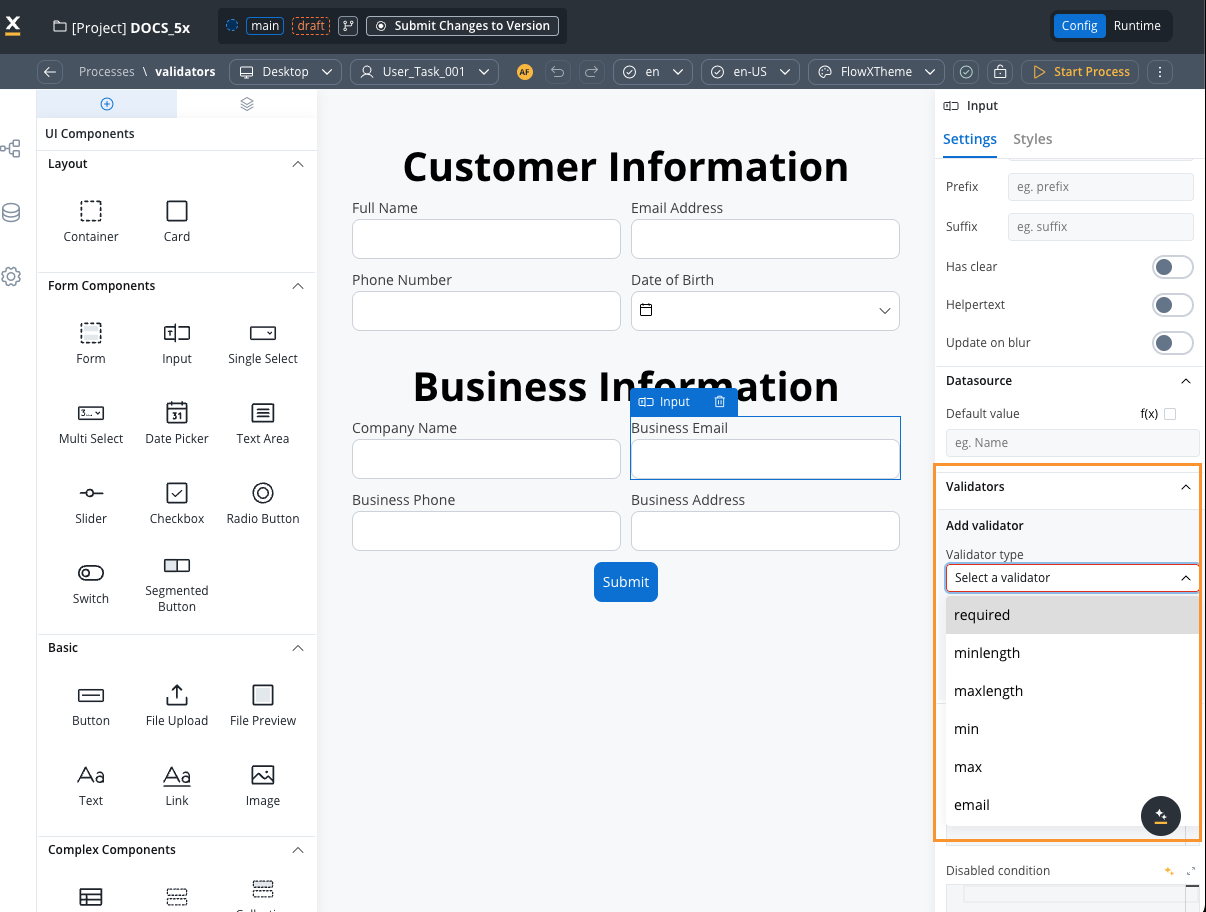
Predefined validators
min validator
min validator
This validator checks whether a numeric value is smaller than the specified value. If there are no characters at all, this validator will not trigger. It is advisable to use this validator with a required validator.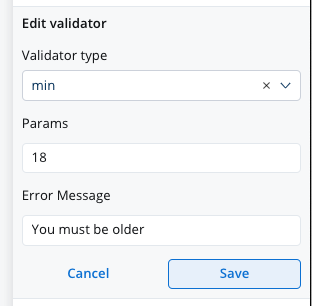

