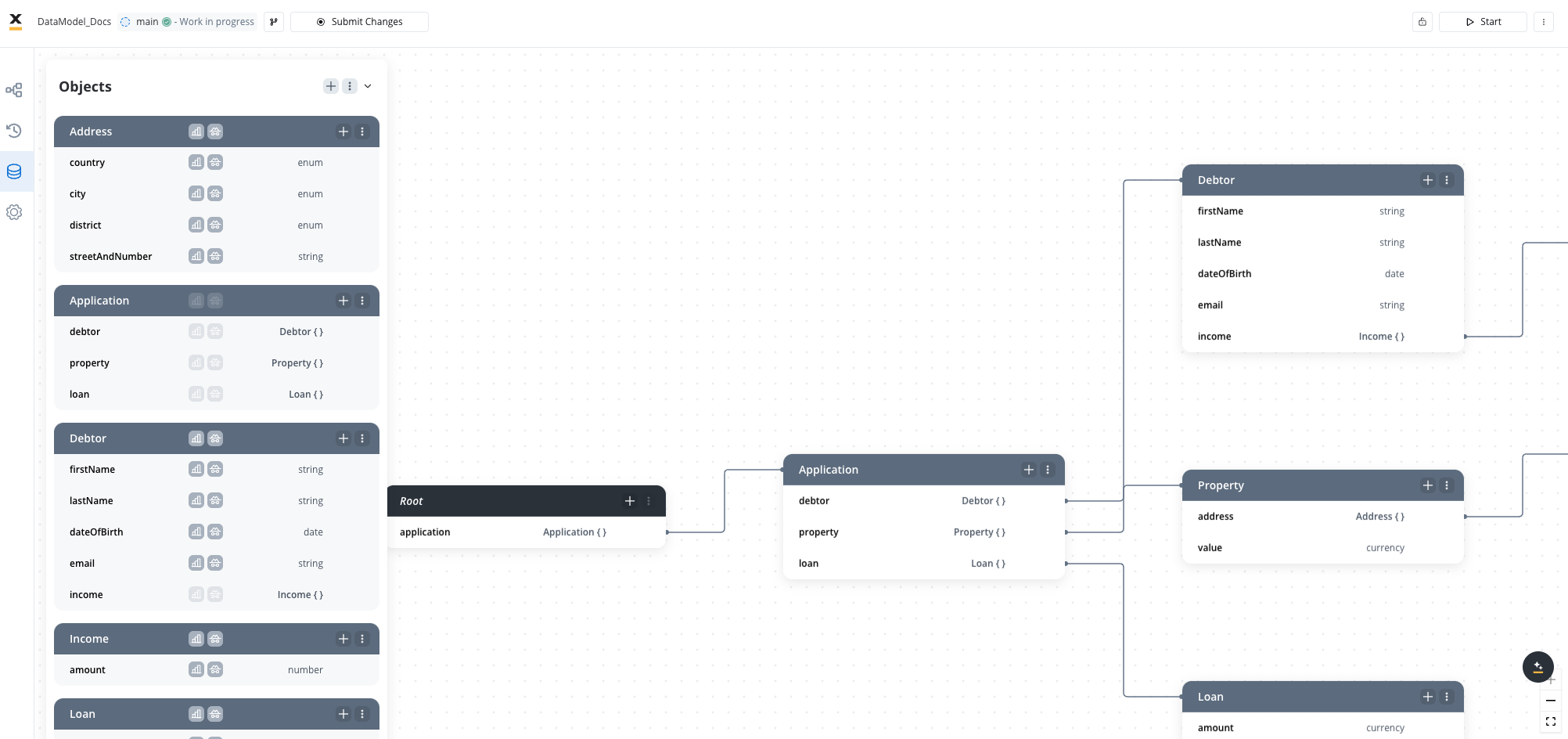
Overview
The Data Model serves as the foundation for managing structured information throughout your process definitions. It provides a centralized approach to define, organize, and maintain the data attributes that drive your business processes and user interfaces.Attribute types
The Data Model supports the following attribute types:- STRING
- NUMBER
- CURRENCY
- BOOLEAN
- OBJECT
- ARRAY
- ARRAY OF STRINGS
- ARRAY OF NUMBERS
- ARRAY OF BOOLEANS
- ARRAY OF OBJECTS
- ARRAY OF ENUMS
- ENUM
- DATE
Currency attribute
Currencies are managed using an object structure that ensures accurate representation and localization.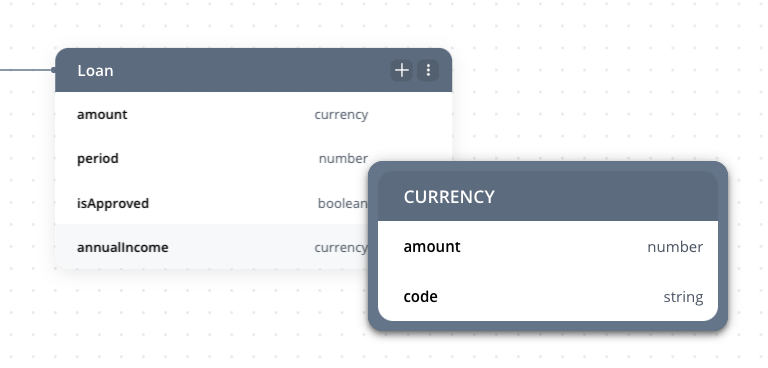
- Currency Object Structure:
- Includes
amount(numerical value) andcode(ISO 4217 currency code, e.g., USD, EUR). - Example:
- Includes
- Regional Formatting:
- Currency values adapt to regional conventions for grouping, decimals, and symbol placement. For instance:
- en-US (United States):
$12,000.78(symbol before the value, comma for grouping, dot for decimals). - ro-RO (Romania):
12.000,78 RON(dot for grouping, comma for decimals, code appended).
