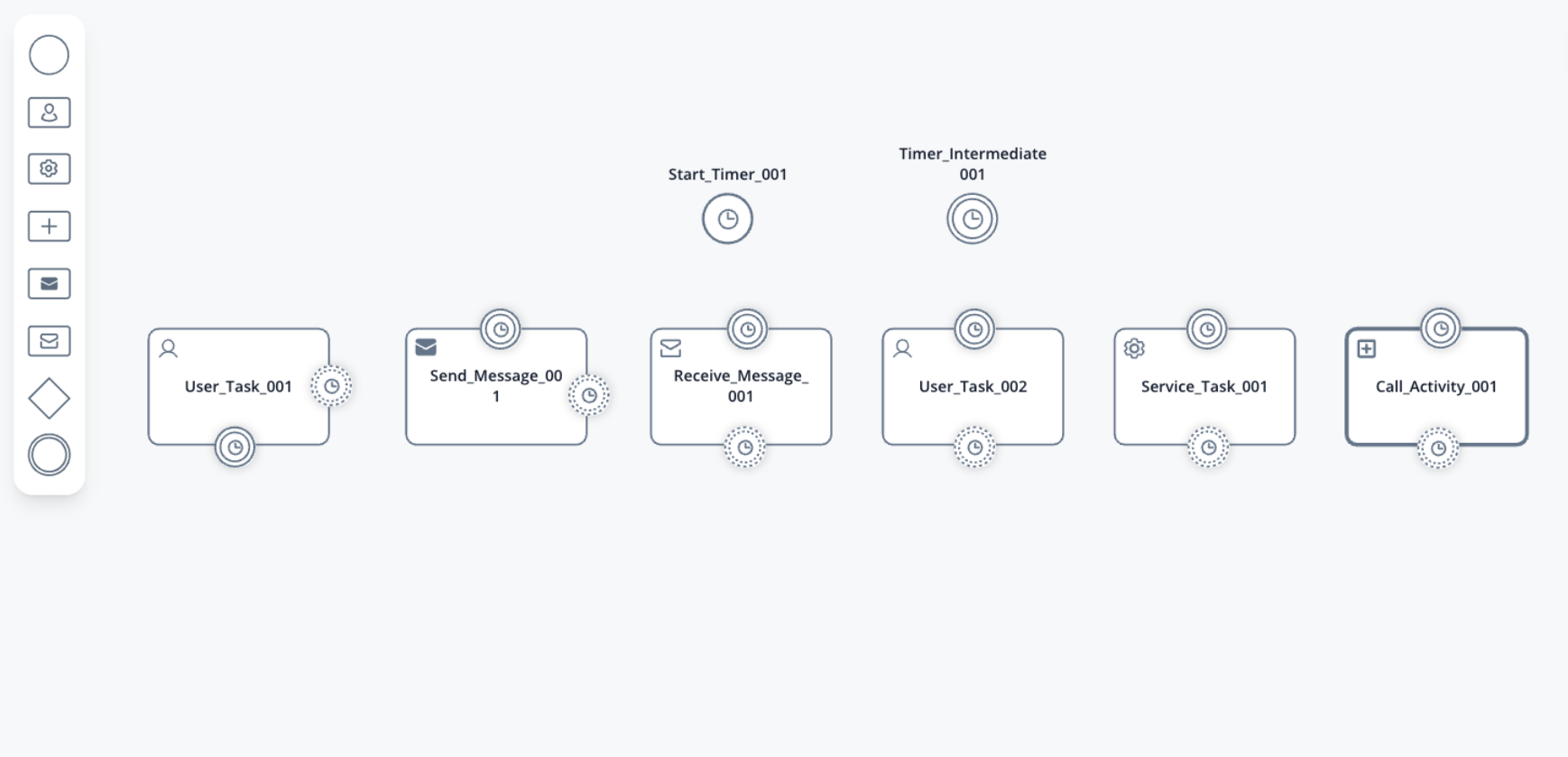
Timer events
Timer event nodes are a powerful feature in BPMN that allow you to introduce time-based behavior into your processes. These nodes enable you to trigger specific actions or events at predefined time intervals, durations, or cycles. With timer event nodes, you can design processes that respond to time-related conditions, ensuring smoother workflow execution and enhanced automation.
