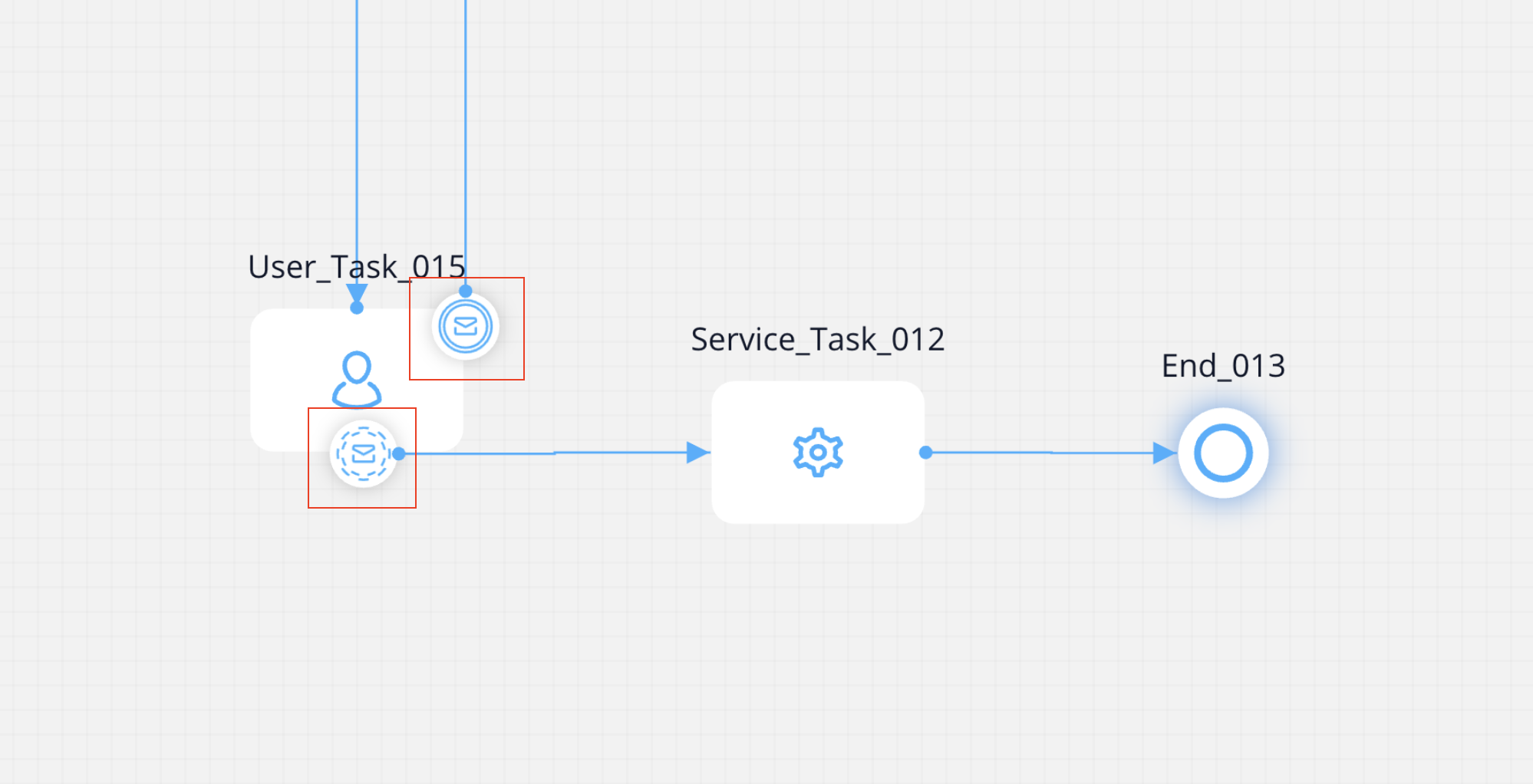
 Message Catch Boundary Events can be categorized by their behavior, resulting in two main classifications:
Message Catch Boundary Events can be categorized by their behavior, resulting in two main classifications:
Message catch interrupting event

-
Use Cases:
- Suitable for scenarios where the receipt of a specific message requires an immediate interruption of the current activity.
- Often used when the received message signifies a critical event that demands prompt attention.
-
Example:
- A user task is interrupted as soon as a high-priority message is received, and the process flow moves forward to handle the critical event.
Message catch non-interrupting event

-
Use Cases:
- Appropriate for scenarios where multiple messages need to be captured during the execution of a user task without disrupting its flow.
- Useful when the received messages are important but do not require an immediate interruption of the ongoing activity.
-
Example:
- A user task continues its execution while simultaneously capturing and processing non-critical messages.
Configuring a message catch interrupting/non-interrupting event
General config
- Correlate with Throwing Events - the dropdown lists all throw events from accessible process definitions
Establishes correlation between the catch event and the corresponding throw event. Selection of the relevant throw event triggers the catch event upon message propagation.