min validator
Refer to MDN documentation for more details about the min attribute.
max validator
max validator
This validator checks whether a numeric value is larger than the specified value. If there are no characters at all, this validator will not trigger. It is advisable to use this validator with a required validator.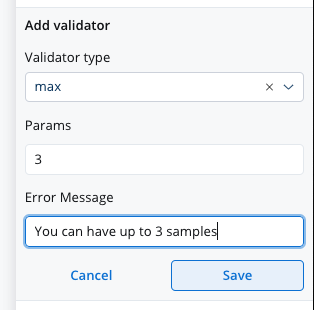

max validator
Refer to MDN documentation for more details about the max attribute.
minLength
minLength
This validator checks whether the input value has a minimum number of characters. If there are no characters at all, this validator will not trigger. It is advisable to use this validator with a required validator.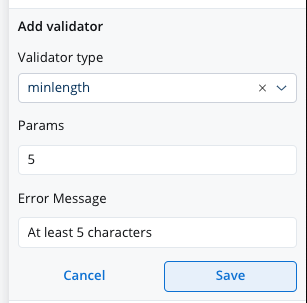

minLength
Refer to MDN documentation for more details about the minlength attribute.
maxLength
maxLength
This validator checks whether the input value has a maximum number of characters. If there are no characters at all, this validator will not trigger. It is advisable to use this validator with a required validator.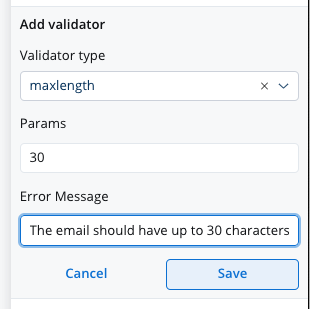

maxLength
Refer to MDN documentation for more details about the maxlength attribute.
required
required
This validator checks whether a value exists in the input field.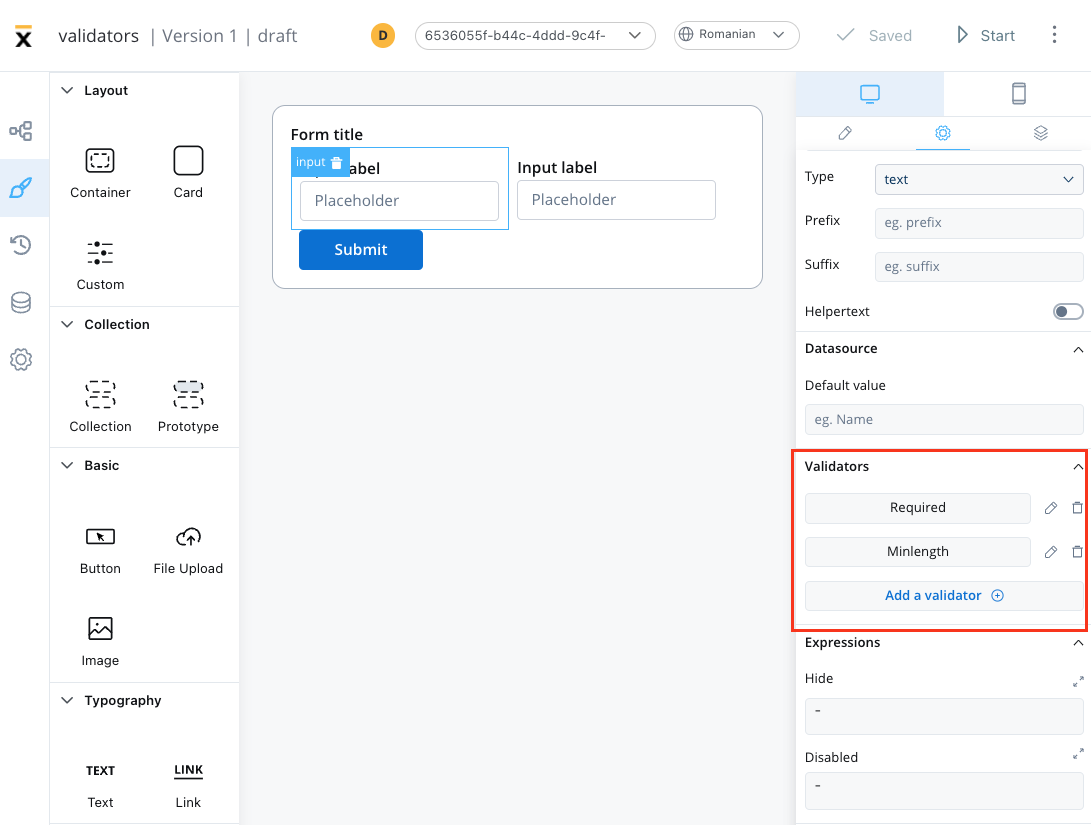 It is recommended to use this validator with other validators like minlength to check if there is no value at all.
It is recommended to use this validator with other validators like minlength to check if there is no value at all.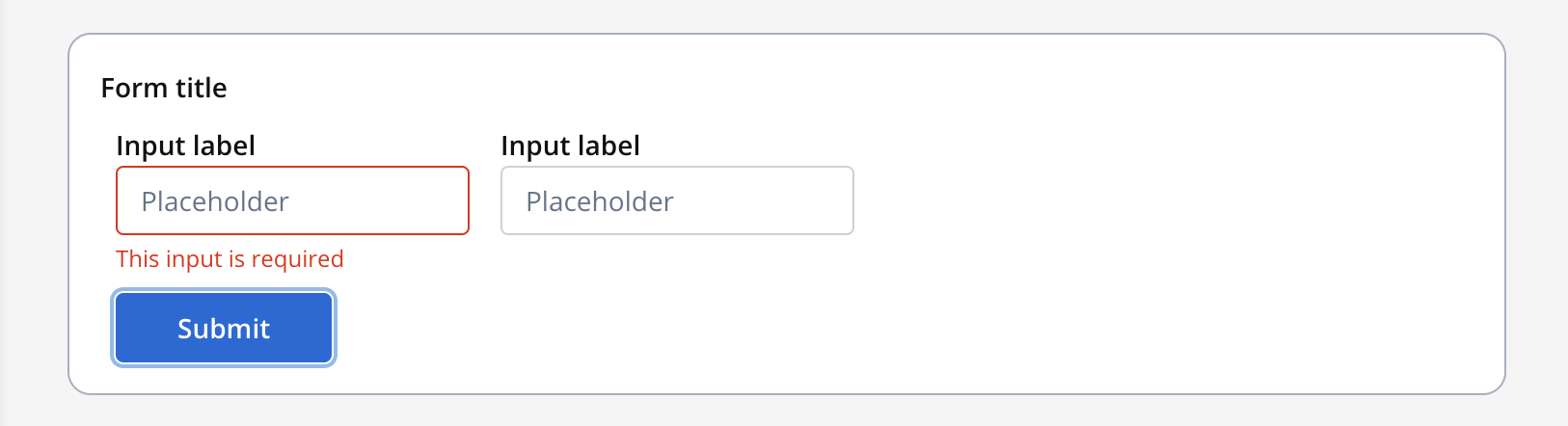


required
Refer to MDN documentation for more details about the required attribute.
email
This validator checks whether the input value is a valid email. If there are no characters at all, this validator will not trigger. It is advisable to use this validator with a required validator.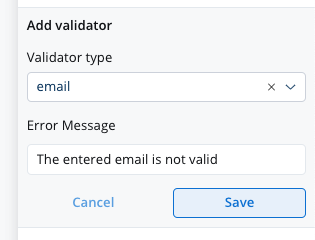
email

Refer to MDN documentation for more details about email input validation.
pattern validator
pattern validator
This validator checks whether the input value matches the specified pattern (for example, a regex expression).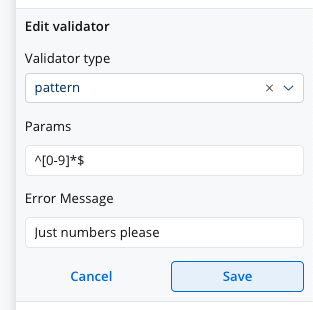
Important: Pattern validators can only be applied to input fields of type “text” or “string”. They cannot be used with input fields of type “number”. If you need to validate numeric input with specific patterns (such as preventing leading zeros), you must either:
- Use a text input field instead of a number input field, or
- Create a custom validator that handles the numeric validation logic

pattern validator
Refer to MDN documentation for more details about the pattern attribute.
custom expression validator
custom expression validator
This validator allows you to validate a form element based on computed expressions that can reference other values from the process data store, not just the current form element being validated.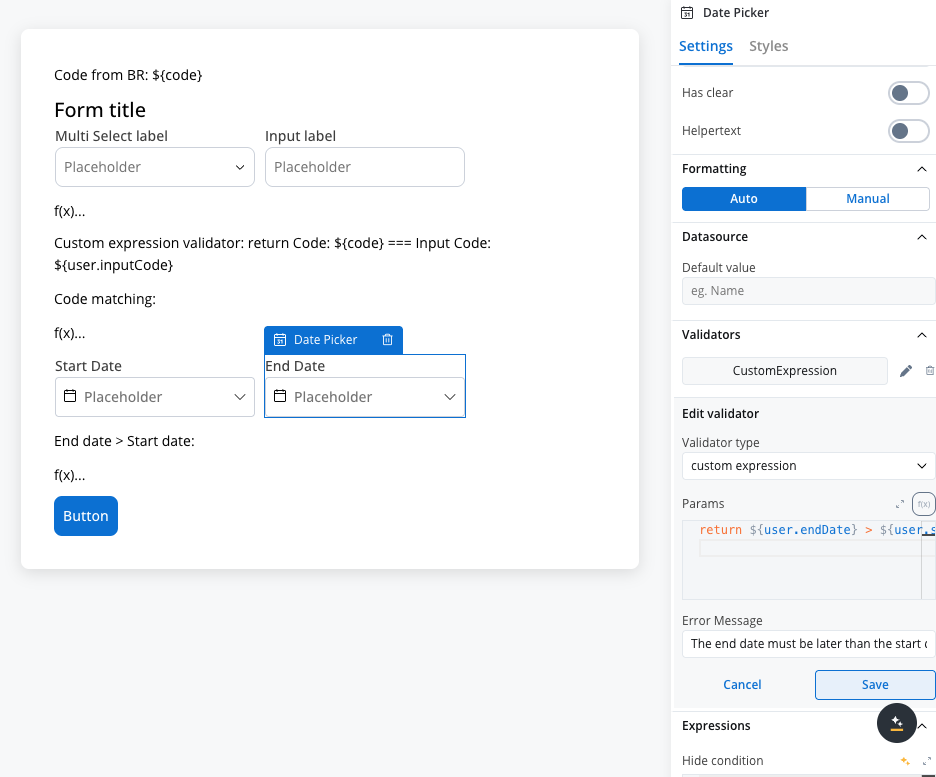 Example used:The validator uses a code editor where you can write computed expressions that must eventually return Key features:
Example used:The validator uses a code editor where you can write computed expressions that must eventually return Key features:

Simple comparison
true (valid) or false (invalid). The expression can contain process data store values and will be evaluated dynamically.The
customExpression validator runs only when the field value is not empty or missing, similar to other predefined validators. Once run for the first time, it will be re-evaluated each time process data store keys referenced in the expression update their values.- Dynamic validation: Based on other process values, not just the current field
- Computed expressions: Write JavaScript expressions that return boolean values
- Real-time updates: Re-evaluates when referenced process data changes
- Universal compatibility: Available for all form elements
Important considerations:
- The expression must return a boolean value (
truefor valid,falsefor invalid) - Use proper syntax when referencing process data store values with
${} - Ensure referenced process data keys exist to avoid runtime errors
- The validator is asynchronous and will be re-evaluated when dependent data changes
isSameOrBeforeToday
isSameOrBeforeToday
This validator can be used to validate datepicker inputs. It checks whether the selected date is today or in the past. If there are no characters at all, this validator will not trigger. It is advisable to use this validator with a required validator.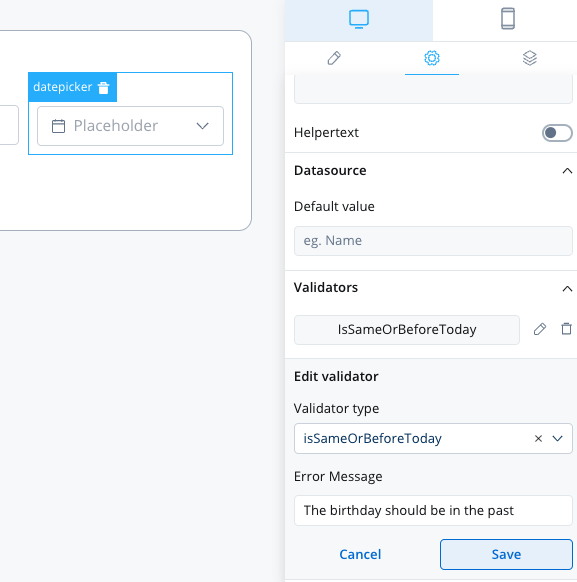

isSameOrAfterToday
isSameOrAfterToday
This validator can be used to validate datepicker inputs. It checks whether the selected date is today or in the future. If there are no characters at all, this validator will not trigger. It is advisable to use this validator with a required validator.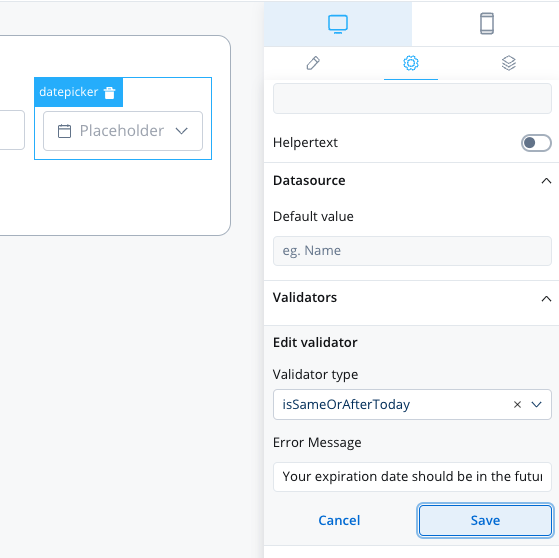