There are three primary types of timer event nodes:
- Timer Start Event (interrupting/non-interrupting): This node initiates a process instance at a scheduled time, either interrupting or non-interrupting ongoing processes. It allows you to set a specific date, duration, or cycle for the process to start. You can configure it to trigger a process instance just once or repeatedly.
- Timer Intermediate Event (interrupting): This node introduces time-based triggers within a process. It’s used to pause the process execution until a specified time duration or date is reached. Once triggered, the process continues its execution.
- Timer Boundary Event (interrupting/non-interrupting): Attached to a task or subprocess, this node monitors the passage of time while the task is being executed. When the predefined time condition is met, the boundary event triggers an associated action, interrupting or non-interrupting the ongoing task or subprocess.
Timers
Timers introduce the ability to trigger events at specific time intervals. They can be configured in three different ways: as a date, a duration, or a cycle. These configurations can use static values or dynamic/computed values.
-
Date: Events triggered on a specific date and time.
- Format: ISO 8601 (e.g.,
2019-10-01T12:00:00Zor2019-10-02T08:09:40+02:00)
- Format: ISO 8601 (e.g.,
-
Time Duration: Events triggered after a specified duration.
- Format: ISO 8601 duration expression (
P(n)Y(n)M(n)DT(n)H(n)M(n)S)- P: Duration designator
- Y: Years
- M: Months