- en-US (United States):
- Currency values adapt to regional conventions for grouping, decimals, and symbol placement. For instance:
- Fallback Behavior: If the
codeis null, the system defaults to the locale’s predefined currency settings. - UI Integration:
- Currency input fields dynamically format values based on locale settings and save the
amountandcodeinto the data store. - Sliders and other components follow the same behavior, formatting values and labels according to the locale.
- Currency input fields dynamically format values based on locale settings and save the
Localization and internationalization
Check this section for more details about l10n & i18n
Date attribute
Dates are represented in ISO 8601 format and dynamically formatted based on locale and application settings.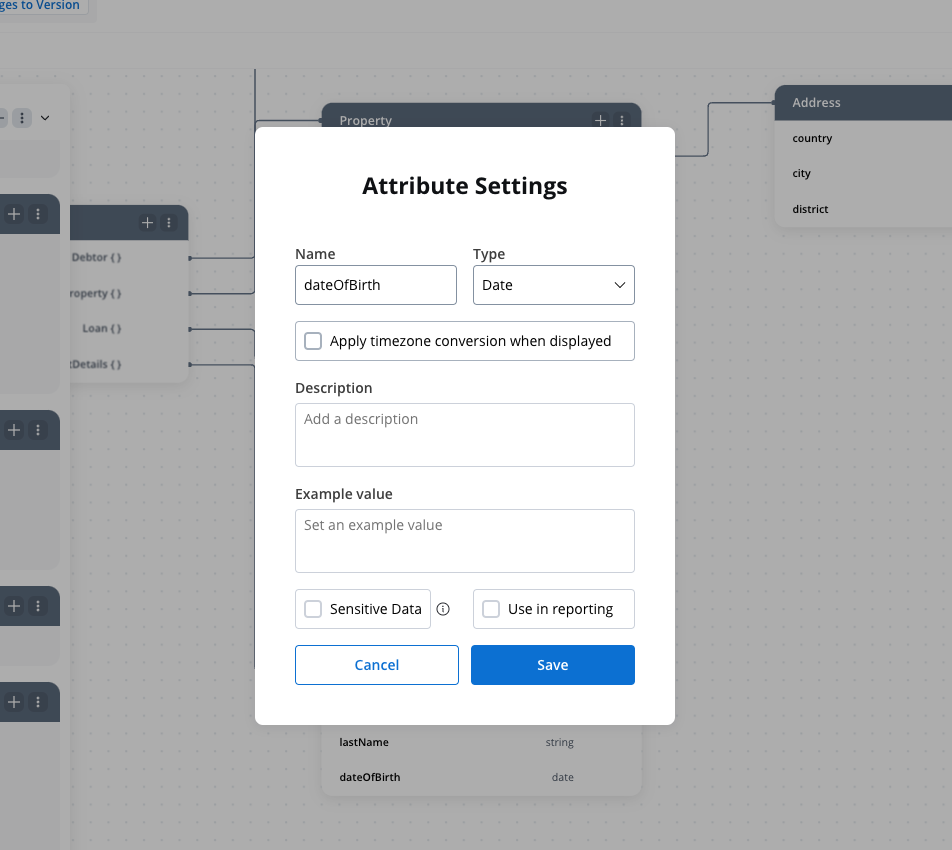
- Locale-Specific Date Formats: FlowX dynamically applies regional date formatting rules based on the locale. For instance:
- en-US (United States):
MM/DD/YYYY→09/28/2024 - fr-FR (France):
DD/MM/YYYY→28/09/2024
- en-US (United States):
- Customizable Formats: You can choose from predefined formats (e.g., short, medium, long, full) or define custom formats at both application and UI Designer levels.
- Timezone Handling:
- Standard Date: Adjusts to the current timezone.
- Date Agnostic: Ignores time zones, using GMT for consistent representation.
- ISO 8601 Compliance: Ensures compatibility with international standards.
Localization and internationalization
Check this section for more details about l10n & i18n
Number attribute
The Number attribute type supports two subtypes: integers and floating point numbers, providing flexibility to represent whole numbers or decimal values as required.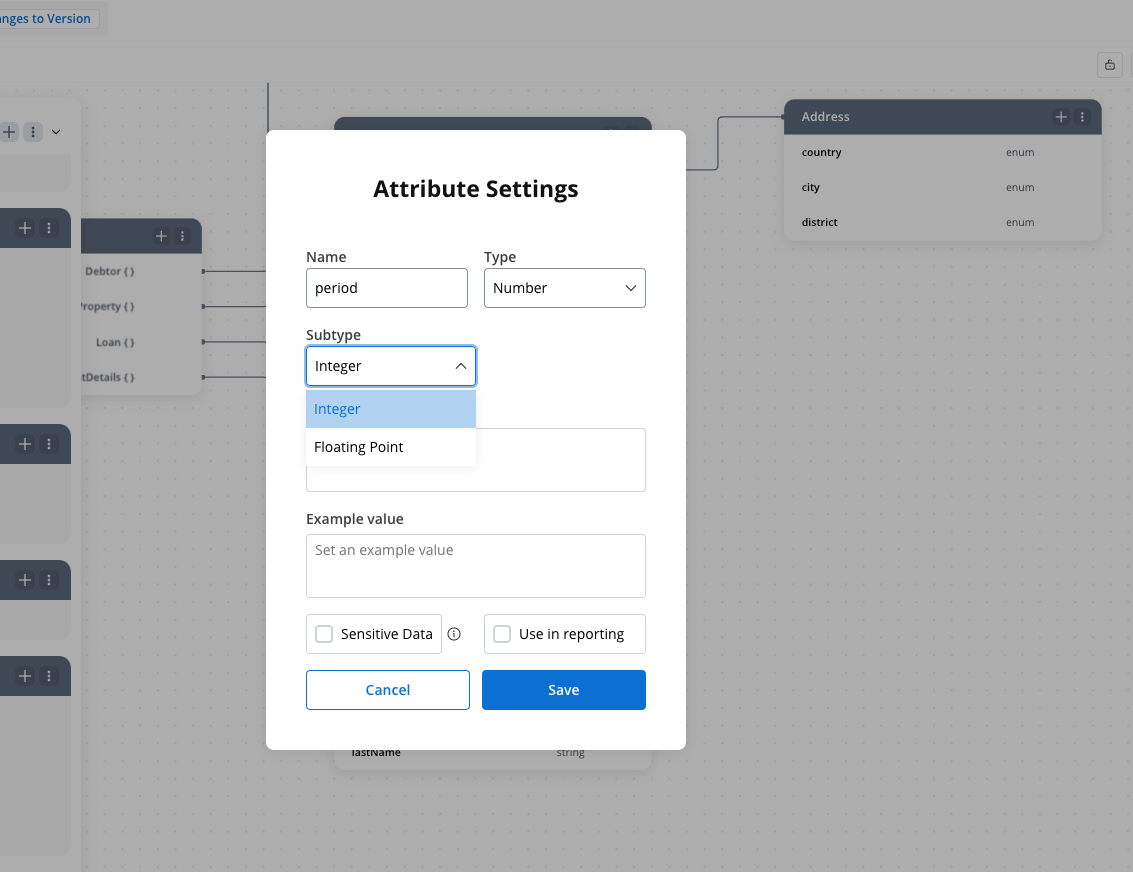
- Subtypes
- Integer: Represents whole numbers without any fractional or decimal part.
- Example:
1, 42, 1000
- Example:
- Floating Point: Represents numbers with a decimal point, enabling precise storage and representation of fractional values.
- Example:
3.14, 0.01, -123.456
- Example:
- Integer: Represents whole numbers without any fractional or decimal part.
- Locale-Specific Formatting:
- Numbers adapt to regional conventions for decimal separators and digit grouping. For example:
- en-US (United States):
1,234.56(comma for grouping, dot for decimals) - de-DE (Germany):
1.234,56(dot for grouping, comma for decimals) - fr-FR (France):
1 234,56(space for grouping, comma for decimals)
- en-US (United States):
- Numbers adapt to regional conventions for decimal separators and digit grouping. For example:
- Precision Settings:
- Minimum Decimals: Ensures a minimum number of decimal places are displayed, adding trailing zeros if necessary.
- Maximum Decimals: Limits the number of decimal places stored, rounding values to the defined precision.
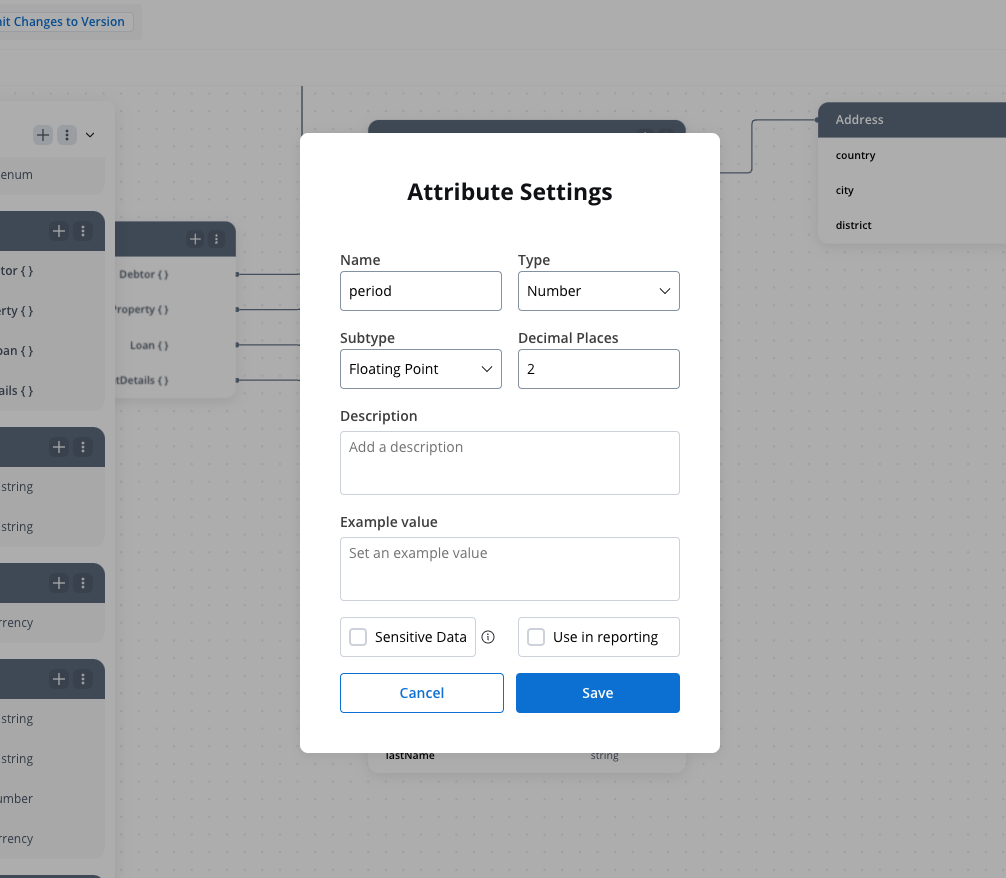
- Validation:
- Enforce range constraints (e.g., minimum and maximum values).
- Input fields automatically apply formatting masks to prevent invalid data entry.
Localization and internationalization
Check this section for more details about l10n & i18n
Creating and managing a data model
In the Data Model, you can add new key-pair values, allowing seamless integration with the UI Designer. This functionality enables quick shortcuts for adding new keys without switching between menus. Example:Validation rules
You can define validation rules for your data model attributes to ensure data integrity throughout your processes:- Required Fields: Mark attributes that must have values before a process can proceed
- Range Validation: Set minimum and maximum values for numeric attributes
- Pattern Matching: Define regular expression patterns for string validation
- Custom Validation: Implement custom validation logic using business rules
Data model reference
The “View References” feature allows you to see where specific attributes are used within the data model. This includes:- Process Keys: Lists all process keys linked to an attribute.
- UI Elements: Displays references such as the element label, node name, and UI Element key.
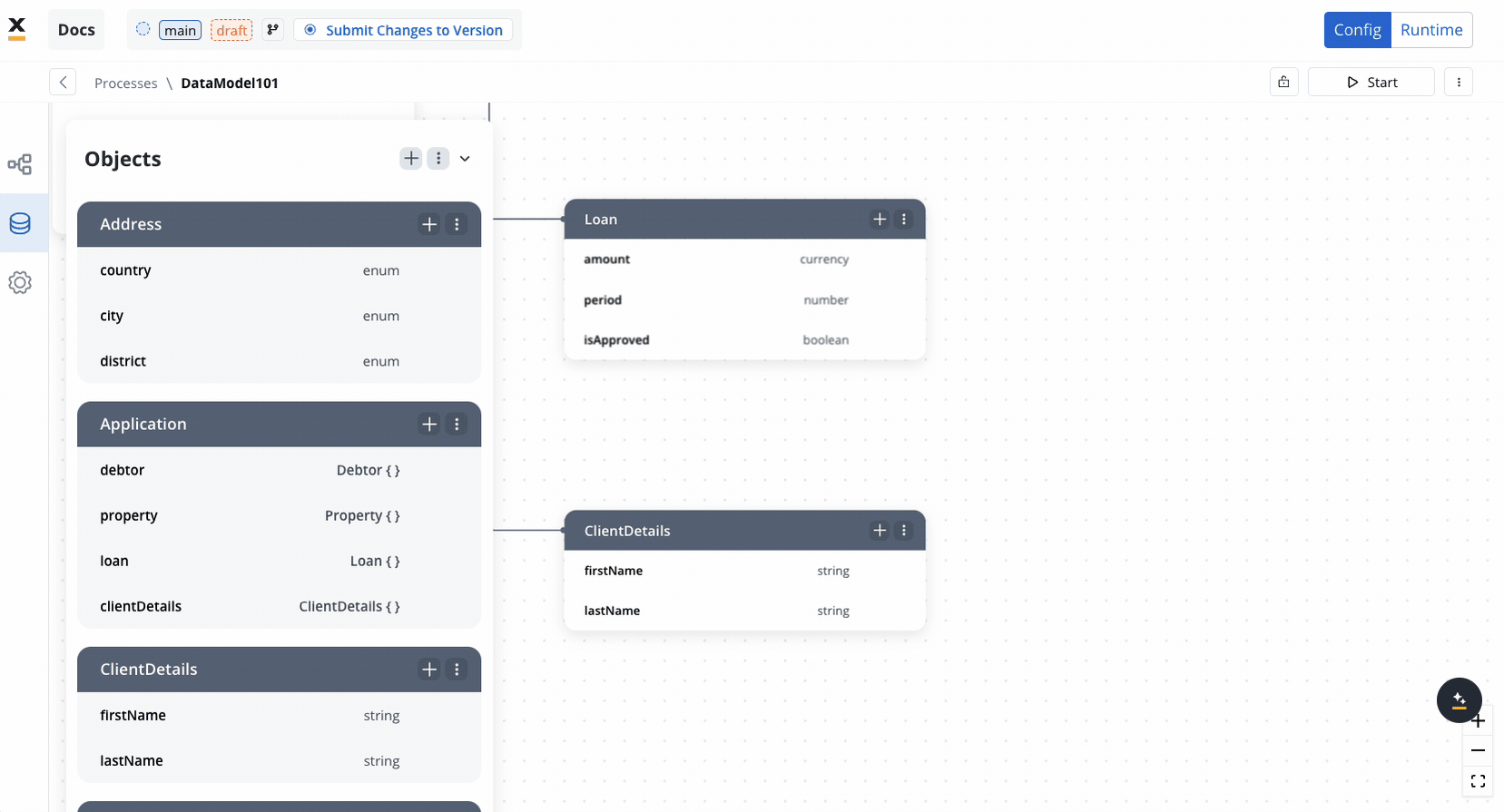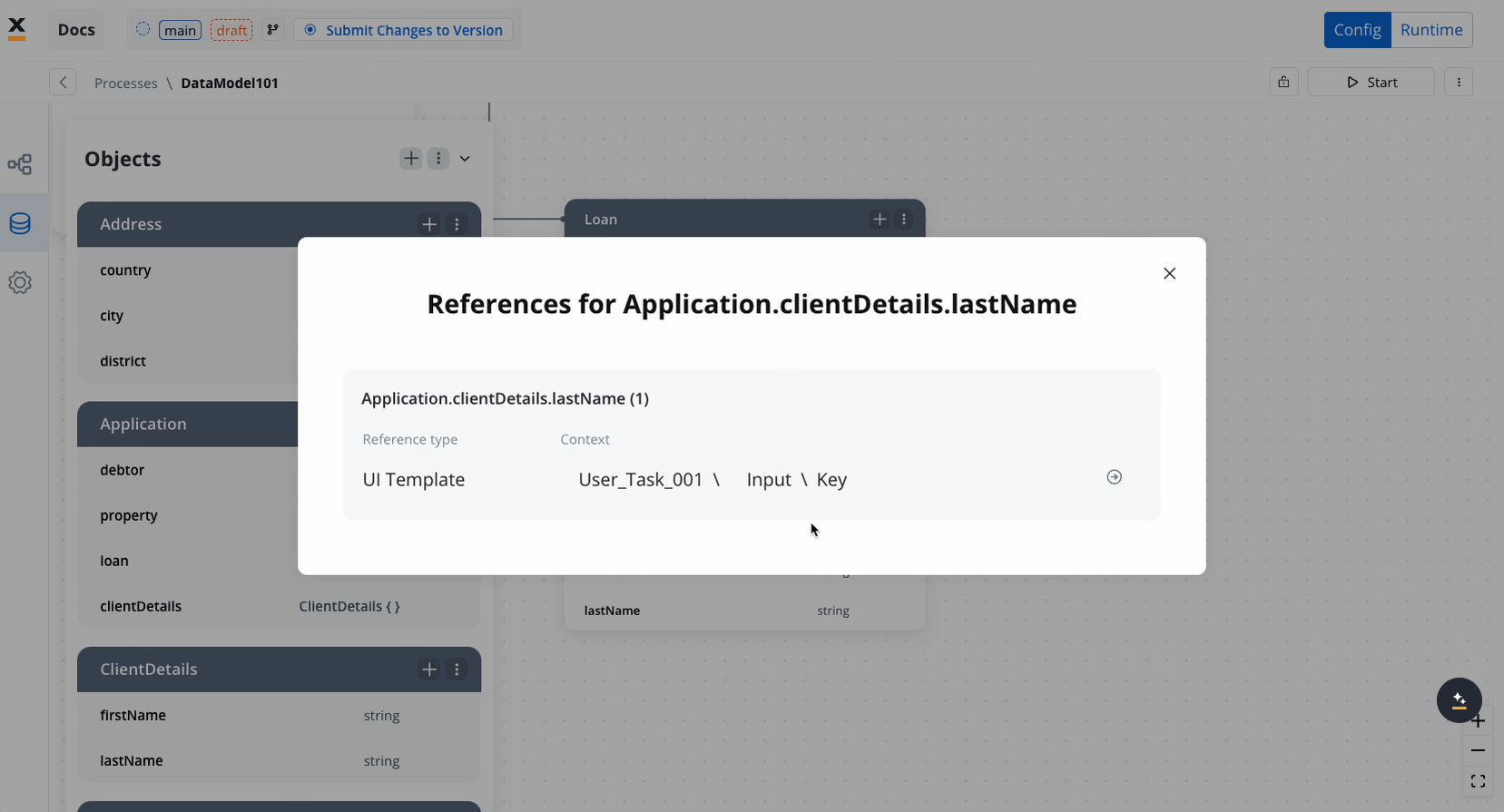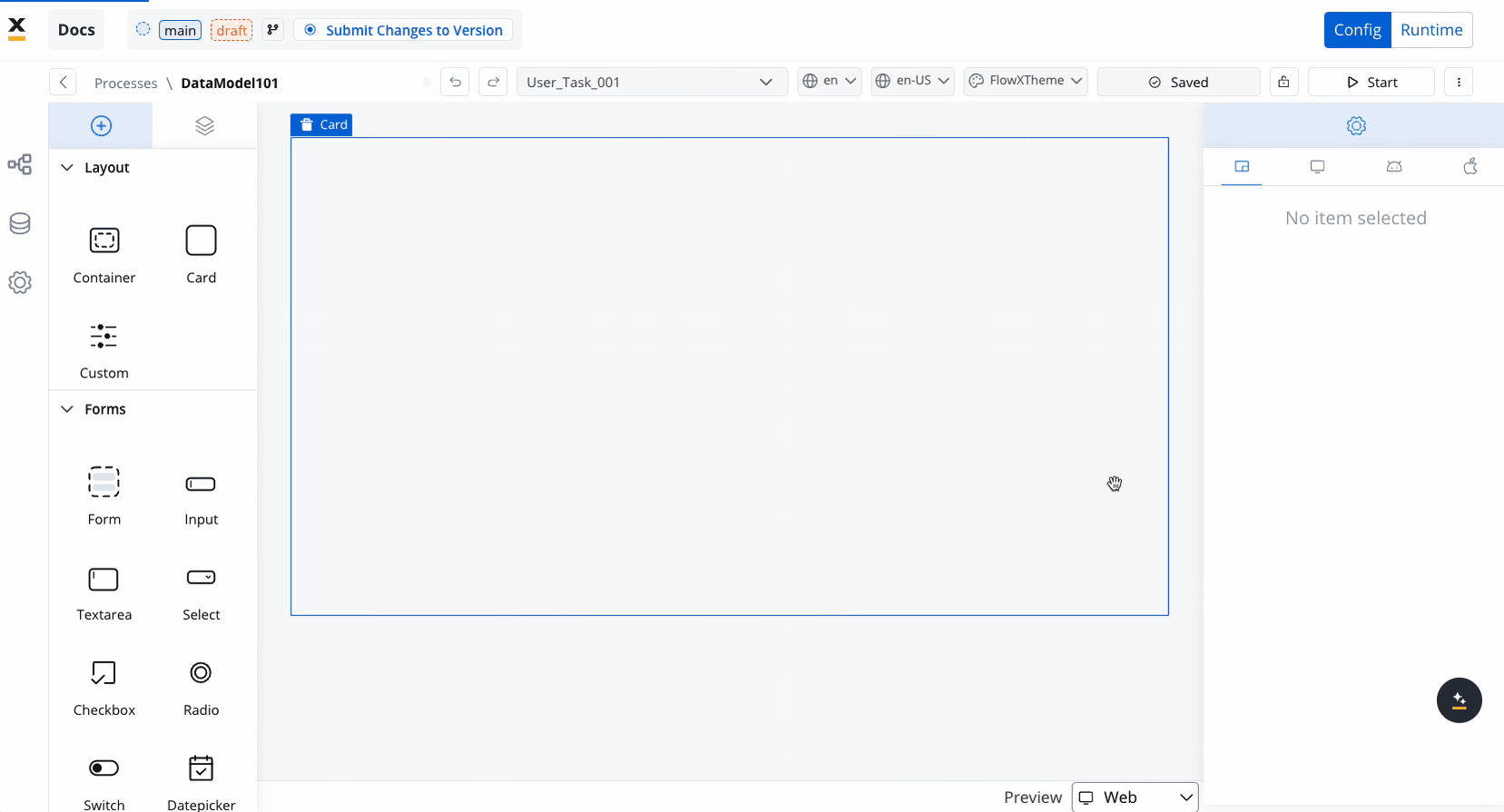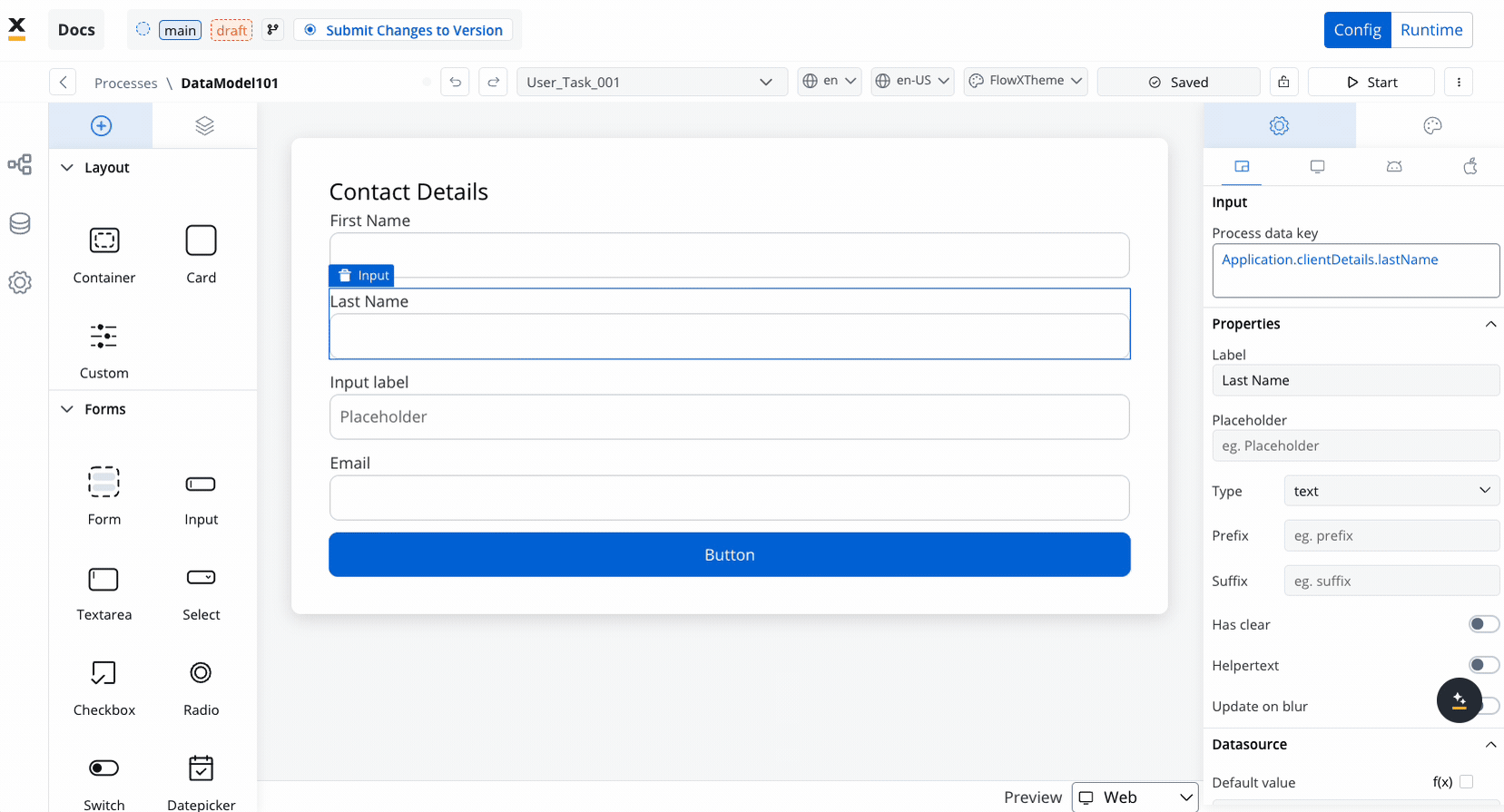
Sensitive data
Protect sensitive information by flagging specific keys in the data model. This ensures data is hidden from process details and browser console outputs.Reporting
The Use in Reporting tag allows you to designate keys for use in the reporting plugin, enabling efficient tracking and analysis.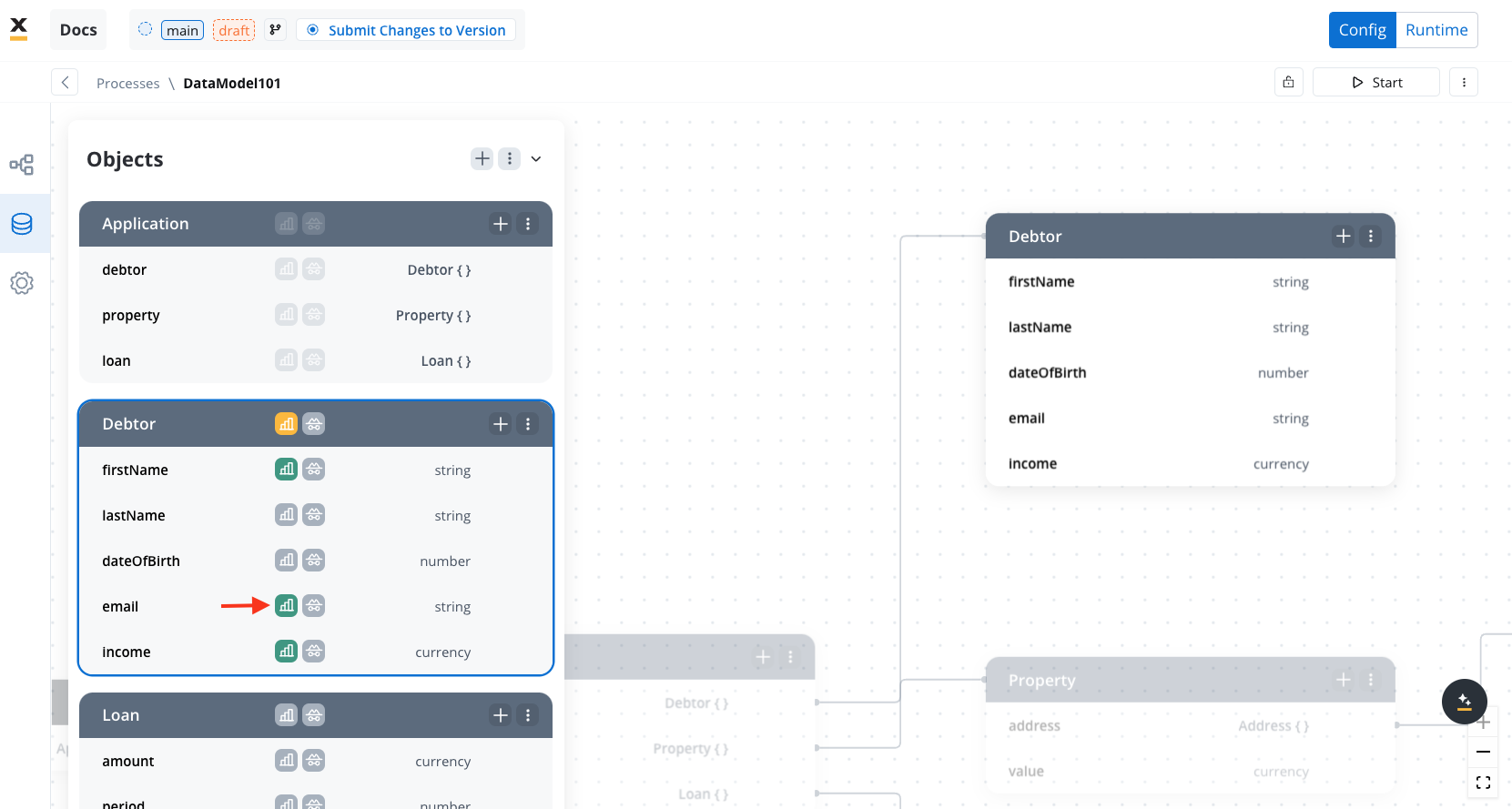
Reporting
Learn more about how to use Data Model attributes in the Reporting plugin.
Integration with other platform features
The Data Model serves as the backbone for numerous platform features, enabling seamless data flow between different components of your FlowX application.Integration with UI Designer
The Data Model directly integrates with the UI Designer, allowing you to:- Bind UI components to data model attributes
- Create dynamic UI layouts based on data model values
- Implement validation and formatting rules consistently across interfaces
Integration with workflows
When designing workflows in the Integration Designer, you can leverage the Data Model to:- Pass data from processes to workflows using the Start Integration Workflow action
- Map data between your process and external systems
- Transform and validate data during integration flows
Workflow integration
Learn more about integrating Data Model with workflows
Decision model integration
Data model attributes can be used as inputs for business rules, enabling:- Complex business rule implementation using structured data
- Consistent data handling across decision points
Best practices
Structuring your data model
- Use hierarchical structures: Organize related data in nested objects to improve maintainability
- Consistent naming: Adopt a consistent naming convention for all attributes
- Documentation: Add clear descriptions for complex attributes to improve team understanding
- Modularization: Group related attributes into logical objects rather than using flat structures
Version control and migration
When evolving your data model across versions:- Backwards compatibility: Ensure changes don’t break existing processes
- Migration strategy: Plan for how existing process instances will handle schema changes
- Documentation: Maintain clear documentation of data model changes between versions
Troubleshooting
Common issues
- Missing data: Ensure all required attributes are defined in your data model before referencing them
- Type mismatches: Verify that attributes are assigned the correct data type
- Validation errors: Check validation rules when data appears to be rejected
Debugging tips
- Use the data model reference feature to track attribute usage
- Examine process instance data to verify attribute values
- Review UI component bindings to ensure proper data mapping