- Correlation Key - process key used to correlate received messages with specific process instances
The correlation key associates incoming messages with specific process instances. Upon receiving a message with a matching correlation key, the catch event is triggered.
- Receive Data (Process Key) - the catch event can receive and store data associated with the message in a process variable with the specified process key
This received data becomes available within the process instance, facilitating further processing or decision-making.
Illustrating boundary events (interrupting and non-interrupting)
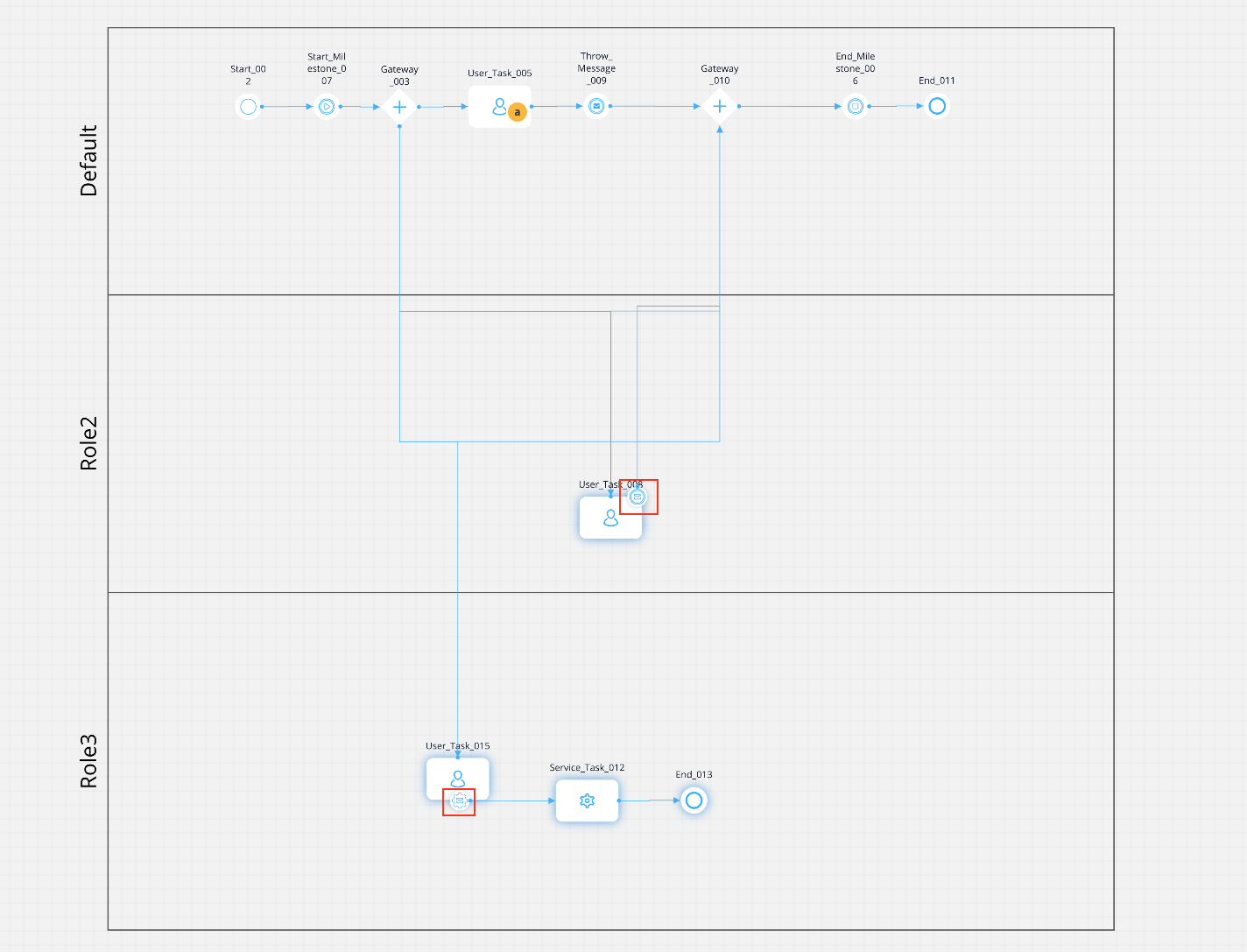 Business Scenario:
A customer initiates the account opening process. Identity verification occurs, and after successful verification, a message is thrown to signal that the account is ready for activation.
Simultaneously, the account activation process begins. If there are issues during activation, they are handled through the interruption process. The overall process ensures a streamlined account opening experience while handling potential interruptions during activation, and also addresses exceptions through the third lane.
Business Scenario:
A customer initiates the account opening process. Identity verification occurs, and after successful verification, a message is thrown to signal that the account is ready for activation.
Simultaneously, the account activation process begins. If there are issues during activation, they are handled through the interruption process. The overall process ensures a streamlined account opening experience while handling potential interruptions during activation, and also addresses exceptions through the third lane.
