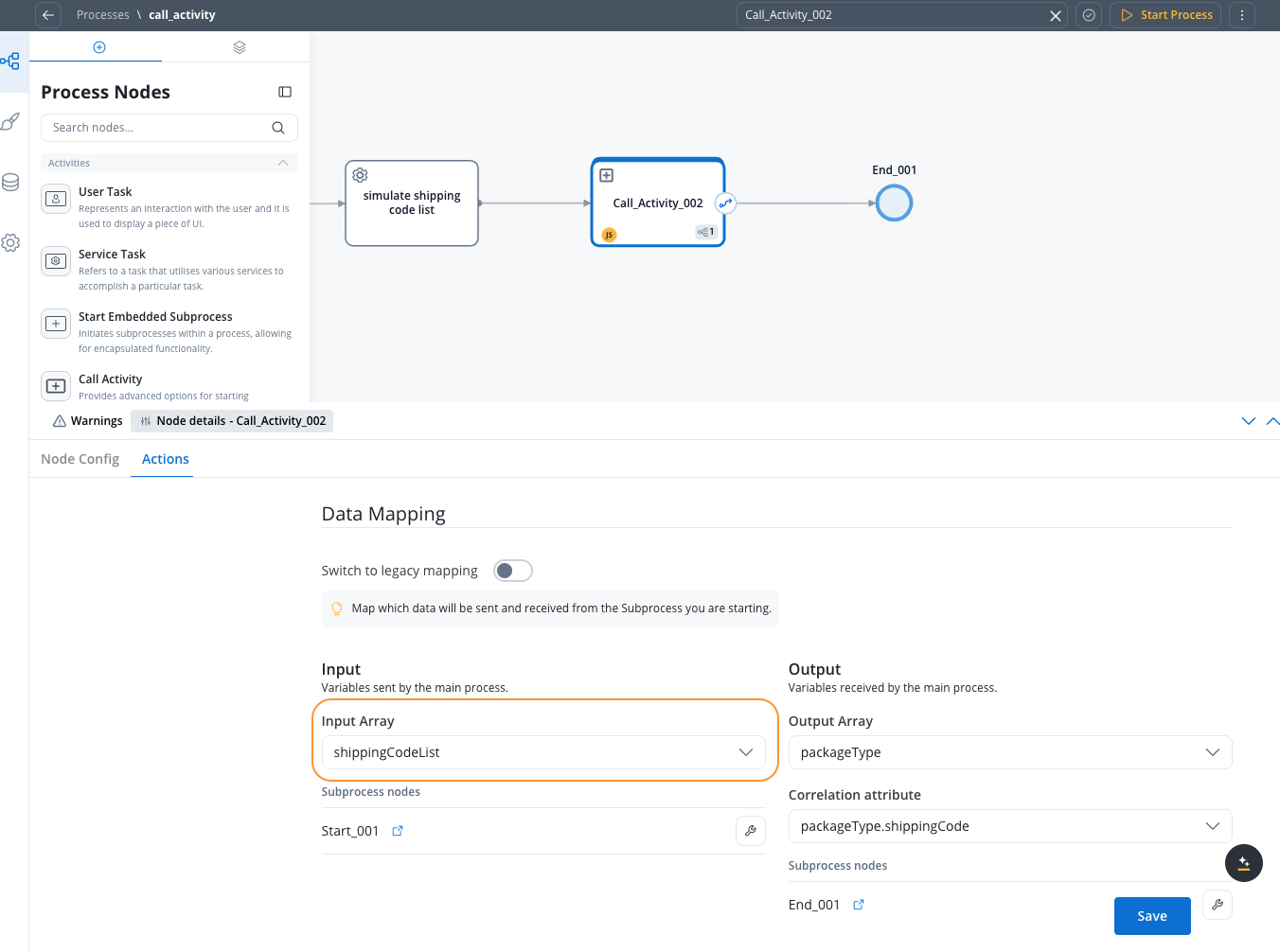
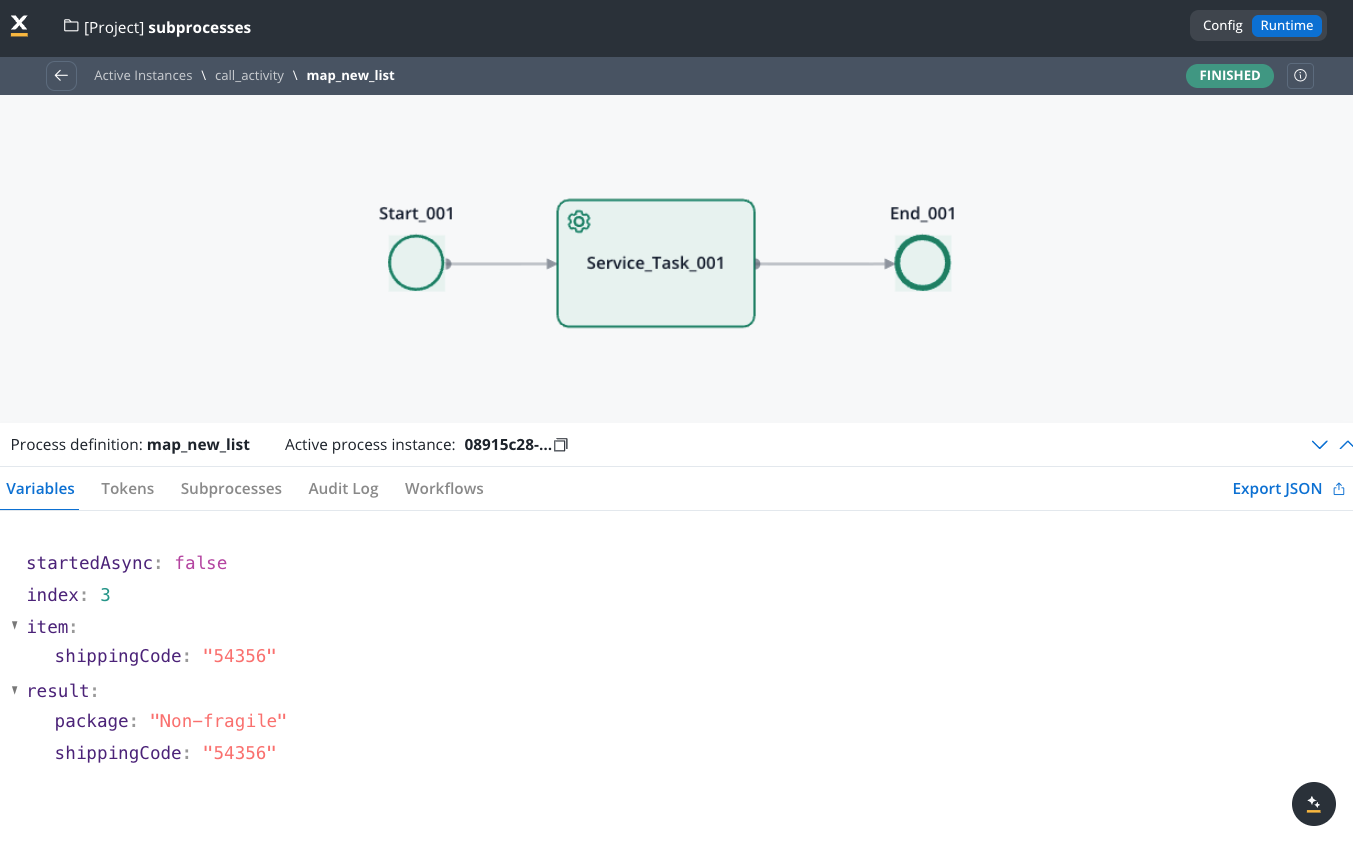
When designing such a subprocess that will be started in a loop, remember that the input value for the subprocess (one of the values from the array in the parent process) will be stored in the subprocess parameter values under the key named item. This key should be used inside the subprocess. If this subprocess produces any results, they should be stored under a key named result to be sent back to the parent process.
