Types of BPMN nodes
The following sections explore each type of BPMN node available in FlowX.AI:Start and End nodes
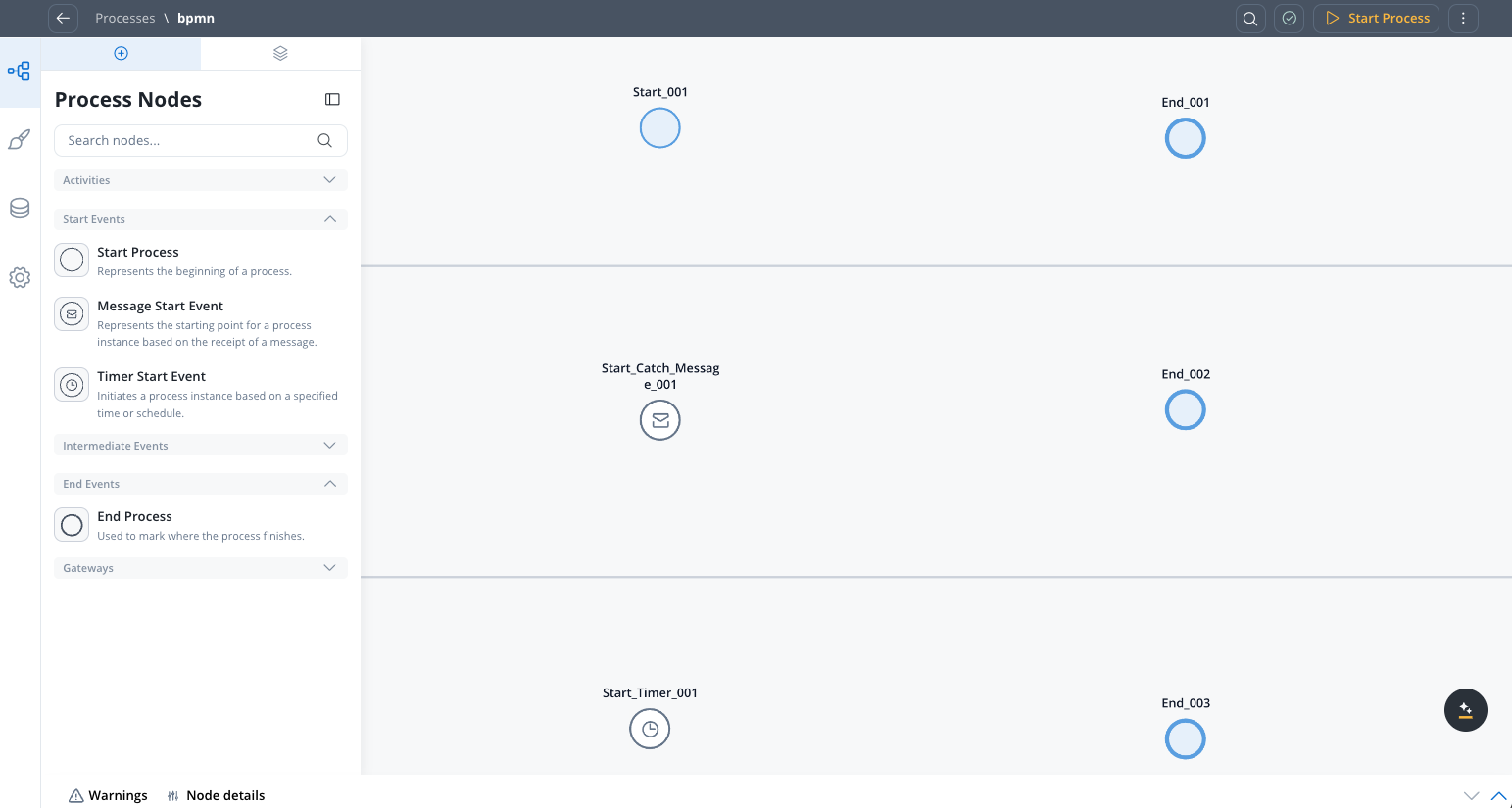
- Start Node: Defines the beginning of a process flow and how a process instance is initiated.
- Message Start Event: Starts a process instance when a specific message is received.
- Timer Start Event: Initiates a process instance based on a specified time or schedule.
- End Node: Marks where the process finishes.
A process definition may have multiple start nodes (only if they are in different swimlanes, only one start node per swimlane) and end nodes based on the flow outcomes.
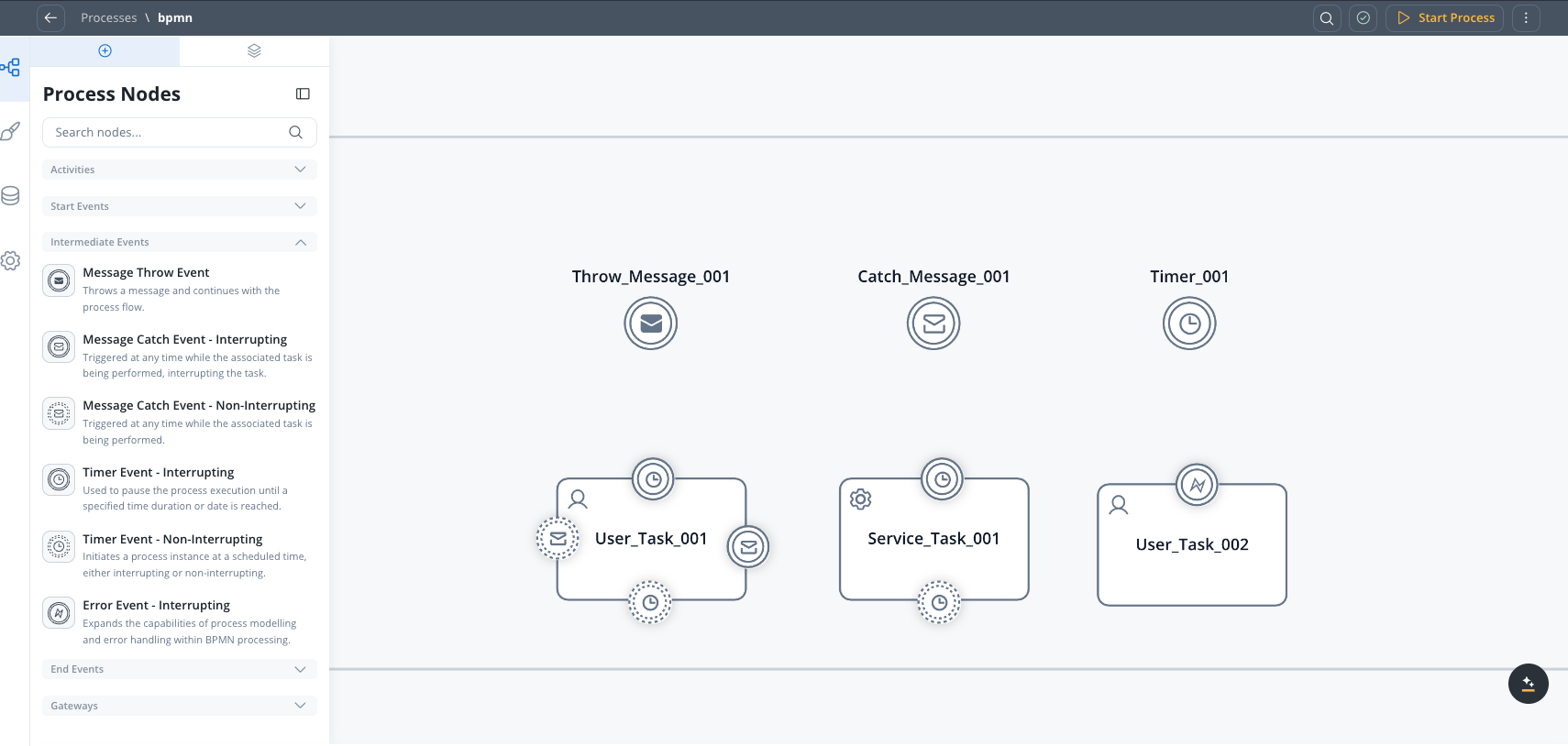
Activity nodes
- User Task: Represents user interactions and displays UI components.
- Service Task: Executes tasks using various services to accomplish specific functions.
- Start Embedded Subprocess: Initiates subprocesses within a parent process, providing encapsulated functionality and enhanced process management.
- Call Activity: Provides advanced options for starting subprocesses with enhanced control.
- Send Message Task: Sends messages to external systems, integrations, and plugins.
- Receive Message Task: Receives messages from external systems, integrations, and plugins.

Intermediate events
- Message Throw Event: Throws a message and continues with the process flow.
- Message Catch Event - Interrupting: Waits for a message before continuing with the process flow.
- Message Catch Event - Non-Interrupting: Waits for a message before continuing with the process flow.
- Timer Event - Interrupting: Triggers based on a specific time duration, date, or cycle. Can also be used as a boundary event.
- Timer Event - Non-Interrupting: Triggers based on a specific time duration, date, or cycle. Can also be used as a boundary event.
Boundary events
Boundary events attach to the boundary of specific nodes (e.g., User Task, Service Task, Subprocess, or Call Activity) and are triggered when predefined conditions occur. These events can interrupt the ongoing activity or allow it to continue while starting a parallel flow. They include:- Message Catch Event - Interrupting: Waits for and responds to a specific incoming message during a task.
- Message Catch Event - Non-Interrupting: Waits for and responds to a specific incoming message during a task.
- Timer Event - Interrupting: Activates based on elapsed time, a specific date, or a recurring cycle, useful for timeouts or deadlines.
- Timer Event - Non-Interrupting: Activates based on elapsed time, a specific date, or a recurring cycle, useful for timeouts or deadlines.
- Error Event - Interrupting: This event catches errors during a task or subprocess and redirects the process flow to handle them appropriately.
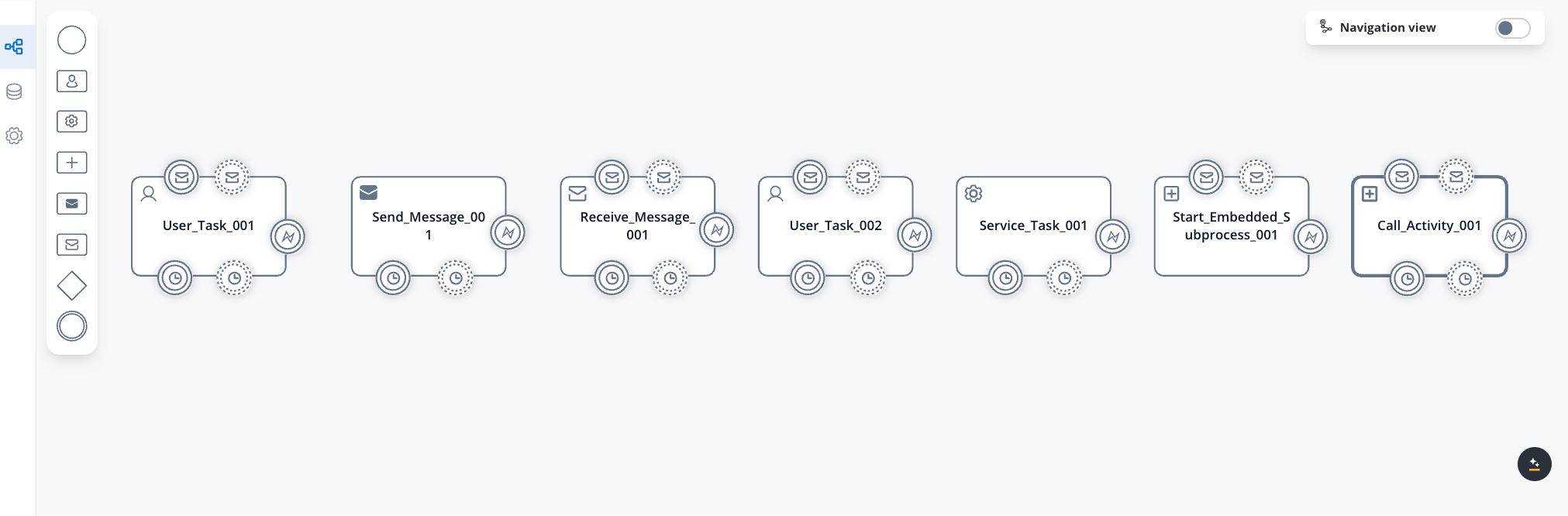
Compatibility matrix
Boundary events can attach to the following node types:Compatible node types
Compatible node types
- User Task: All boundary event types supported
- Service Task: Supports Message Catch Event - Interrupting, Timer Event - Interrupting, and Error Event - Interrupting boundary events.
- Send Message/Receive Message Tasks: Supports Message Catch Event - Interrupting, Timer Event - Interrupting, and Error Event - Interrupting boundary events.
- Start Embedded Subprocess: Supports Message Catch Event - Interrupting, Timer Event - Interrupting, and Error Event - Interrupting boundary events.
- Call Activity: Supports Message Catch Event - Interrupting/Non-Interrupting, Timer Event - Interrupting/Non-Interrupting, and Error Event - Interrupting boundary events.
Next steps
Now that you understand the different types of BPMN nodes available in FlowX.AI, you can start building your own processes. Each node type offers specific configuration options and capabilities that you’ll explore as you design your workflows. For hands-on guidance on creating and configuring nodes in your processes, see: Managing a process flow For comprehensive insights into BPMN and its various node types, explore our course at FlowX Academy:BPMN 101
- What’s BPMN (Business Process Model Notation) and how does it work?
- How is BPMN used in FlowX?