Validator compatibility with input field types
Different validators work with different input field types. Here’s a compatibility matrix:| Validator | Text Fields | Number Fields | Email Fields | Date Fields |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| required | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| min | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| max | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| minLength | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| maxLength | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | |
| pattern | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| customExpression | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| isSameOrBeforeToday | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| isSameOrAfterToday | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
To ensure the validation of all form elements within a card upon executing a Save Data action such as “Submit” or “Continue,” follow these steps: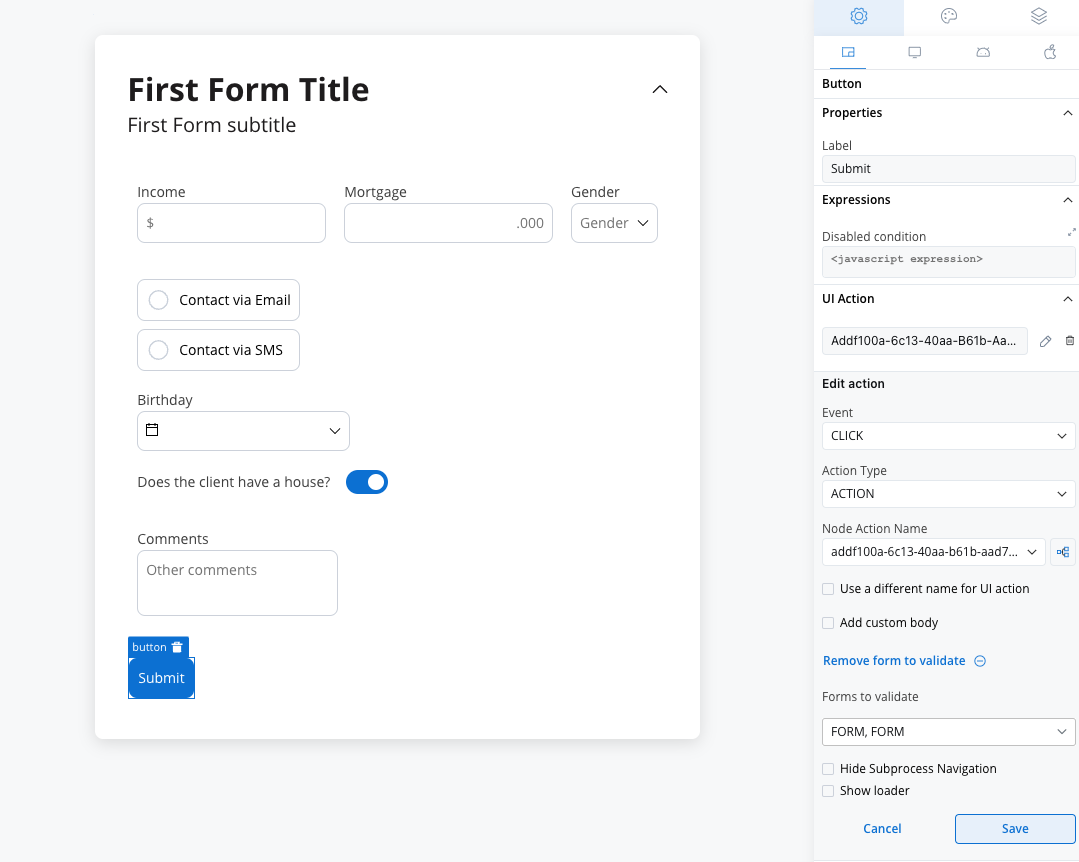
- When adding a UI action to a button inside a card, locate the dropdown menu labeled Add form to validate.
- From the dropdown menu, select the specific form or individual form elements that you wish to validate.
- By choosing the appropriate form or elements from this dropdown, you can ensure comprehensive validation of your form.

Custom validators
Additionally, custom validators can be created within the web application and referenced by name. These custom validators can have various configurations such as execution type, name, parameters, and error message.- Execution type - synchronous/asynchronous validator
- Name - name provided by the developer to uniquely identify the validator
- Params - if the validator needs inputs to decide if the field is valid or not, you can pass them using this list
- Error Message - the message that will be displayed if the field is not valid
The error that the validator returns MUST match the validator name.
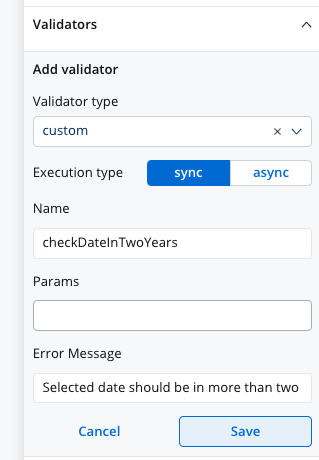
Custom validator example
Below you can find an example of a custom validator (currentOrLastYear) that restricts date selection to the current or the previous year:
currentOrLastYear
smallerOrEqualsToNumber
Below is another custom validator example that validates form input asynchronously. The validator is calledsmallerOrEqualsToNumber and takes an array of params as an input.
For this custom validator the execution type should be marked as
async using the UI Designer.null, indicating that the input is valid. If the input value is greater than the maximum loan amount value, the function returns a validation error object with a key smallerOrEqualsToNumber and a value of true, indicating that the input is invalid.
For more details about custom validators please check the SDK documentation.
Using validators in your application can help ensure that the data entered by users is valid, accurate, and consistent, improving the overall quality of your application.

