What are Reusable UI Templates?
Reusable UI Templates are self-contained UI component hierarchies that you design once and instantiate multiple times throughout your application. They solve common UI development challenges:- Repetitive styling: No more redoing component styles and properties for similar UI patterns
- Manual updates: Reduce the need to manually change components across multiple locations
- Template management: Centralized configuration and management of UI templates
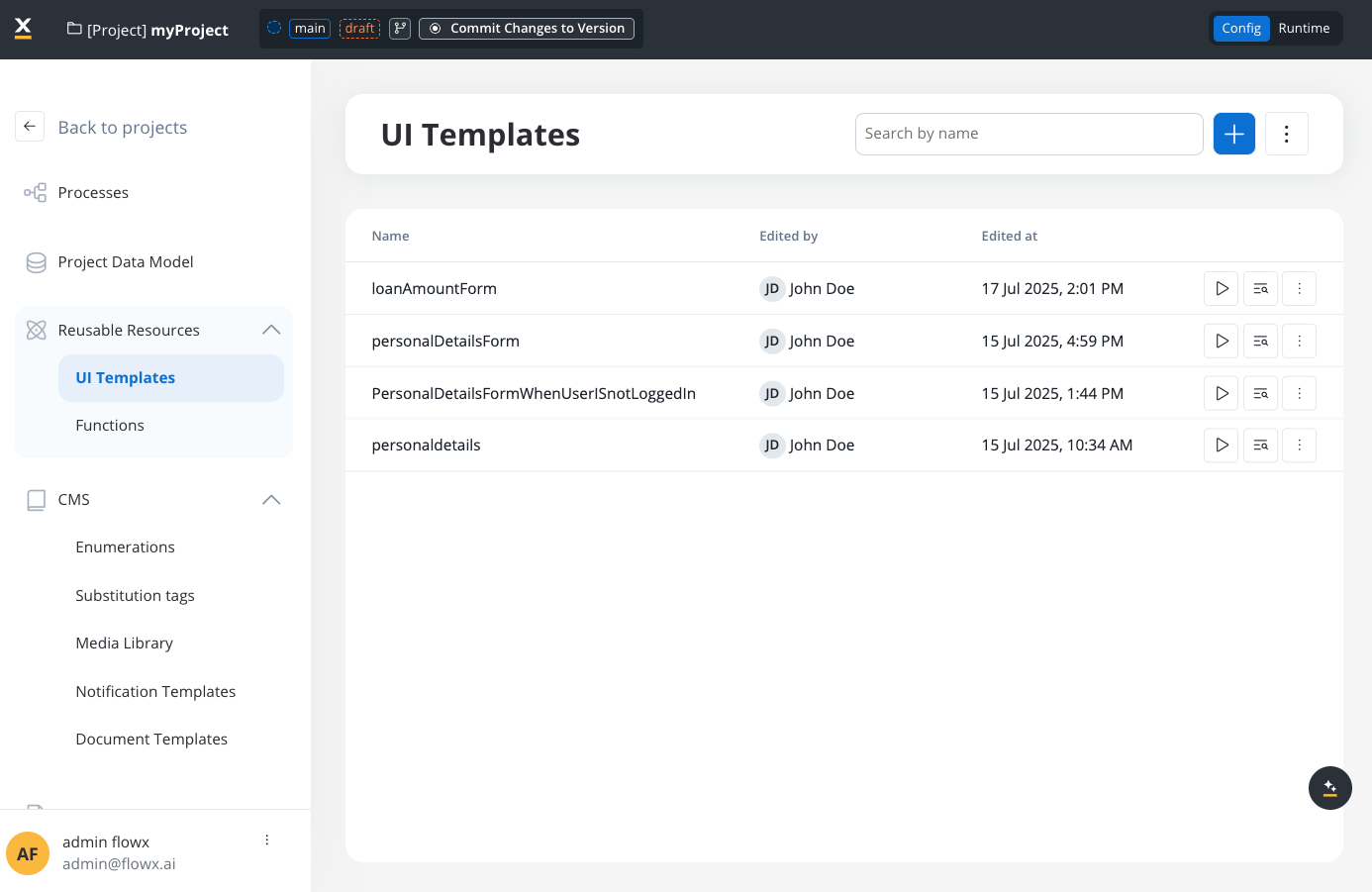
Reusable UI Templates focus on visual components and layout. They cannot include reusable business rules or complex business logic.
Key benefits
Consistency
Ensure uniform UI patterns across your entire application
Efficiency
Design once and use many times - no more recreating similar patterns
Maintainability
Update templates in one place to affect all instances automatically
Omnichannel support
Templates work across different platforms and channels
Template types
FlowX.AI supports two main types of reusable UI templates:- Dynamic Templates (with inputs)
- Static Templates (without inputs)
Characteristics:
- Include input parameters that receive data from the process
- Support output parameters that send data back to the process
- Contextualized based on runtime data
- Ideal for forms and data-driven interfaces
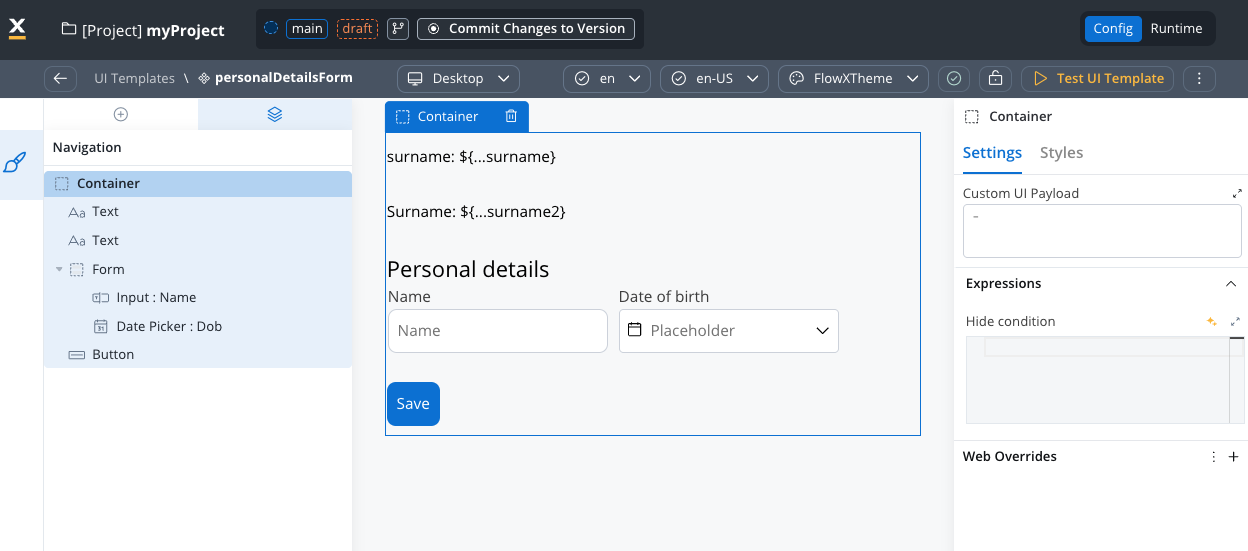
Template structure
A reusable template consists of:- Root component: A single container (Card, Container, or Custom Component)
- UI hierarchy: Child components arranged in a hierarchical structure
- UI actions: Interactive elements that can trigger process actions
- Data model: Input and output parameters for template configuration
- Configuration: Name, description, and resource metadata
Before you begin
Make sure you have:- Access to FlowX.AI Designer
- Appropriate permissions to create and manage reusable resources
- A clear understanding of the UI pattern you want to standardize
Create a reusable template
1
Access template management
- In FlowX.AI Designer, go to your project
- Navigate to Reusable Resources > Templates
- Click + New Reusable Template
2
Configure basic settings
-
Enter a descriptive name for your template (required)
- ✅ Good:
PersonalDetailsCard,User_Registration_Form - ❌ Avoid:
Personal Details Card,user-form
- ✅ Good:
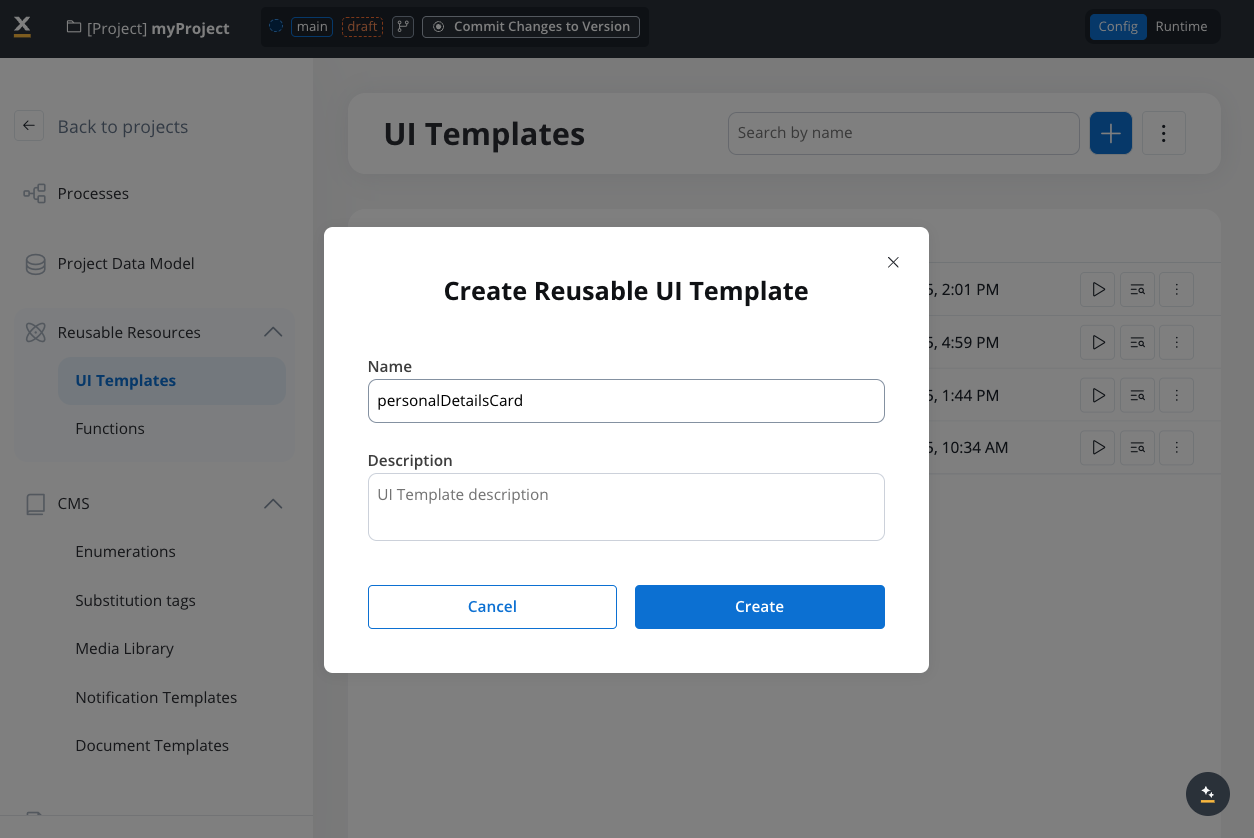
- Add an optional description explaining the template’s purpose
- Choose your root component type:
- Card: Best for content needing visual separation and styling
- Container: Ideal for layout and grouping without visual styling
- Configure the data model with input and output parameters
3
Define the data model
Set up the internal data structure that your template will use:
- Set the root element (e.g.,
applicationUI) - Define field attributes with appropriate data types:
4
Configure input and output parameters
Define the data contract between your template and the process:Input Parameters:Once parameters are defined, click Done to establish the template’s data contract.
- Data that flows INTO the template from the process
- Example:
ssn(pre-filled from existing process data)
- Data that flows OUT of the template back to the process
- Example:
firstName_UI,lastName_UI,emailAddress_UI,phoneNumber_UI,dob_UI,gender_UI,consent_UI
Parameters control data flow only. They don’t determine field visibility or editability - you can still edit input parameter fields unless explicitly made read-only.
5
Design the UI hierarchy
Use the template UI designer to build your component structure:
The template UI designer focuses on screen parts without navigation concepts or process-related navigation.
6
Configure UI actions (optional)
Define interactive elements within your template:
- Template-defined actions
- Form-centric actions
- Define UI actions within the reusable template
- Assign node actions when instantiated in User Tasks
- Use for standard actions like “Save”, “Submit”, or “Cancel”
7
Test your template
- Use Preview Mode to see how your template renders
- Verify component hierarchy and basic functionality
- Test with different themes and configurations
- Save your template when testing is successful
Preview Mode provides visual-only testing. Templates are not functional until embedded in a live process with proper parameter mapping.
Use templates in User Tasks
To integrate reusable templates into your processes, follow this complete workflow:Prerequisites: Set up data models
1
Configure Project Data Model
- In your project, define the main entity (e.g.,
Application) - Add child objects that match your template structure (e.g.,
Client) - Include all fields from your template’s data model:
firstName,lastName,emailAddressphoneNumber,dob,gender,consent,ssn
2
Configure Process Data Model
- Reference the project entity in your process
- Select
applicationas the root entity - Include
Clientas a child object - The data model will automatically populate with the correct entities
Add and configure templates
1
Add template to User Task
- Open the UI Designer for your User Task
- In the component panel, locate Reusable Templates
- Drag and drop your desired template into the UI hierarchy
- The template will appear with red warning icons indicating unmapped parameters
2
Map input parameters
- Select the template instance in the UI hierarchy
- Navigate to the template settings panel
- Click Define Parameters for Input Parameters
-
Map each input to process data using dynamic keys:
Example mapping:
3
Map output parameters
- Click Define Parameters for Output Parameters
- Select all fields that should return data to the process
-
Map each output to the corresponding process data structure:
Example mappings:
- Test the parameter mappings to ensure data flows correctly
4
Connect template actions to process
- Define process action: In Process Designer, create a new UI action (e.g.,
saveData) - Link to template: Return to UI Designer, select the action button within the template
- Configure action: Click Add UI Action and select your process action
- FlowX.AI automatically fills in the action identifier and establishes the connection
Runtime behavior
At runtime, the process engine expands reusable templates by:- Replacing the
REUSABLE_TEMPLATEplaceholder with the actual component hierarchy - Maintaining proper parent-child relationships
- Ensuring unique identifiers for each instance
- Preserving configured UI actions and data bindings
Manage templates
View template usage
To see where a template is used:- Go to Reusable Resources > Templates
- Select your template
- Click the Usages tab
- Review all processes and User Tasks using the template
Update templates
When you modify a reusable template:- Changes automatically propagate to all instances
- Existing process instances may need to restart for updates
- Instance-specific configurations are preserved
- The system validates changes to prevent breaking existing implementations
Template dependencies
Reusable templates can reference these project resources:Enumerations
Enumerations
Use for dropdown menus and selection components within your templates
Media items
Media items
Include images, documents, and other media assets in your templates
Substitution tags
Substitution tags
Themes
Themes
Apply consistent styling across all template instances
UI actions in templates
Current capabilities
UI actions in reusable templates support basic interactive functionality. The system handles:- Action context management: Unique identification for template instances
- Form submission: Automatic identification of form elements within template context
- Data mapping: Proper mapping of data keys to process variables
- Validation preservation: Template validation rules are maintained across instances
Planned scenarios
- Template-defined actions
- Form-centric actions
How it works:
- Define a UI action within the reusable template
- Assign the node action when instantiated in a User Task
- Use for standard actions needing different backend connections
Reusable UI Templates are designed as self-contained components and do not support nesting within other reusable templates
Troubleshooting
Template not displaying
Template not displaying
Possible causes:
- Invalid template hierarchy
- Missing dependencies (enumerations, media, themes)
- Insufficient permissions
- Invalid component configurations
- Verify template structure in the designer
- Check all referenced resources exist
- Confirm user permissions for template access
- Validate component property settings
UI actions not working
UI actions not working
Possible causes:
- Incorrect action context configuration
- Invalid form submission setup
- Data model compatibility issues
- Missing action permissions
- Verify action context is properly set
- Check form submission configuration
- Ensure data models match between template and process
- Review user permissions for action execution
Data binding issues
Data binding issues
Possible causes:
- Invalid key mappings in template instances
- Mismatched process data model structure
- Data type incompatibilities
- Incorrect substitution tag usage
- Validate key mappings match expected data structure
- Check process data model compatibility
- Ensure data types align between components and data sources
- Review substitution tag configurations
Reusable UI Templates vs. Reusable Functions
Understanding the difference between these two reusable components is crucial:- Reusable UI Templates
- Reusable Functions
Purpose: UI Designer components for creating reusable interface elementsScope:
- Visual components and layout
- Styling and basic UI interactions
- Form structure and input patterns
Advanced features
Planned enhancements
Template nesting
Future support for using templates within other templates for enhanced modularity
Enhanced data model
Input and output parameters with function-like behavior and type safety
Advanced testing
Mock data testing and interactive validation capabilities
Cross-project sharing
Export/import templates and library dependency management

