Audit log
In the top-right contextual menu you will find the Audit feature containing the following information:- Timestamp
- User
- Application version
- Subject
- Event
- Subject Identifier
- Status
Some items in the Audit log are filterable, making it easy to track changes in the process.
Audit
Data model
In the Data Model, you can add new key-pair values, which enables you to use shortcuts when adding new keys using the UI Designer, without having to switch back and forth between menus.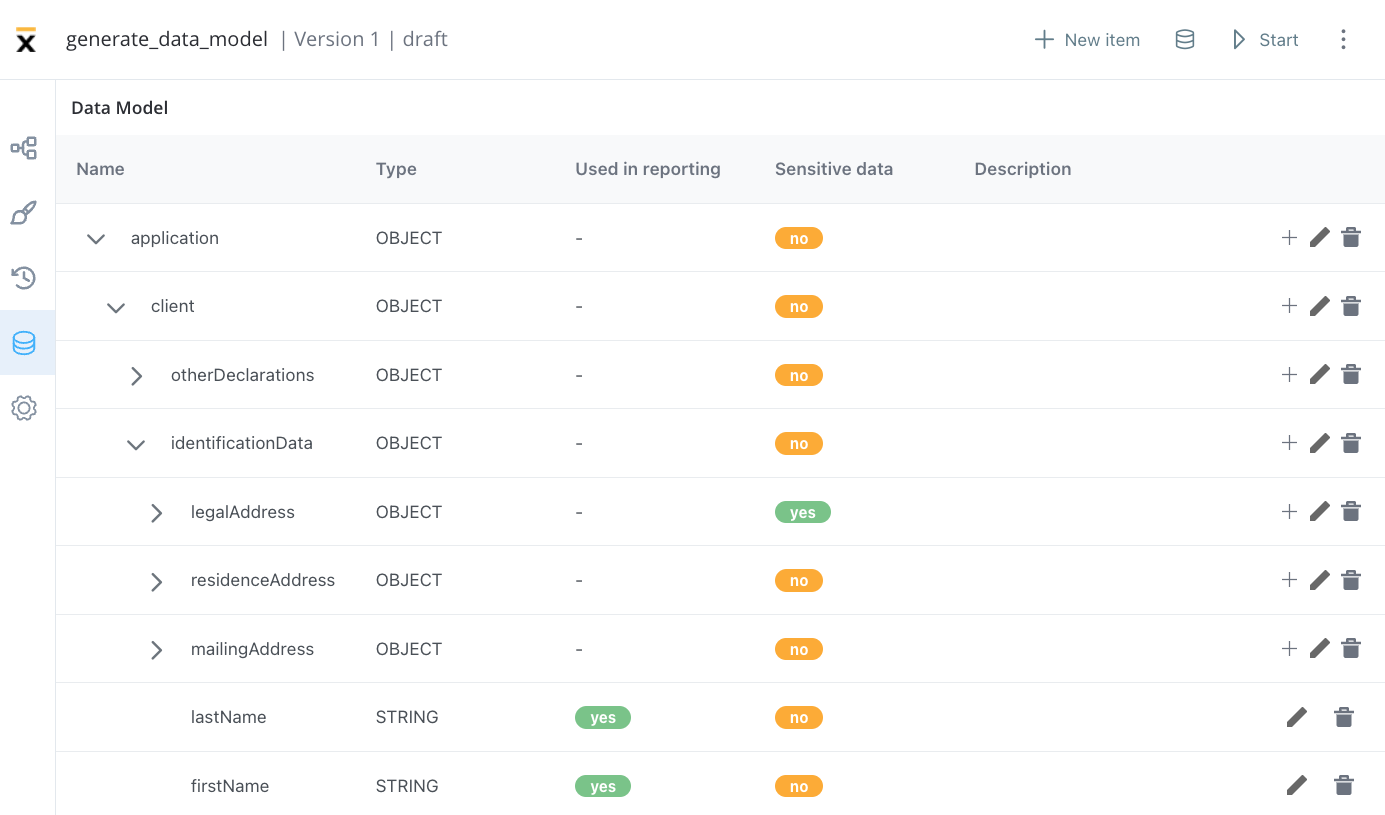
Data model
Swimlanes
Swimlanes offer a useful method of organizing process nodes based on process participants. By utilizing swimlanes, you can establish controlled access to specific process nodes for particular user roles.Adding new swimlanes
To add new swimlanes, please follow these steps:- Access the FlowX.AI Designer.