- D: Days
- T: Time designator
- H: Hours
- M: Minutes
- S: Seconds
- Format: ISO 8601 duration expression (
Examples:
PT15S- 15 secondsPT1H30M- 1 hour and 30 minutesP14D- 14 daysP3Y6M4DT12H30M5S- 3 years, 6 months, 4 days, 12 hours, 30 minutes, and 5 seconds
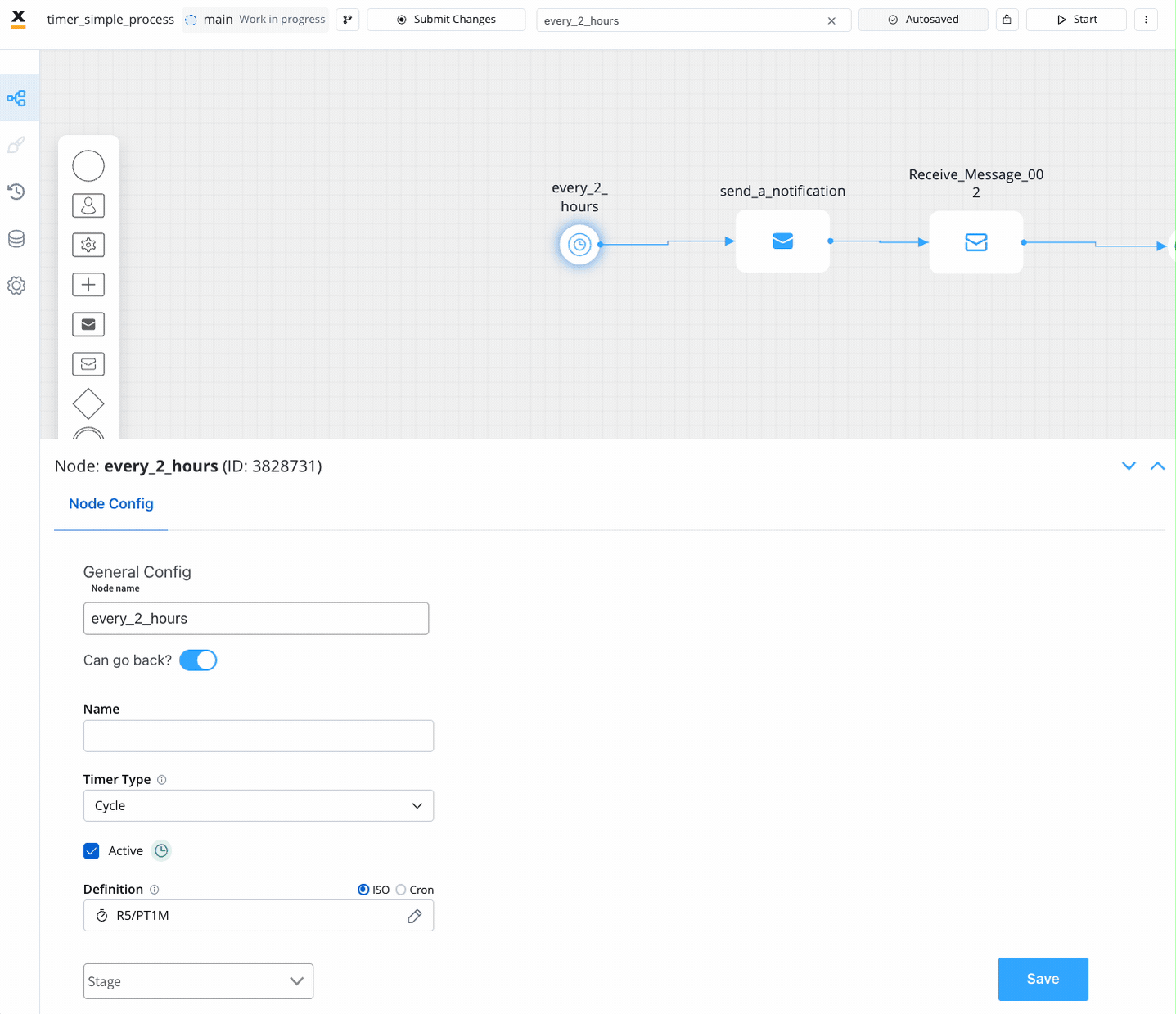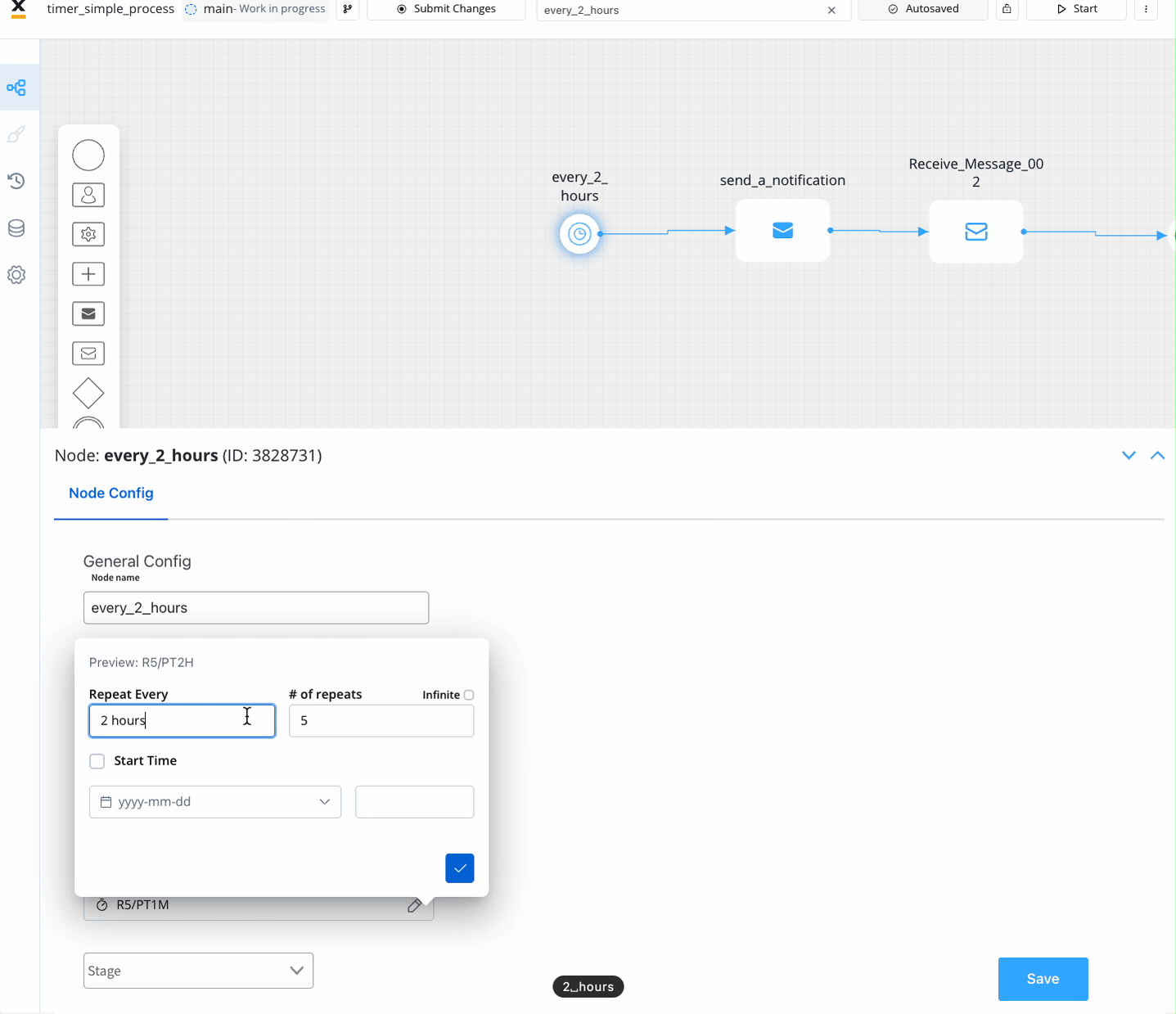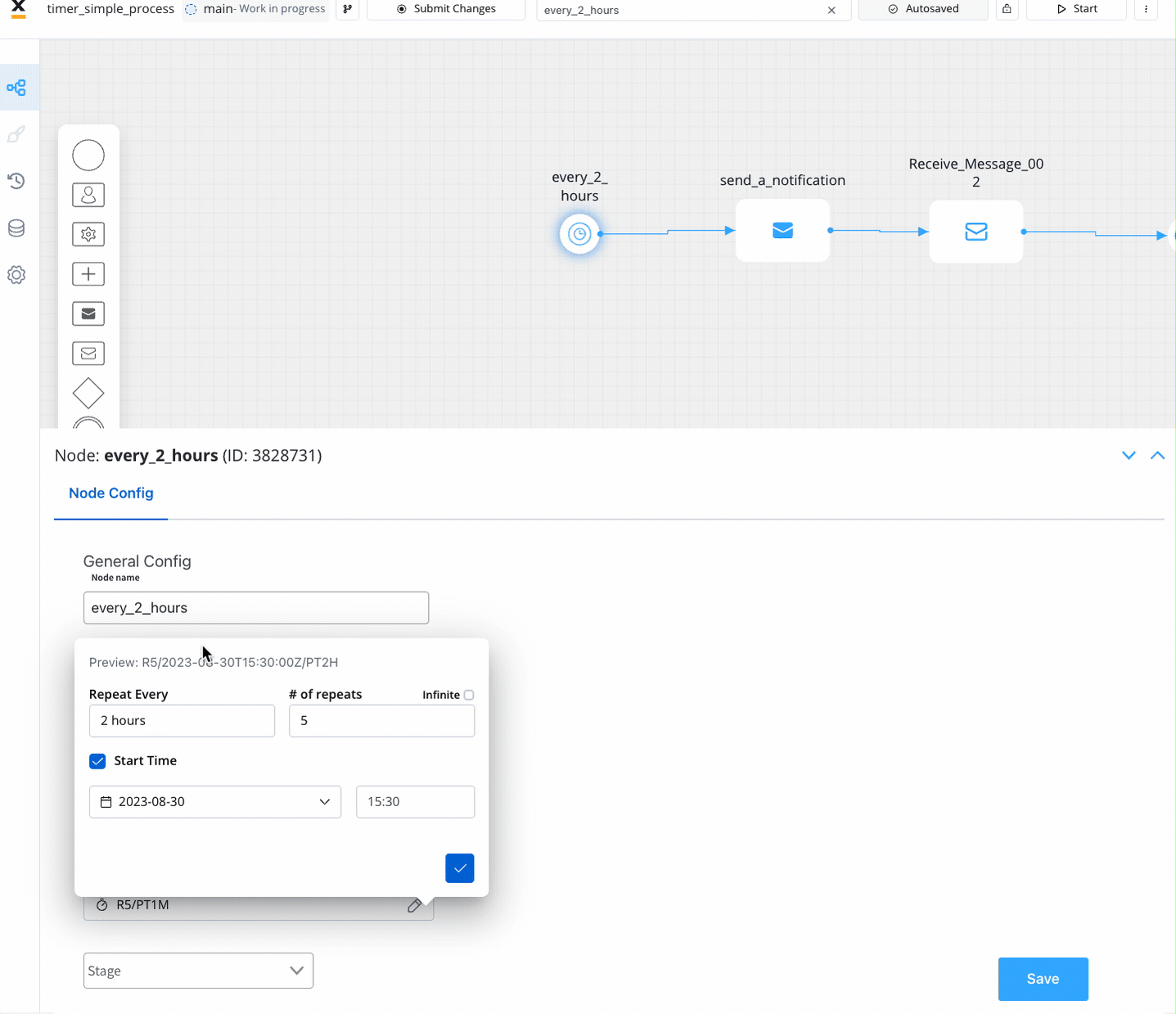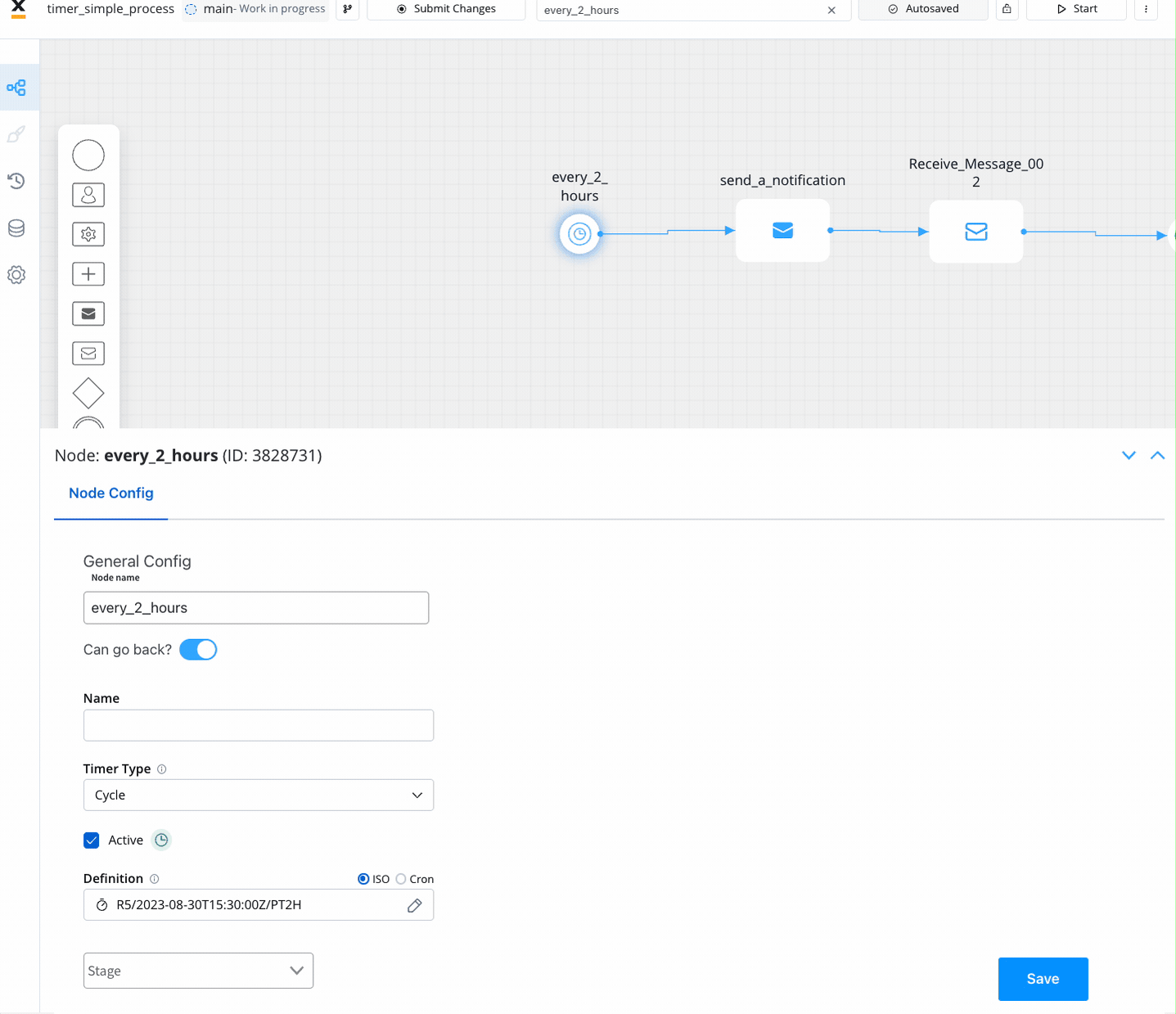
- Time Cycle (available for Timer Start Event): Events triggered at repeating intervals.