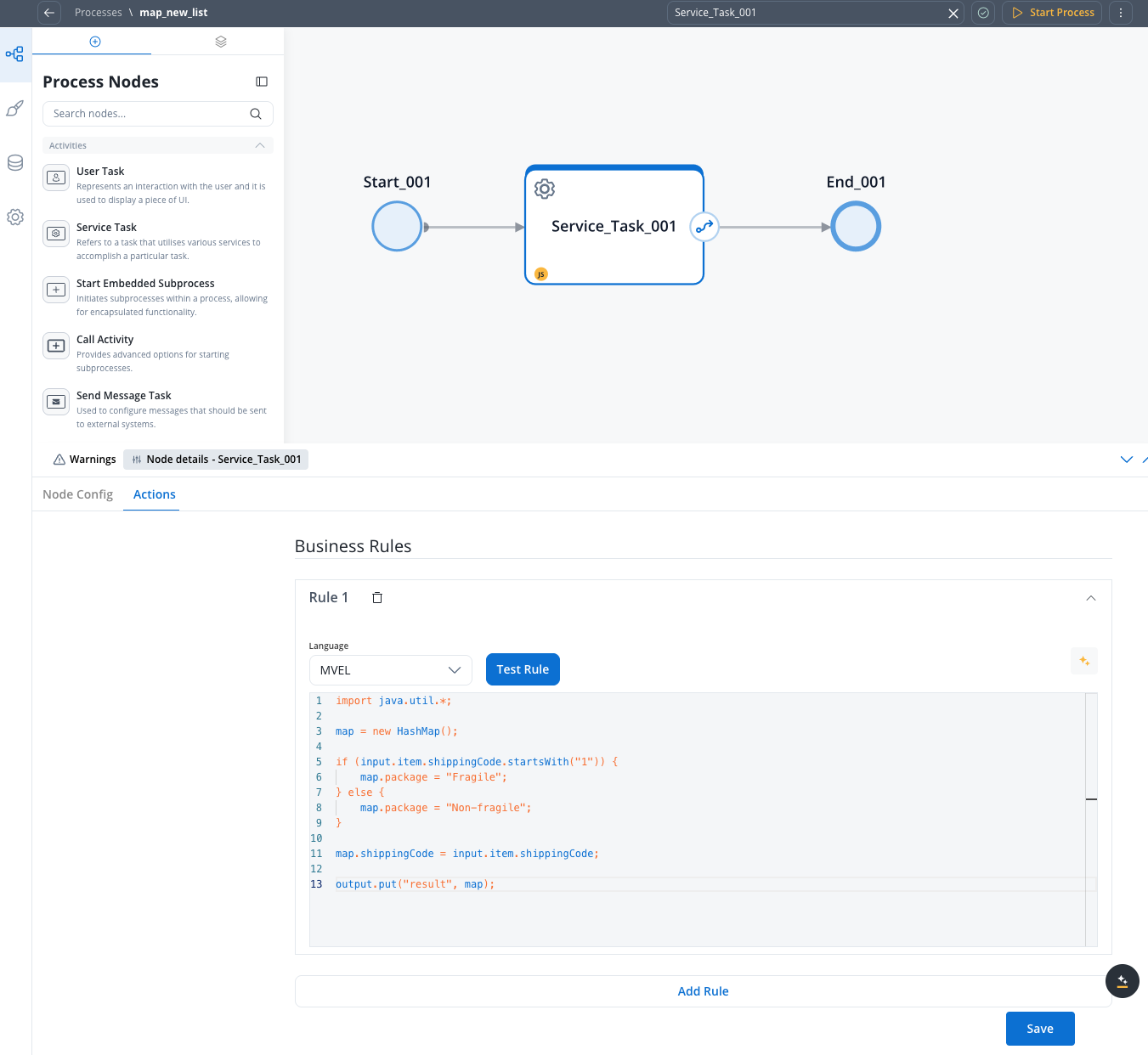
Subprocess business rule example
Here’s an MVEL business rule for a subprocess that processes shipping codes:Result (one of the subprocess instances)
The result shows the output of a process that has handled multiple shipping codes. The structure is: