What is FlowX Database?
- Share data between different process instances
- Store and retrieve data across multiple processes
- Create a persistent data store within the FlowX ecosystem
- Access structured data without directly interacting with external systems
Key concepts
- Data Sources
- Collections
- Operations
| Data Source Type | Description |
|---|---|
| RESTful System | Traditional integration with external REST APIs |
| FlowX Database | Connection to the internal FlowX Database for data persistence |
Prerequisites
Before working with FlowX Database, you should have a solid understanding of:MongoDB Fundamentals
JSON Structure
CRUD Operations
Query Modifiers
Benefits of FlowX Database
Data Sharing
Independence
Extended Use Cases
Simplified Integration
Native Integration
Complete CRUD Operations
Bulk Operations
Flexible Querying
How to use FlowX Database
Creating a collection
Access Data Sources
Accessing Data Sources in the navigation menu
Add a new Data Source
Adding a new FlowX Database data source
Configure the collection
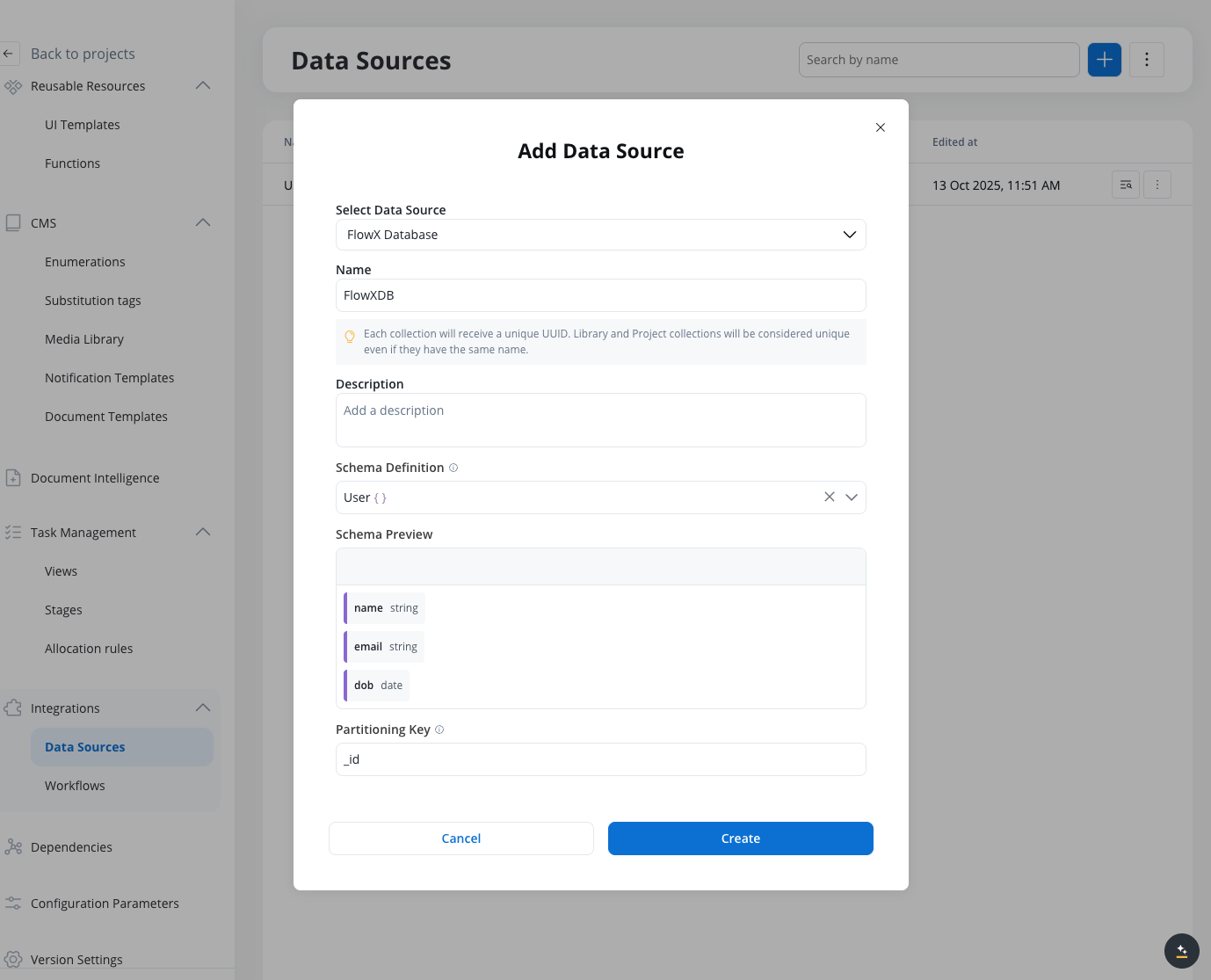
Configuring the collection
- Schema Definition: Define the schema for your collection (the selected schema enhances auto-completion but does not enforce validation during insert or update)
- Partitioning Key: The attribute used to partition data in your collection. By default, this is set to the
idattribute, but you can specify a different field based on your data model.
Create the collection
Viewing collection data
Navigate to collection
Access Documents tab
Browse documents
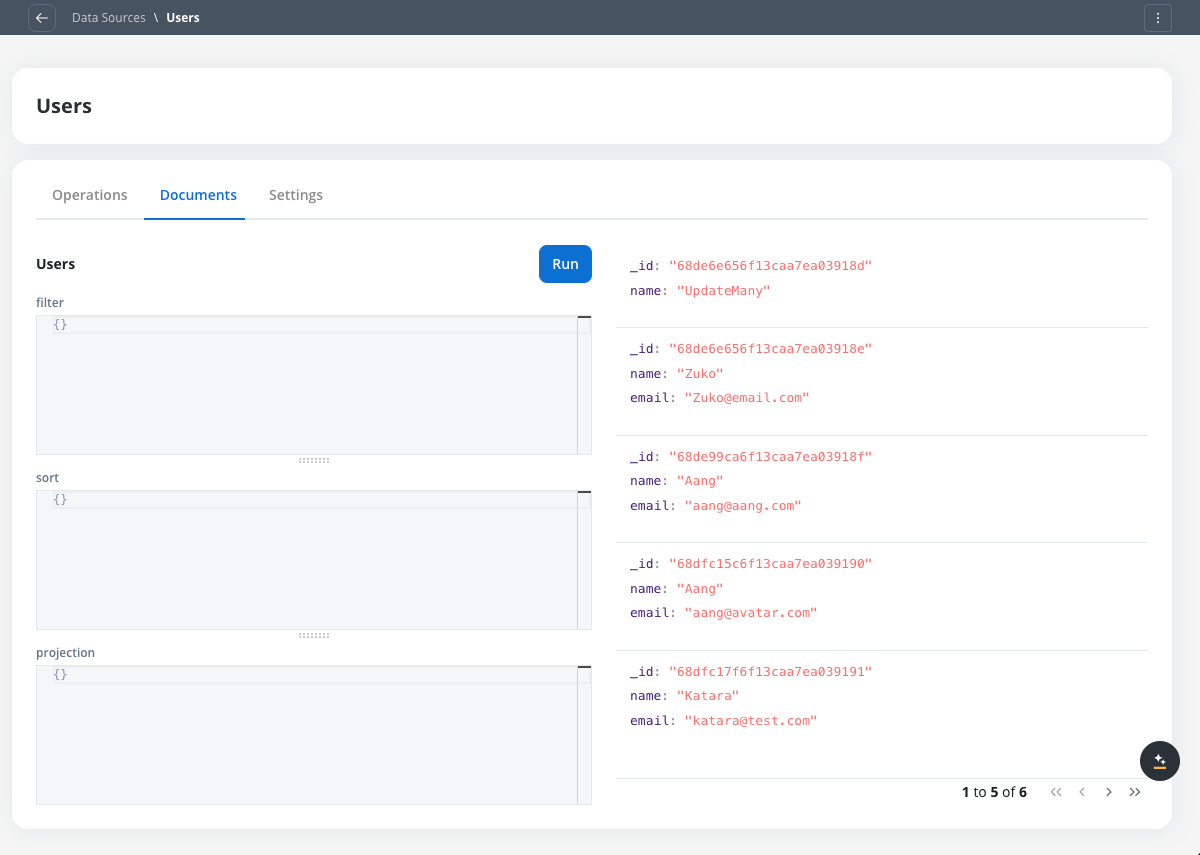
Viewing documents in a FlowX Database collection
Search and filter
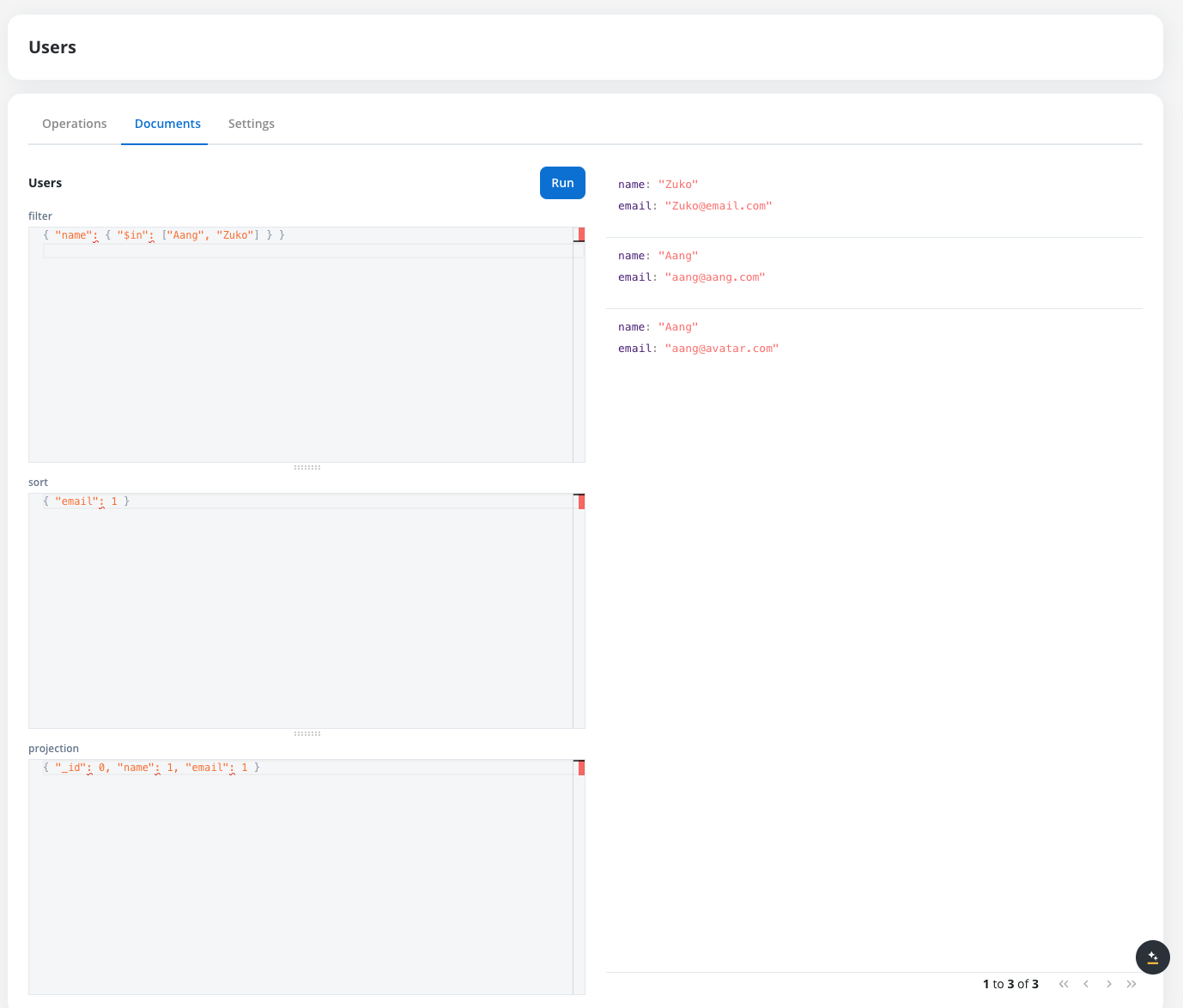
Searching and filtering documents in a FlowX Database collection
Managing collection settings
Each FlowX Database collection has a Settings tab where you can configure performance optimizations:Access Settings tab
Define indexes
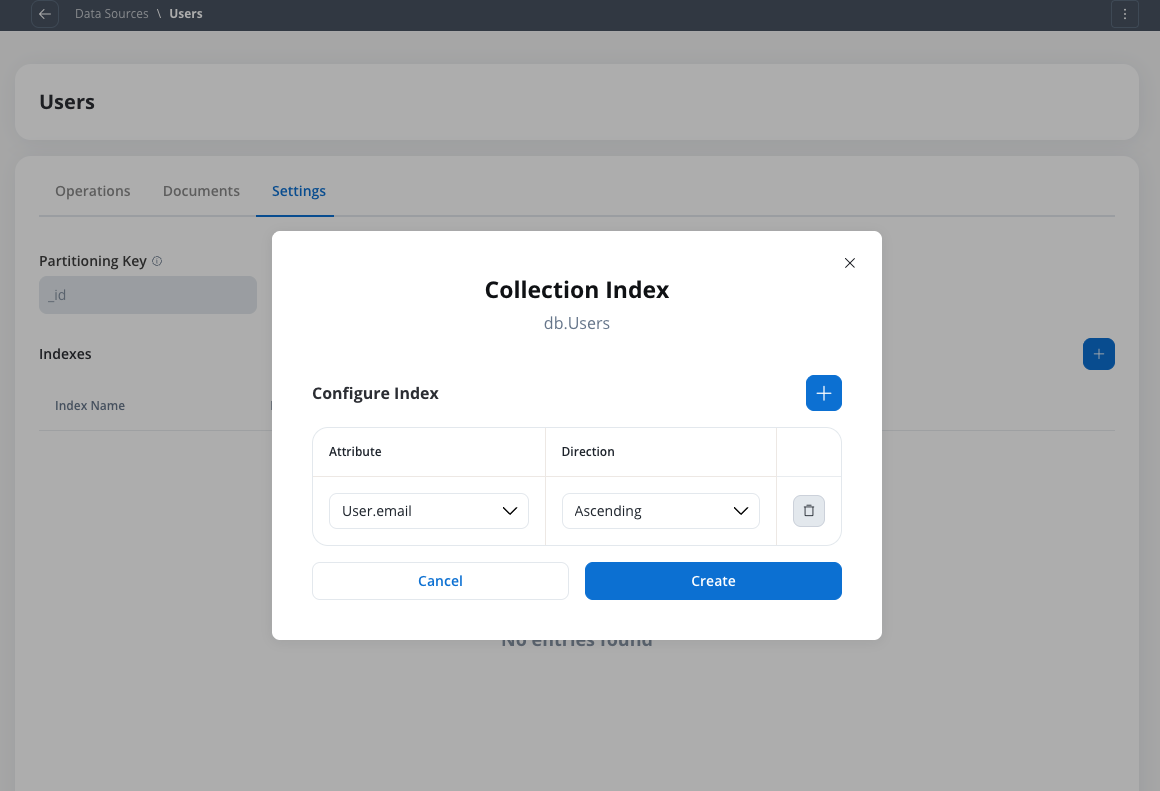
Defining indexes for a FlowX Database collection
Creating database operations
- Create operation
- Update operation
- Delete operation
Access operations list
Create new operation
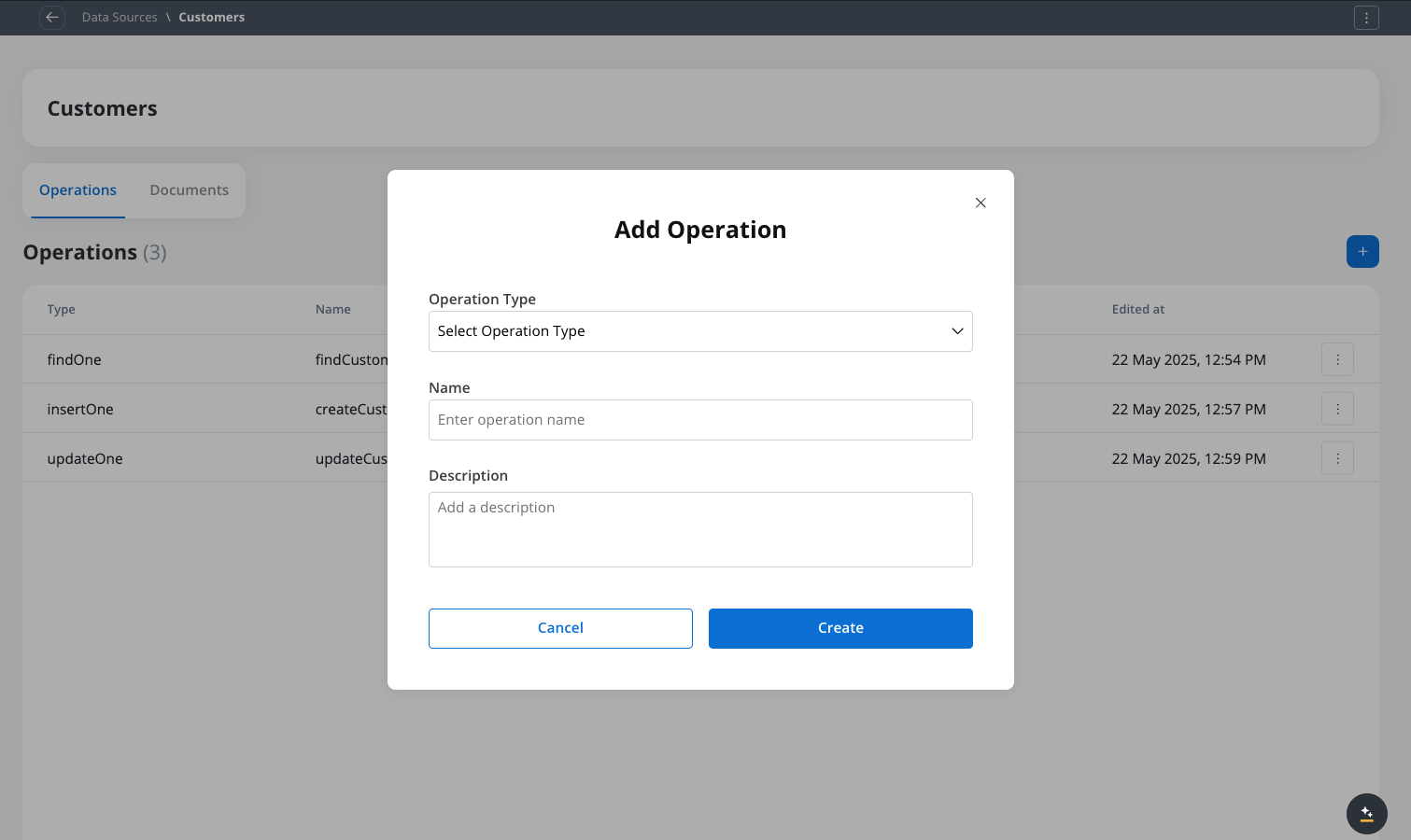
Creating a new operation for a FlowX Database collection
Select operation type
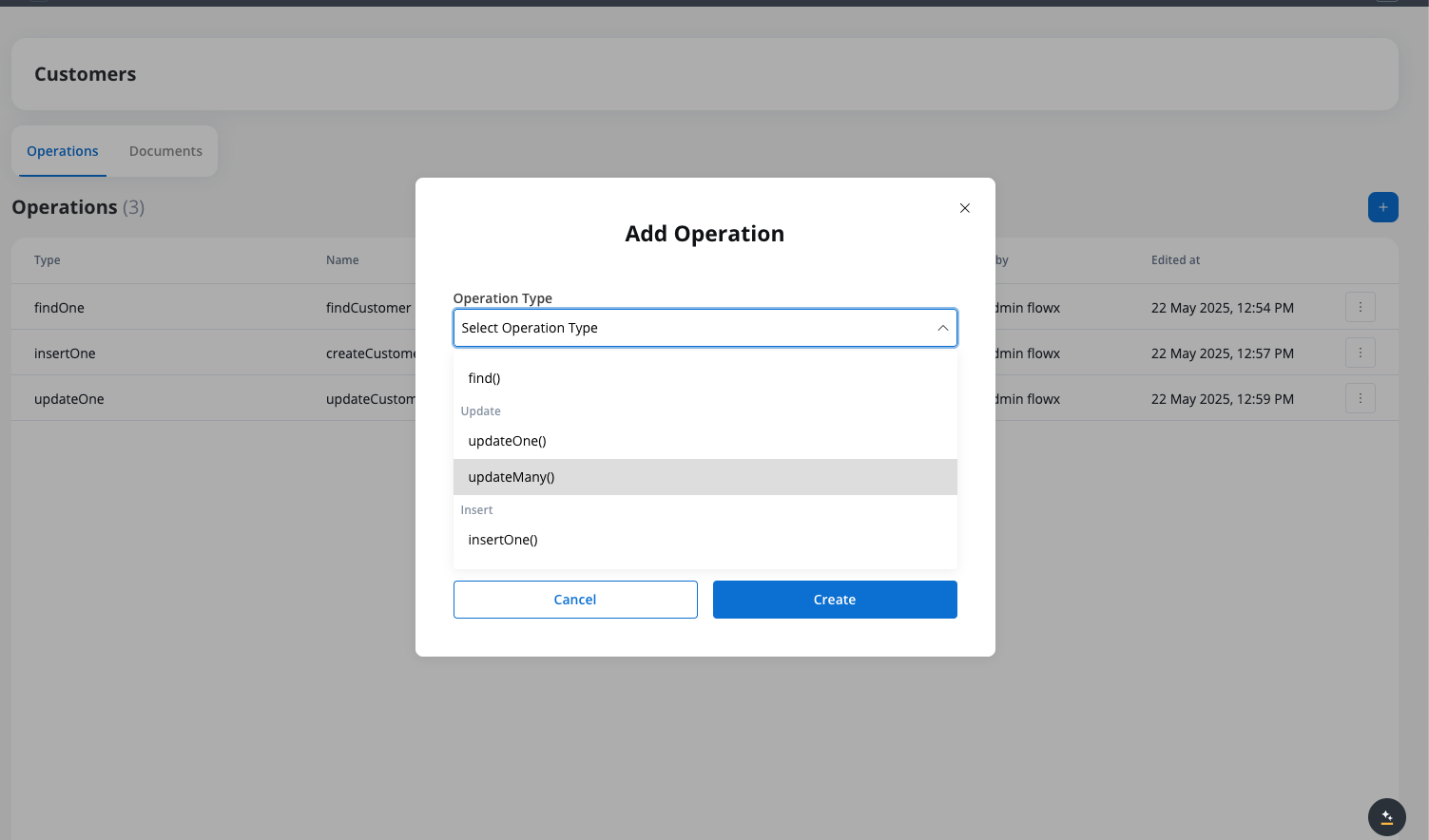
Selecting the operation type
Name the operation
Define the operation parameters
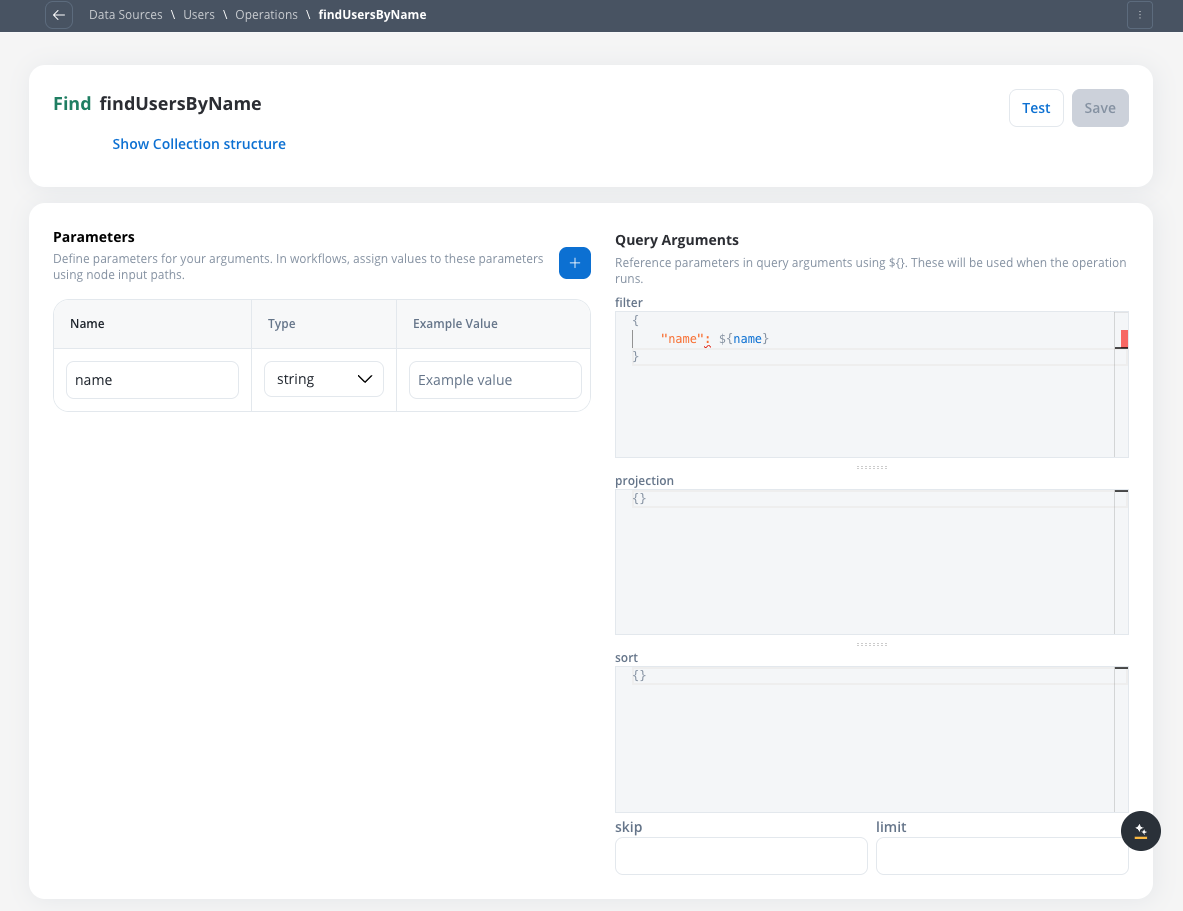
Configuring operation parameters
- Filter: Define the criteria to match documents
- Projection: Select which fields to include in the results
- Sort: Specify the sorting order
- Skip: For find operations, specify the number of documents to skip
- Limit: Set the maximum number of documents to return
- Parameters defined in the operation are referenced using
${parameterName}syntax - Database field names must be in quotes (e.g.,
"firstName","customerId") - Parameters don’t need to match your data model exactly - they’re placeholders that get replaced with actual values
- Field names in quotes must match exactly what’s stored in the database (same as your data model)
Test the operation
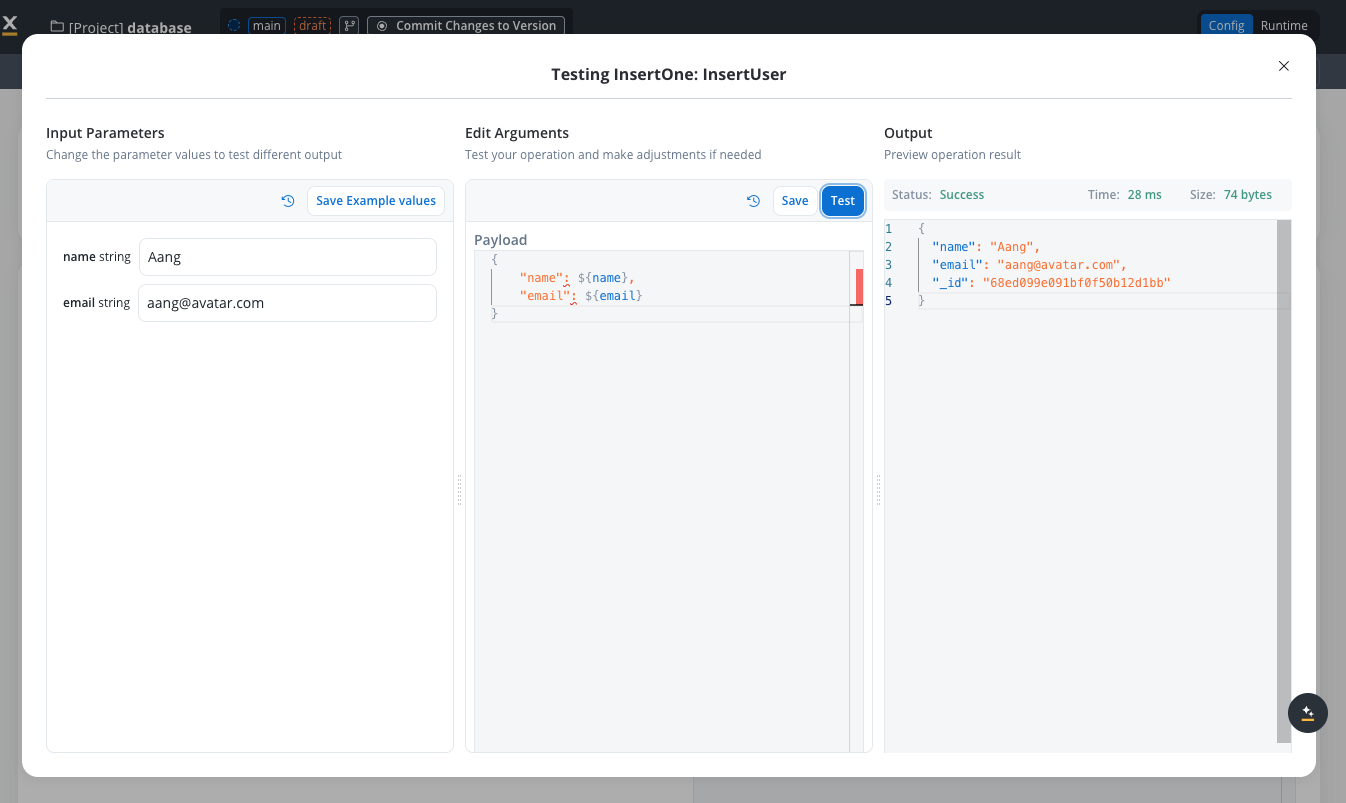
Testing an operation
Save the operation
Working with FlowX Database in workflows
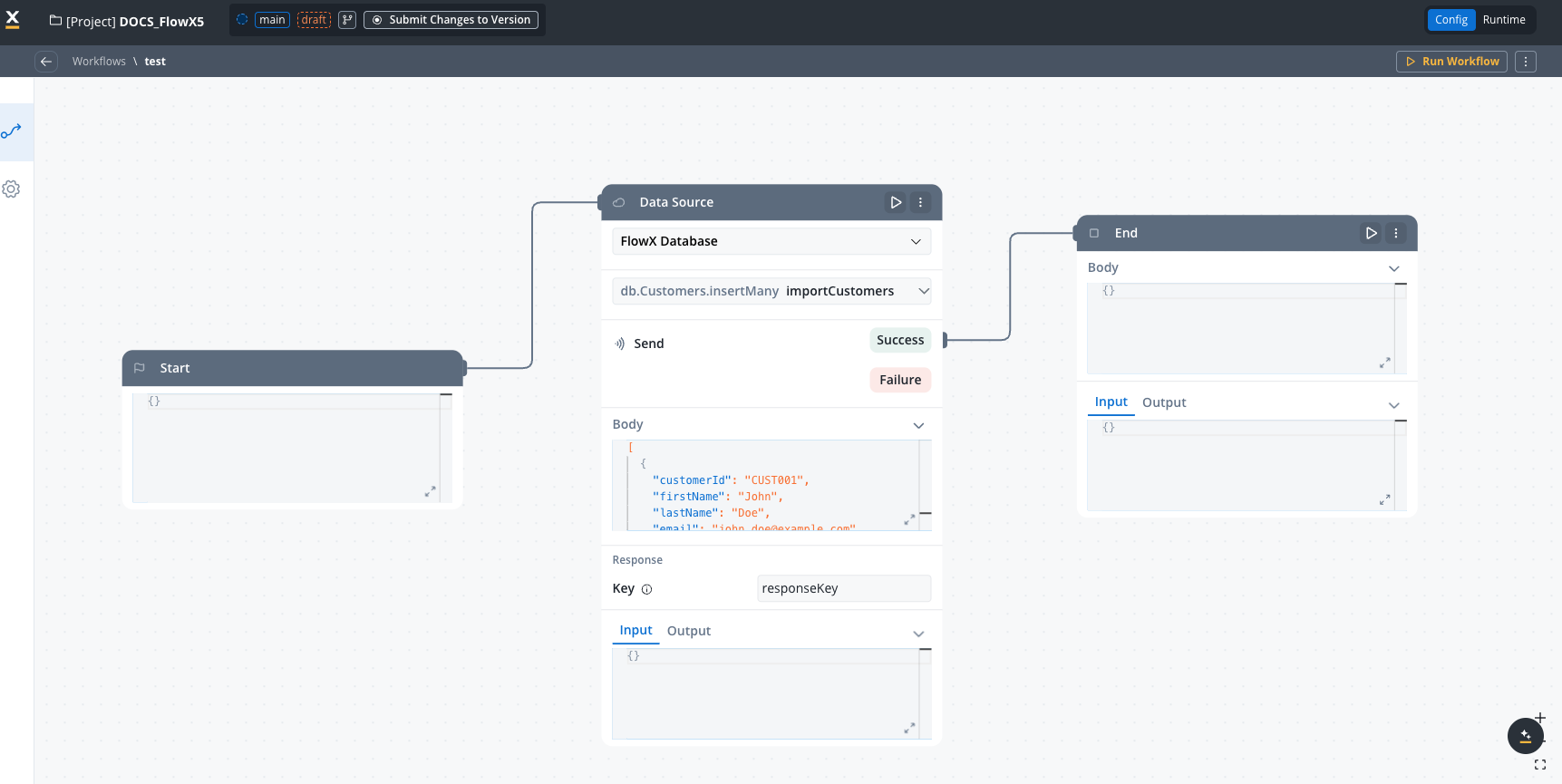
Database node in a workflow
Add Data Source node
Configure data source
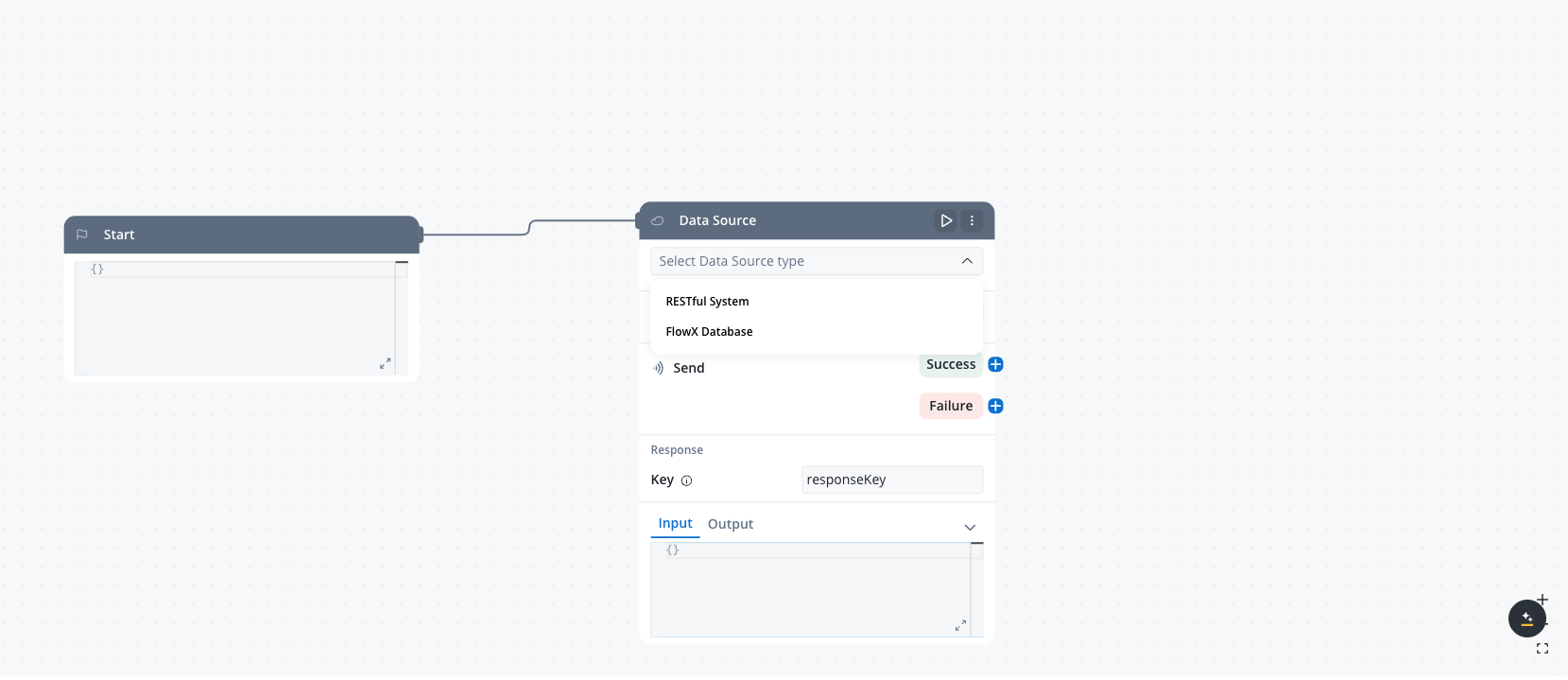
Data Source node configuration
- Choose “FlowX Database” as the system type from the dropdown
- Select your collection from the available options
- Choose the operation you want to perform (find, findOne, insertOne, insertMany, updateOne, updateMany, deleteOne, deleteMany)
Configure operation parameters
- filter - For find operations, define the criteria to match documents
- sort - For find operations, specify the sorting order for results
- document - For insert operations, define the document to insert
- update - For update operations, define the document to update
- delete - For delete operations, define the criteria to match documents
- skip - For find operations, specify the number of documents to skip
- limit - For find operations, specify the maximum number of documents to return
- projection - For find operations, specify the fields to include or exclude in the results
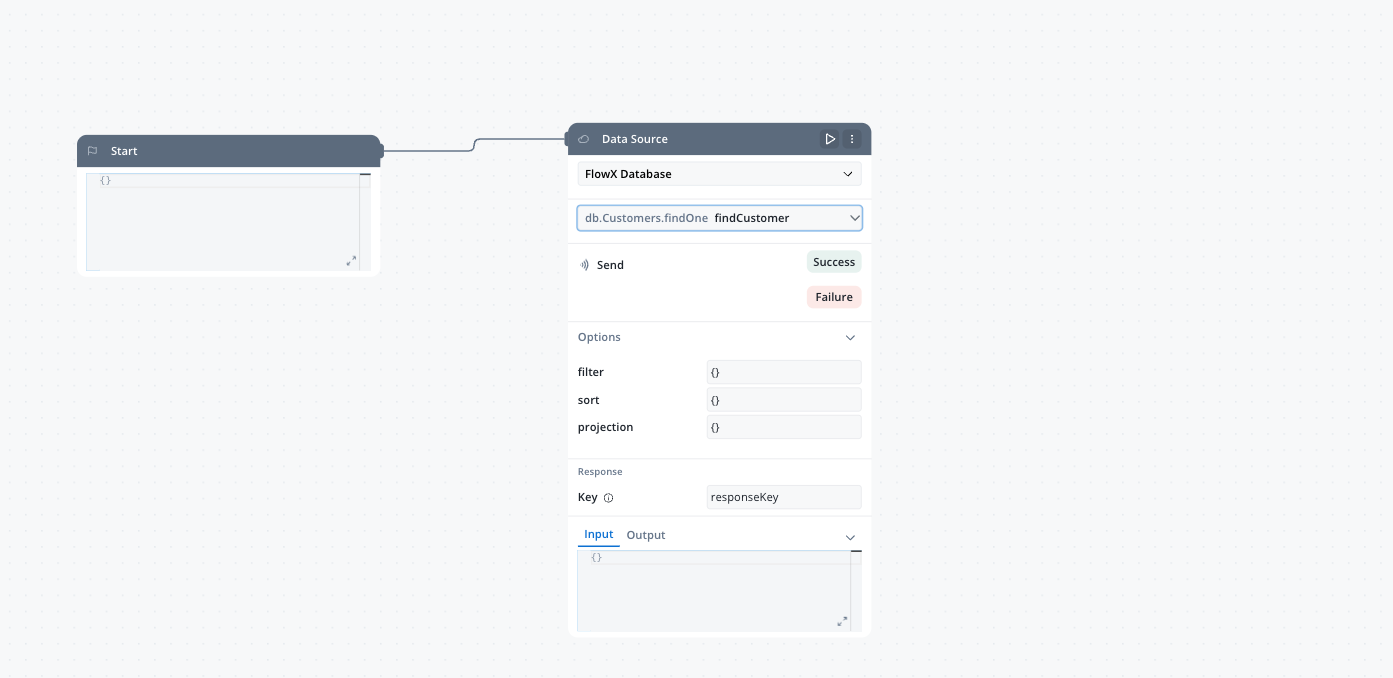
Configuring operation parameters
Set response key
Example: Using filter parameter in find operation
Example: Using filter parameter in find operation
Example: Using process variables in parameters
Example: Using process variables in parameters
MongoDB operations supported
FlowX Database leverages MongoDB’s powerful query capabilities through the nosql-db-runner service, providing pure MongoDB functionality. For detailed information about MongoDB query operators, filters, and syntax, refer to the MongoDB Query and Projection Operators documentation. The following MongoDB operations are supported in FlowX Database. Each tab includes practical examples that you can use as a starting point for your own operations.- find
- findOne
- insertOne
- insertMany
- updateOne
- updateMany
- deleteOne
- deleteMany
- filter (document, optional): Criteria to match documents. See Query Filter Documents
- sort (document, optional): Document specifying the sorting order. See Sort Query Results
- skip (integer, optional): Number of documents to skip. See Limit Query Results
- limit (integer, optional): Maximum number of documents to return. See Limit Query Results
- projection (document, optional): Fields to include or exclude. See Project Fields
Example: List active customers
Example: List active customers
- filter
- sort
- projection
- skip
- limit
Example: Find products by category and price
Example: Find products by category and price
- filter
- sort
- projection
- limit
Real-world example: Customer management system
This example demonstrates how a customer management system could use FlowX Database to persist and share customer data across different processes.Setup
Setup
Create Customer collection
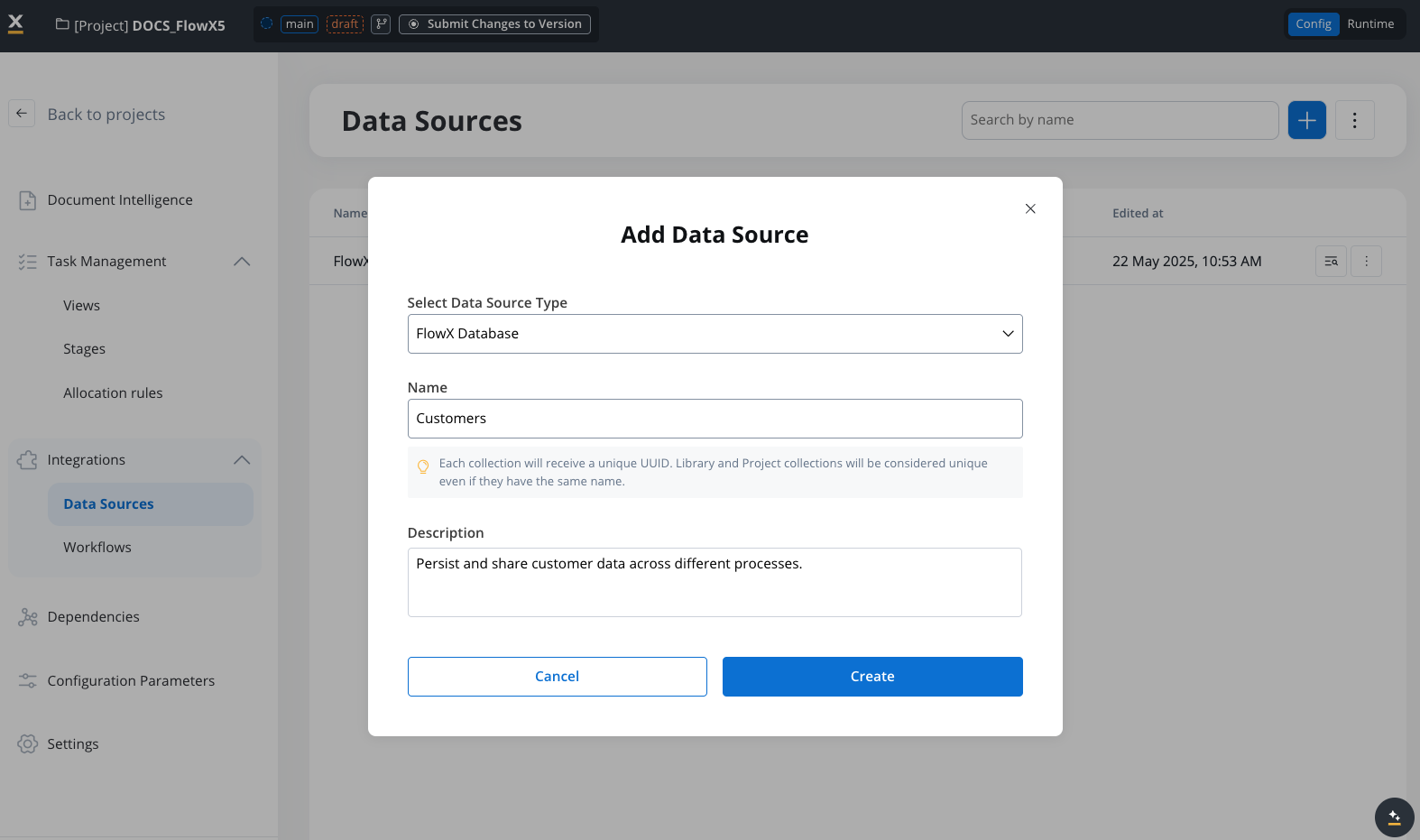
Define operations
- findCustomer
- createCustomer
- updateCustomerStatus
- listActiveCustomers
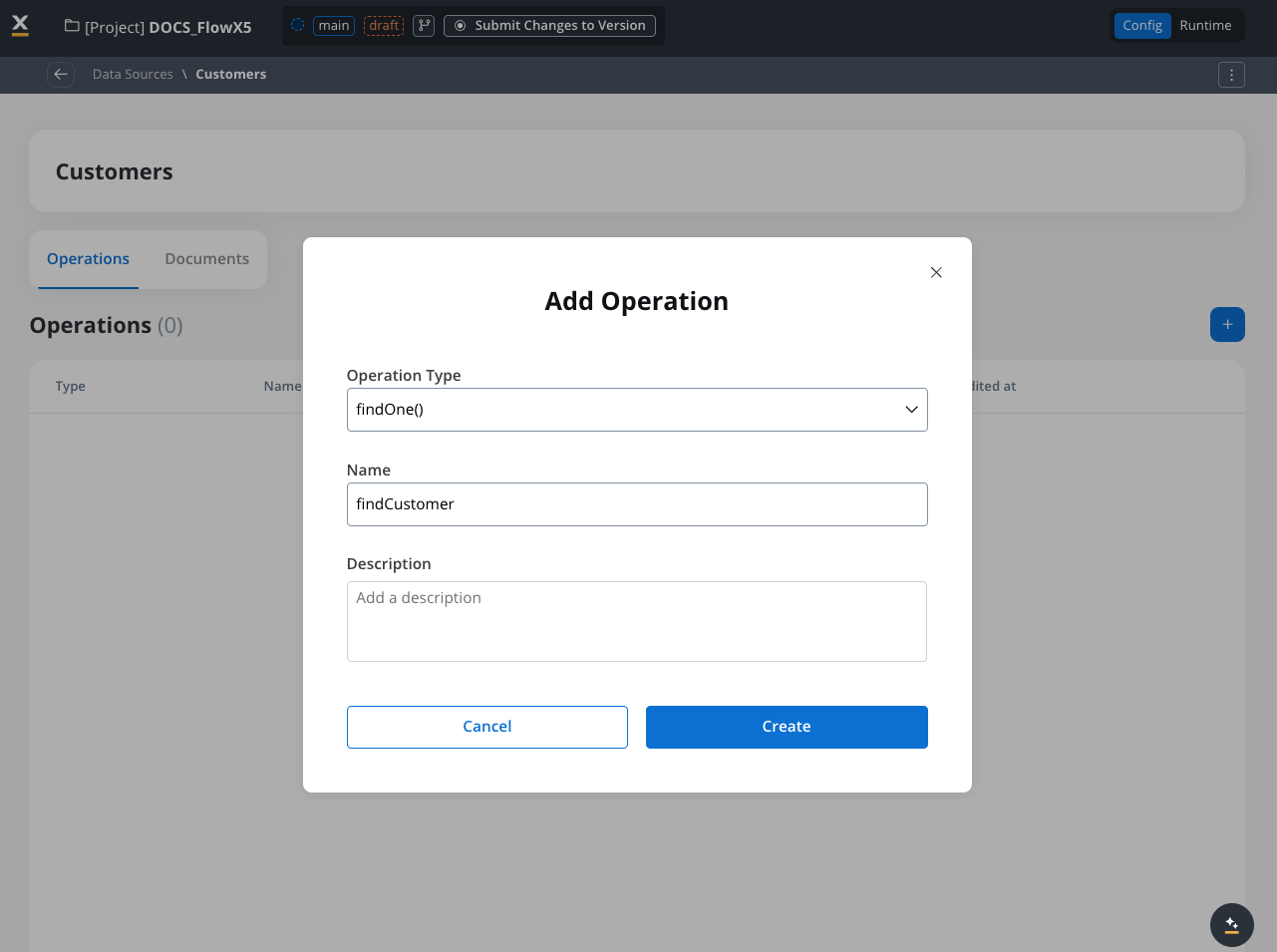
Customer support process
Customer support process
- Support agent enters the customer ID
- A Data Source node retrieves the customer details from the Customers collection
- Customer information is displayed to the agent
- After resolving the issue, the support agent updates the customer status
- Another Data Source node updates the customer record in the database
Benefits demonstrated
Benefits demonstrated
- Enables data persistence across multiple processes
- Provides a single source of truth for customer data
- Simplifies data retrieval and updates
- Eliminates the need for external systems to store basic customer information
Limitations and considerations
Best practices
Troubleshooting
Operation fails with filter error
Operation fails with filter error
Problem
Solution
- Missing quotes around string values
- Incorrect operator syntax (e.g., using > instead of $gt)
- Mismatched brackets or braces
Documents not appearing in results
Documents not appearing in results
Problem
Solution
- Verify your filter conditions are correct
- Check if documents actually exist in the collection
- Try a more general query to see if documents are returned
- Check if field names in your filter match exactly with the document structure
Performance issues with large result sets
Performance issues with large result sets
Problem
Solution
- Add pagination using skip and limit parameters
- Add more specific filter conditions
- Use projection to return only needed fields
- Consider indexing frequently queried fields
Insert operation fails
Insert operation fails
Problem
Solution
- Check that your document JSON is valid
- Ensure document size is under 16MB
- Verify all required fields are present
- Check for any unique constraint violations
Related features
Data Search
Integration Management
Workflow
Process Data Model
Summary
FlowX Database provides a powerful persistence layer that enables you to store and share data across different processes and projects. By leveraging MongoDB’s capabilities through the nosql-db-runner service, FlowX Database offers:- Flexible data storage for any structured data
- Data sharing between process instances
- Integration with workflows
- Independence from external systems for basic data persistence
MongoDB learning resources
To get the most out of FlowX Database, familiarize yourself with MongoDB concepts and operations:MongoDB Manual
Query Tutorial
Update Operations
Data Modeling
FAQs
When should I use Data Search vs. FlowX Database?
When should I use Data Search vs. FlowX Database?
- FlowX Database
- Data Search
- Acts as a persistent data store
- Optimized for CRUD operations
- Stores structured business data
- Designed for sharing data across processes
- Uses MongoDB as the underlying technology (via nosql-db-runner service)
What types of data should I store in FlowX Database?
What types of data should I store in FlowX Database?
- Dashboard data: Aggregated information for reporting and visualization. For example, create operations that gather information from multiple processes and pull all the data to calculate sums, averages, or other metrics for executive dashboards
- Cached data: Frequently accessed information that changes periodically, such as:
- Daily exchange rates for financial calculations
- Product catalogs that update weekly
- Configuration data that multiple processes need to access
- Internal operational comments: Information that needs to be shared between users but shouldn’t reach business systems, such as:
- Internal comments in a client’s profile for bank tellers
- Notes and annotations that support decision-making across different process instances
- Communication logs between team members working on the same case
- Shared process data: Information that needs to be accessed across multiple process instances - this solves the key pain point of data sharing between different process instances
- Temporary operational data: Working data that supports business processes but isn’t part of your permanent records
Can I share FlowX Database collections between different projects?
Can I share FlowX Database collections between different projects?
Why doesn't FlowX Database support automatic data migration?
Why doesn't FlowX Database support automatic data migration?
- Data integrity: Many documents need to remain in their original format to maintain historical accuracy and compliance requirements
- Process dependencies: Existing processes may depend on specific data structures, and automatic changes could break functionality
- Business context: Data migration often requires business logic and context that automated systems cannot provide
- Risk management: Manual migration allows for proper testing and validation before changes are applied
Can I store different types of documents in the same collection?
Can I store different types of documents in the same collection?
- Query complexity: Filtering becomes more complex when documents have different schemas
- Performance issues: Indexes become less effective with mixed document types
- Maintenance problems: Updates and changes become harder to manage
- Data consistency: Harder to ensure data quality and validation
How does FlowX Database solve cross-process data sharing?
How does FlowX Database solve cross-process data sharing?
- Cross-instance access: Multiple process instances can read from and write to the same collections simultaneously
- Data persistence: Data remains available even after individual processes complete
- Concurrent access: The underlying MongoDB technology (via nosql-db-runner) handles concurrent read/write operations safely
- Shared state: Enables complex workflows where processes need to coordinate through shared data
What's the relationship between FlowX Database and the nosql-db-runner service?
What's the relationship between FlowX Database and the nosql-db-runner service?
- Pure MongoDB functionality: Direct access to MongoDB operations within the FlowX ecosystem
- Native integration: Connection between FlowX workflows and MongoDB operations
- Scalable architecture: A dedicated service that can be scaled independently based on database operation needs