- Option 1: ISO 8601 repeating intervals format (
R)- Examples:
R5/2023-08-29T15:30:00Z/PT2H: Every 2 hours seconds, up to five times, starting with 29 August, 15:30 UTC timeR/P1D: Every day, infinitely
- Examples:
- Option 1: ISO 8601 repeating intervals format (
- Option 2: Using cron expressions
- Example:
0 0 9-17 * * MON-FRI: Every hour on the hour from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. UTC, Monday to Friday
- Example:
Important: Only Spring cron expressions are permissible for configuration. Refer to the official documentation for detailed information on configuring Spring Cron expressions.
Scheduled timer events are clearly indicated within the process definition list of an application at Runtime, as illustrated in the following example:
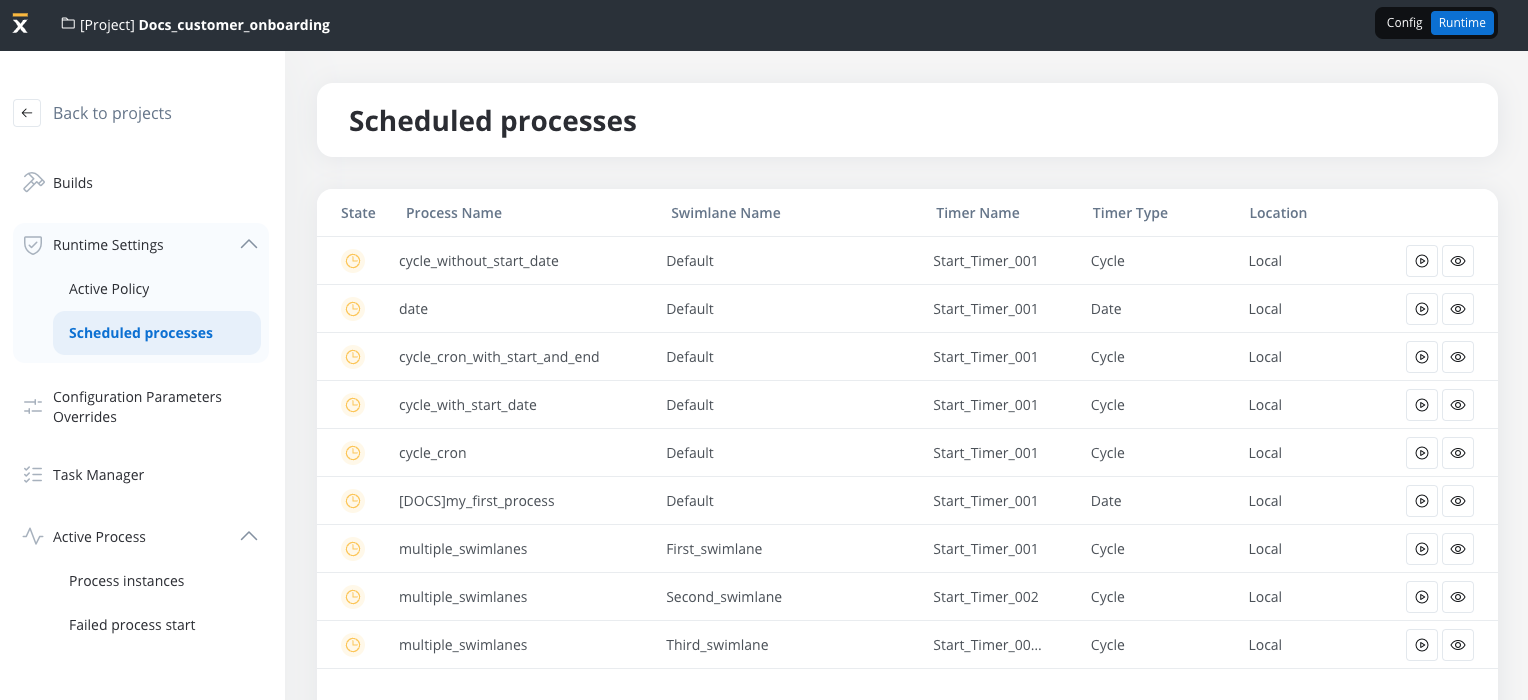
Scheduled processes
More information about timer expressions you can find in the below section:
Configuration
For each node type, the following timer types can be configured:
| Node Type | Date | Duration | Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timer Start Event | Yes | No | Yes |
| Timer Intermediate Event | Yes | Yes | No |
| Timer Boundary Event | Yes | Yes | No |
A process definition version should have a single Timer Start Event per swmilane.
For comprehensive details on each timer event node in this section, please refer to the corresponding documentation:

