What are Reusable Functions?
Reusable Functions are self-contained business logic components that process data according to your specified rules. Instead of writing the same logic multiple times across different processes, you can:- Define the logic once in a reusable function
- Use the function in multiple processes through data mapping
- Automatically propagate updates to all instances when you modify the function
Functions execute in isolated environments and cannot be edited within individual process contexts. All changes must be made to the original function definition.
Key benefits
Reduce duplication
Write business logic once and reuse it across multiple processes
Improve maintainability
Update logic in one place and automatically apply changes everywhere
Ensure consistency
Standardize business rules across your entire application
Increase efficiency
Spend less time rewriting similar logic for different processes
Before you begin
Make sure you have:- Access to the FlowX.AI Designer
- Appropriate permissions to create and manage reusable resources
- A clear understanding of the business logic you want to implement
Create a reusable function
1
Access the Functions section
- In FlowX.AI Designer, go to your project
- Navigate to Reusable Resources > Functions
- Click the + icon to create a new function
2
Configure basic settings
- Enter a descriptive name for your function
- Add an optional description explaining the function’s purpose
- Click Save to create the function and open the editor
3
Define the data model
- Go to the Model tab
- Add attributes that your function will work with:
- Click Add Attribute to create new fields
- Set attribute types by selecting existing objects from your project
- Define nested structures as needed
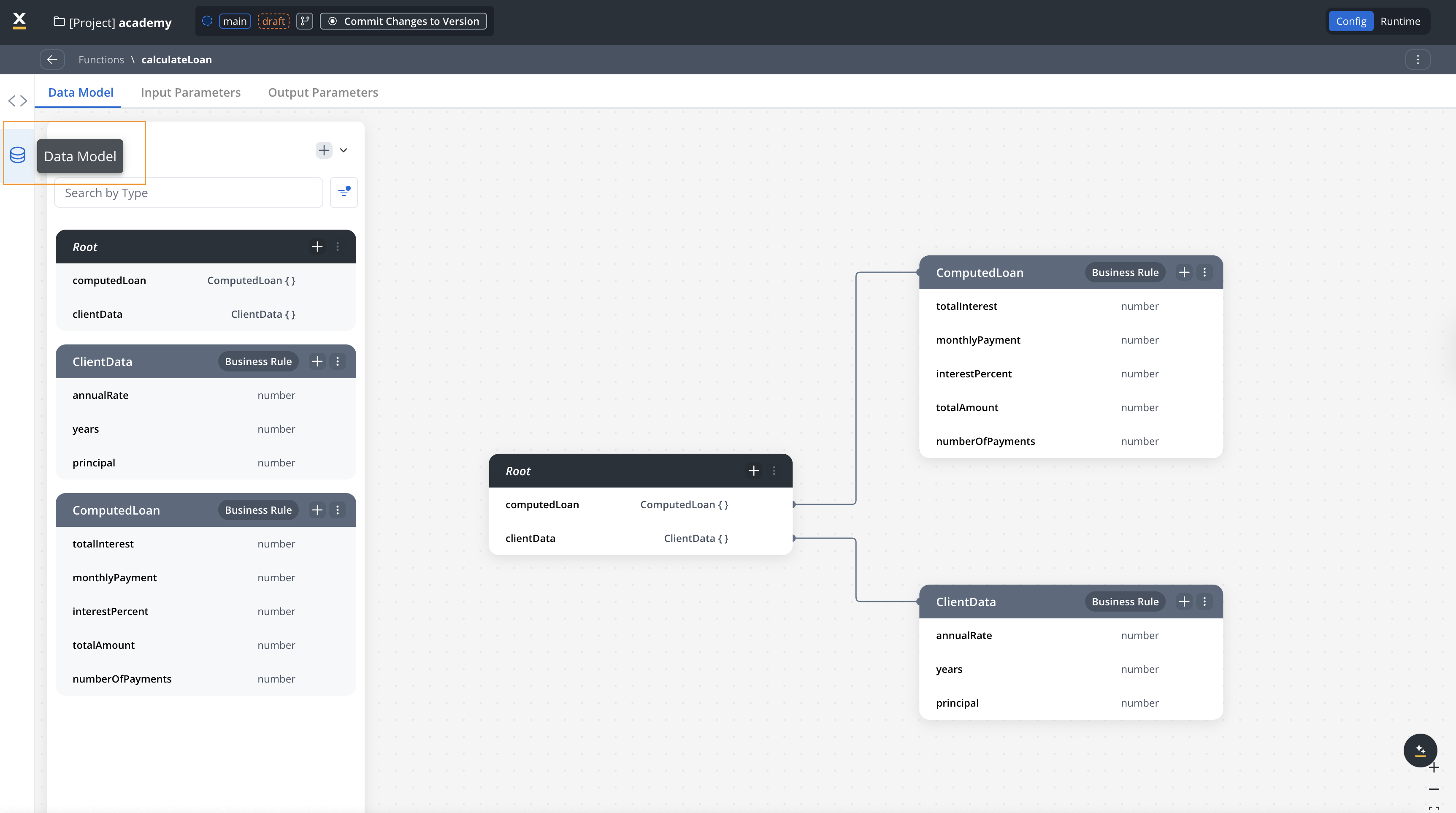
Functions support both primitive data types (string, number, boolean) and complex object data types for input and output parameters. See Understanding Data Types for more information.
- getBasicFacts - Primitive
- getUniverseOverview - Object
- myFirstFunction - Complex
Simple data types for basic universe facts: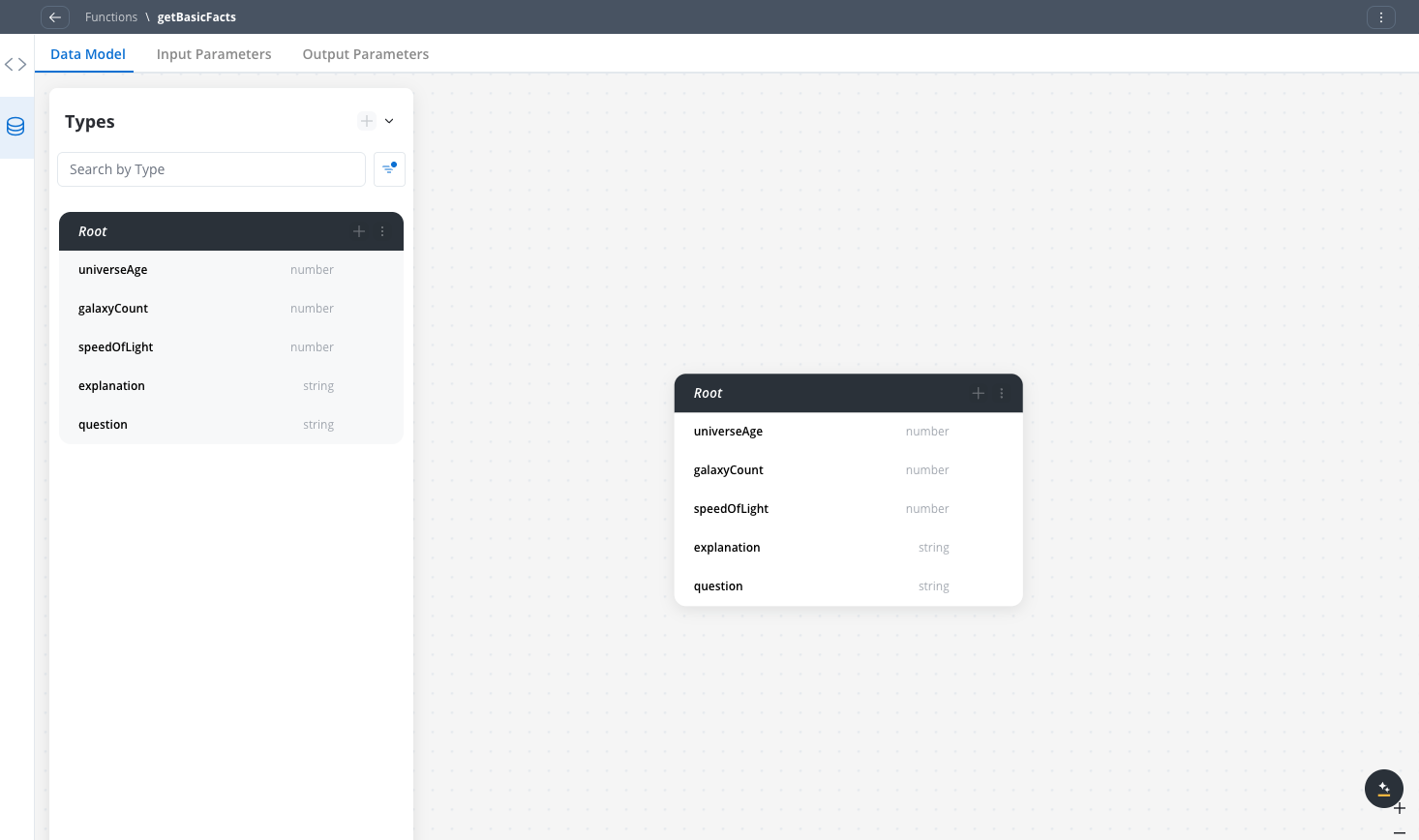

4
Configure input parameters
- Switch to the Input Parameters tab
- Select the fields from your data model that your function needs as input
- Expand objects to choose specific properties
- getBasicFacts - Input
- getUniverseOverview - Input
- myFirstFunction - Input
Select input fields from the data model for basic universe queries:From the data model fields:
Input parameter selection from data model
- ✅ question (string) - SELECT as input
- ❌ universeAge (number) - Do NOT select (output only)
- ❌ galaxyCount (number) - Do NOT select (output only)
- ❌ speedOfLight (number) - Do NOT select (output only)
- ❌ explanation (string) - Do NOT select (output only)
Select only the fields your function needs as input from the data model. The output fields will be selected in the Output Parameters tab.
5
Set output parameters
- Go to the Output Parameters tab
- Select the fields from your data model that the function returns
- Choose individual fields or entire objects as needed
- getBasicFacts - Output
- getUniverseOverview - Output
- myFirstFunction - Output
Select output fields from the data model for basic universe facts:From the data model fields:
Output parameter selection from data model
- ❌ question (string) - Do NOT select (input only)
- ✅ universeAge (number) - SELECT as output
- ✅ galaxyCount (number) - SELECT as output
- ✅ speedOfLight (number) - SELECT as output
- ✅ explanation (string) - SELECT as output
Select the fields that your function calculates and returns. These were the fields showing incorrectly in your Input Parameters tab.
6
Implement the business logic
- Navigate to the Script tab
- Choose your programming language (JavaScript or Python)
- Write your business logic using the appropriate data format
- getBasicFacts - Primitive
- getUniverseOverview - Object
- myFirstFunction - Complex
Simple function with basic universe facts:
Always use
input.attribute format to access function parameters and output.attribute to set return values.7
Test your function
- Go to the Test tab
- Add sample data for your input parameters
- Click Test to execute the function
- Review the output to ensure your logic works correctly
- Save your function when testing is successful
Use functions in processes
After creating a reusable function, you can use it in your business processes through Business Rule actions, or reference it within other reusable functions.Where you can reference functions
Reusable functions can be referenced in two contexts:- Business Rule actions within process nodes
- Other reusable functions to create composite logic
Function referencing syntax
When referencing a reusable function, use this format:functions- Convention to reference any reusable functionprojectName- Name of the project/library where the function is definedfunctionName- Name of the reusable functioninput.params- Input parameters using local process variables
Add a function to a process
- Open your process definition in FlowX.AI Designer
- Select the node where you want to add business logic
- Create a new Business Rule action
- Reference your reusable function using the syntax above
- Configure data mapping between your process and the function
Configure data mapping
Data mapping connects your process data to the function’s input and output parameters.- Input mapping
- Output mapping
Map process variables to function input parameters:
- getBasicFacts Mapping
- getUniverseOverview Mapping
- myFirstFunction Mapping
Simple input mapping for basic universe queries:Process context example:
getBasicFacts input mapping
Use functions within functions
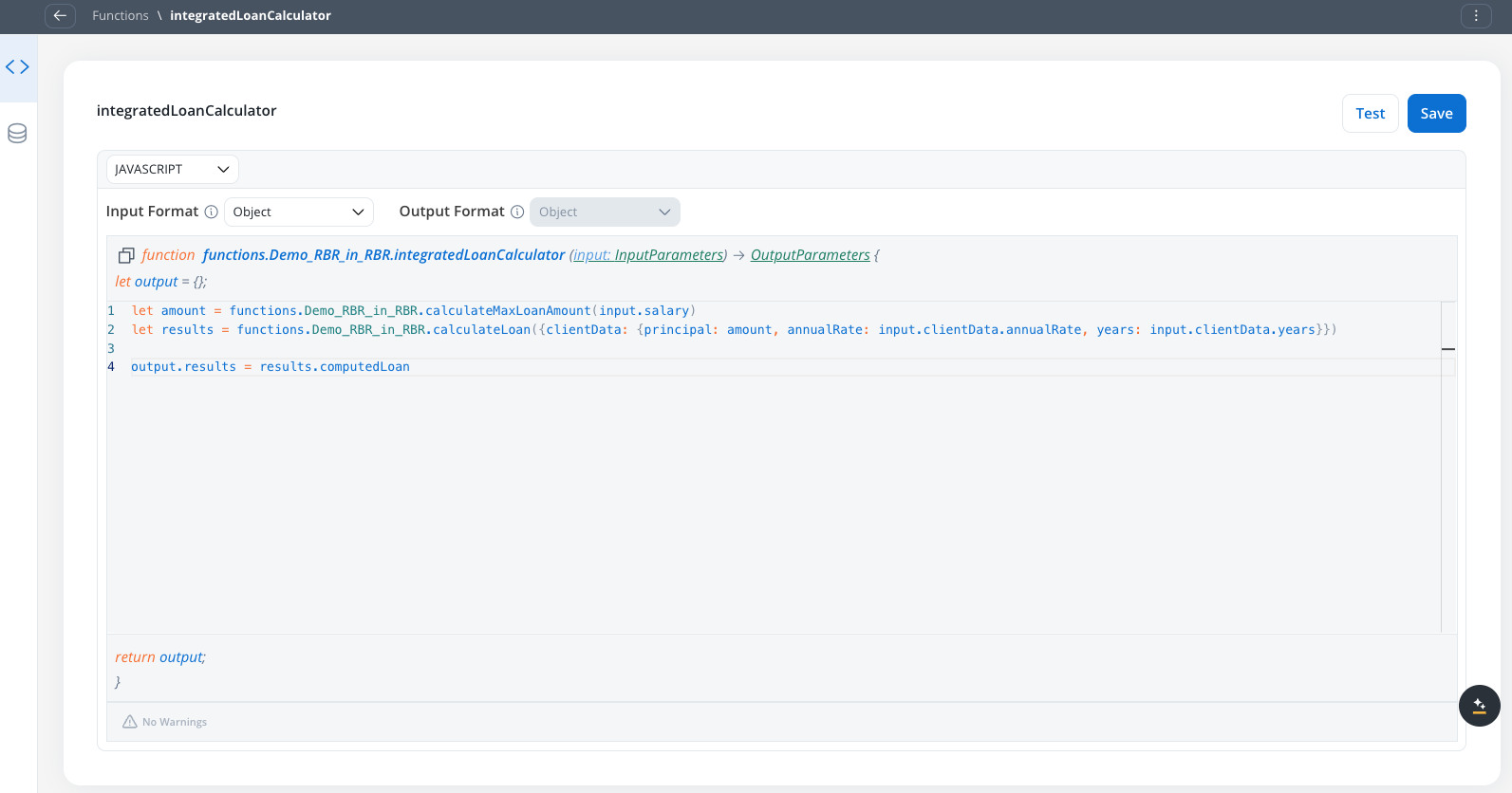
You can create composite business logic by calling one reusable function from within another reusable function. This enables you to build complex functionality from smaller, focused components.1
Reference the function
Use the standard function referencing syntax within your script:
2
Handle data flow
Ensure proper data flow between functions:
- Input format: Always use
input.attributeto access function parameters - Function calls: Use
functions.projectName.functionName(parameters)format - Output assignment: Set results to
output.attribute
3
Test composite functions
Test thoroughly to ensure all nested function calls work correctly:
- Test each individual function first
- Test the composite function with realistic data
- Verify the data flows correctly between function calls
- Check error handling when nested functions fail
Manage functions
View function usage
To see where a function is used:- Select the function in Reusable Resources > Functions
- Click the Usages tab
- Review all processes and nodes that reference the function
The system displays a resource usage modal when you make changes that might affect existing implementations.
Update functions
When you modify a reusable function:- Changes automatically propagate to all instances
- Existing process instances may need to restart to pick up updates
- The system preserves instance-specific configurations like data mapping
Change programming languages
You can change a function’s programming language after creation:- Open the function editor
- Go to the Script tab
- Select a different language from the dropdown
- Rewrite your logic in the new language
- Test thoroughly before saving
The system shows a usage modal to help you understand the impact of language changes on existing implementations.
Understanding data types
Reusable functions support two categories of data types for input and output parameters:Primitive data types
Primitive types represent single, simple values. They are the basic building blocks of data. Available primitive types:- string - Text values (for example, “John Doe,” “active”)
- number - Numeric values (for example, 42, 3.14, 13.8)
- boolean - True/false values (for example, true, false)
- Simple calculations requiring single values
- Basic status flags or indicators
- Individual measurements or counts
- Simple user inputs
Complex object data types
Complex types are structured collections of related data, containing multiple fields that can include both primitives and nested objects. Available complex types:- object - Structured data with named properties
- array - Ordered collections of values
- nested objects - Objects containing other objects
- Grouping related information together
- Representing real-world entities (customers, orders, products)
- Handling structured business data
- Managing hierarchical relationships
Key differences
| Aspect | Primitive Types | Complex Object Types |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single value | Multiple related values |
| Nesting | Not applicable | Can contain nested structures |
| Access pattern | Direct value access | Dot notation for properties (for example, customer.personalInfo.name) |
| Use case | Simple, standalone data | Related data that should be grouped |
| Mapping complexity | Simple one-to-one mapping | Can map entire objects or individual properties |
Choosing the right data type
- Use primitives when
- Use complex objects when
- Working with single, independent values
- Performing basic calculations
- Storing simple flags or settings
- Handling individual measurements
Best practice: Start with primitives for simple functions. Upgrade to complex objects when you find yourself passing multiple related parameters or need better data organization.
Best practices
Design principles
Single responsibility
Single responsibility
Each function should serve one specific, well-defined purpose. Avoid creating functions that handle multiple unrelated tasks.
Clear interfaces
Clear interfaces
Define precise input and output parameters. Well-defined interfaces make functions easier to understand and use correctly.
Self-contained logic
Self-contained logic
Functions shouldn’t depend on external state or global variables. All necessary data should come through input parameters.
Predictable behavior
Predictable behavior
The same inputs should always produce the same outputs. Avoid non-deterministic behavior in your business logic.
Development workflow
- Define data model first: Always establish your data structure before writing code
- Specify parameters early: Define inputs and outputs before implementing logic
- Use descriptive names: Choose clear, business-oriented function names
- Test thoroughly: Validate functions with realistic data before deployment
- Handle errors gracefully: Implement robust error handling in your business logic
Organization strategies
- Group related functions: Organize functions by business domain or use case
- Follow naming conventions: Establish consistent patterns for function names
- Document extensively: Include clear descriptions and usage examples
- Version carefully: Use project versioning to manage function changes safely
Troubleshooting
Common issues
Function not executing
Function not executing
Possible causes:
- Incorrect input parameter mapping
- Data type mismatches between process and function
- Missing required input parameters
- Runtime errors in function logic
- Verify all input mappings are correct
- Check data types match between source and target
- Ensure all required parameters have values
- Review function logs for error details
Unexpected output
Unexpected output
Possible causes:
- Incorrect output parameter mapping
- Logic errors in function implementation
- Invalid test data during development
- Validate output parameter configuration
- Test function with realistic data
- Review business logic implementation
- Check data transformations within the function
Performance issues
Performance issues
Possible causes:
- Complex data processing logic
- Inefficient algorithms
- Large data structures
- Optimize function algorithms
- Simplify data models where possible
- Consider breaking complex functions into smaller components
- Monitor execution times in process context
Debugging strategies
- Use the test environment: Always test functions thoroughly before deploying to production
- Start simple: Build and test functions incrementally rather than implementing everything at once
- Use realistic data: Test with data that matches your production scenarios
- Verify outputs: Carefully check that function outputs match your expectations
- Add logging: Include console output in your function logic to trace execution
Function execution context
Function format and syntax
All reusable functions follow a consistent format and syntax:- Function declaration:
functions.projectName.functionName(parameters) - Input access: Always use
input.attributeto access function parameters - Output assignment: Use
output.attributeto set return values - Function calls: Reference other functions using
functions.projectName.functionName(params)
Data access patterns
When functions execute within processes, they have access to:- Input parameters: Mapped from process data according to your configuration
- Output object: Used to return processed data back to the process
- Standard libraries: Built-in functions available in JavaScript or Python
- Error handling: Mechanisms to report execution problems back to the process
- Input format
- Output format
Access function input using the
input.attribute format:Frequently asked questions
Can you change a reusable function's programming language after creation?
Can you change a reusable function's programming language after creation?
Yes, you can change a function’s programming language after creation. Navigate to the Script tab, select a different language from the dropdown, rewrite your logic in the new language, and test thoroughly before saving. The system will show a usage modal to help you understand the impact on existing implementations.
Where can you reference reusable functions?
Where can you reference reusable functions?
Reusable functions can be referenced in two contexts:
- Business Rule actions within process nodes
- Other reusable functions to create composite logic
How do you reference a function?
How do you reference a function?
Use the format:
functions.projectName.functionName(input.params)Example: functions.library1.calculateAgeFromSSN(input.client.ssn)Where:functions- Convention to reference a functionlibrary1- Name of the project/library where the function is definedcalculateAgeFromSSN- Name of the reusable functioninput.client.ssn- Input parameters using local process variables
Can you use functions within functions?
Can you use functions within functions?
Yes, you can use functions within functions to create composite business logic. Simply reference other functions using the standard syntax:
functions.projectName.functionName(parameters) within your function script.What data types can you use as parameters?
What data types can you use as parameters?
You can use both primitive and object data types as parameters for input and output:Primitive types: string, number, boolean
Object types: Complex structures with nested properties, arrays, and custom business objectsFunctions automatically handle the data format based on your model definition.