- Open an existing process definition or create a new one.
- Identify the default swimlane and select it to display the contextual menu.
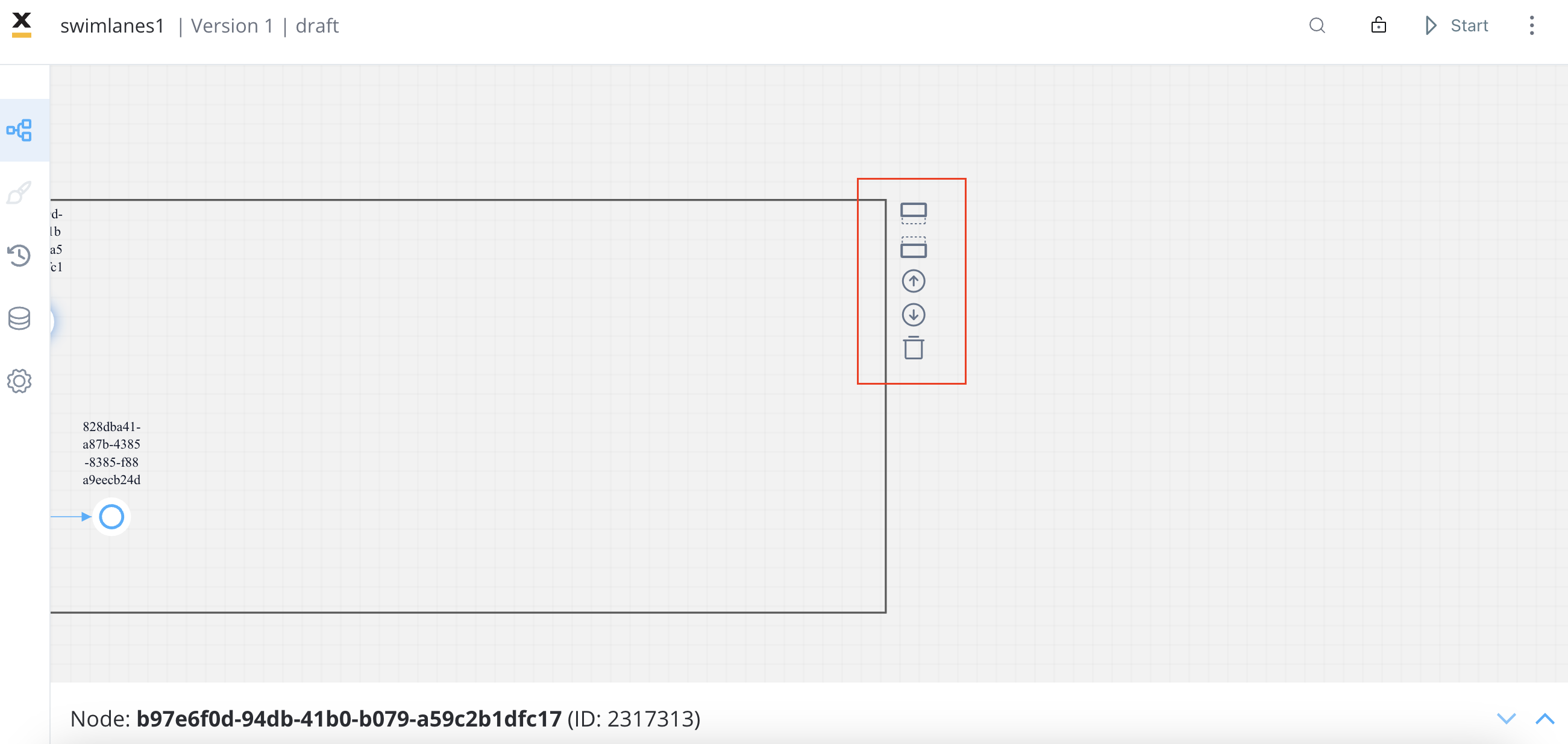
- Choose the desired location for the new swimlane, either below or above the default swimlane.
- Locate and click the add swimlane icon to create the new swimlane.
Settings
Process Name
- Process definition name: Edit the process definition name.
Name can only contain letters, numbers and the following special characters: [] () . _ -
General
In the General settings, you can edit the process definition name, include the process in reporting, set general data, and configure expiry time expression using Cron Expressions and ISO 8601 formatting.-
Available Platforms (Single Choice): This enable configuration (Navigation Areas, UI Designer, Misconfigurations) only for the specific platform selected:
- Web Only: If the navigation areas are defined exclusively for the Web, the process should remain set to Web. This is because it is optimized solely for web usage and would not provide the same level of functionality or user experience on mobile devices
- Mobile Only: If the navigation areas are defined only for Mobile, the process should be set to Mobile. This ensures that the process leverages mobile-specific features and design considerations, providing an optimal experience on mobile devices.
- Omnichannel: If the existing process has navigation areas defined for both Web and Mobile platforms, it should be set to Omnichannel. This ensures that users have a consistent experience regardless of the platform they are using.
Navigation Areas, UI Designer and misconfigurations will be affected by this setting.
By default, new processes are set to Web Only. This ensures that they are initially optimized for web-based usage, providing a starting point for most users and scenarios.
- Use process in reporting: When enabled, this setting includes the process in reporting.
- Use process in task management: Enabling this option creates tasks that are displayed in the Task Manager plugin. For more details, refer to the Task Management section.
- General data: Provides immediate data availability at process start, particularly useful for displaying notifications, banners, or messages before any SSE (Server-Sent Events) updates occur.
General data structure
General data accepts a notifications array that enables immediate display of messages, warnings, or informational content when a process starts:Use cases
General data is particularly useful for:- Supervision messages: Displaying important notices about account supervision or approval requirements
- Document generation status: Showing immediate feedback about document processing
- Process-level notifications: Presenting critical information that needs to be visible from the start
- Banner messages: Displaying persistent notifications at the top of the process interface
Example configuration
- Expiry time: A user can set up an expiryTime expression on a process definition to specify an expiry date.
| Example | Expression | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Expiry at Midnight | 0 0 0 * * ? | Sets the process to expire at 00:00 (midnight) every day. The ? is used in the day-of-week field to ignore its value. |
| Hourly Expiry on Weekdays | 0 0 9-17 * * MON-FRI | Sets the process to expire at the start of each hour between 9 AM and 5 PM on weekdays (Monday to Friday). |
| Expiry After a Duration | PT3M22S | Sets the process to expire after a duration of 3 minutes and 22 seconds from the start, using ISO 8601 format. |
The cron expression format should include seconds (0), minutes (0), hours (0), and then wildcards for the day, month, and day of the week fields. The
? sign in the day-of-week field is used when the day-of-month field is already specified (or ignored in this case).You can use both ISO 8601 duration format (
PT3M22S) and cron expressions (0 0 0 * * ?, 0 0 9-17 * * MON-FRI) to define expiryTime expressions for process definitions.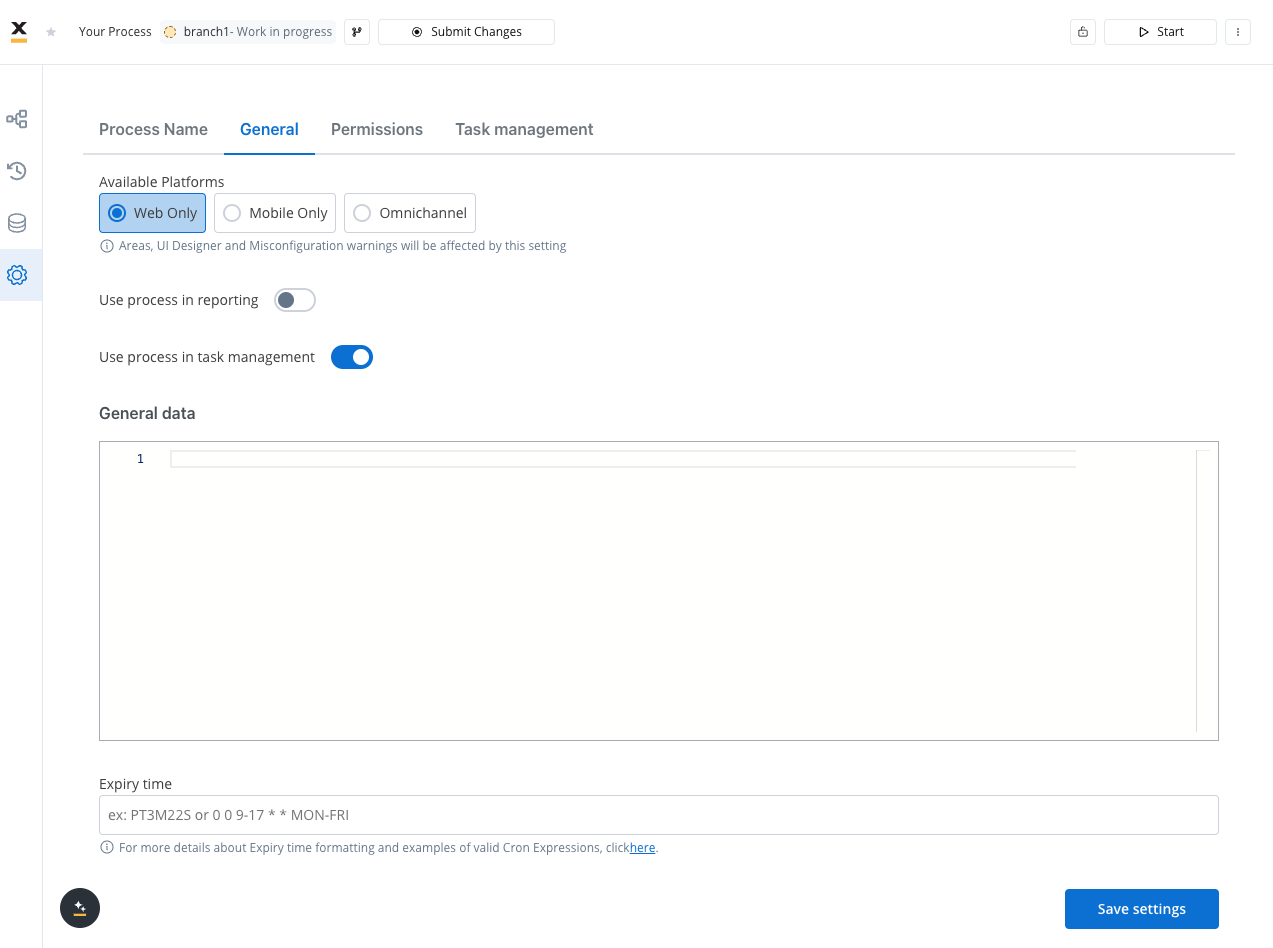
Permissions
After defining roles in the identity provider solution, they will be available to be used in the process definition settings panel for configuring swimlane access. When you create a new swimlane, it comes with two default permissions assigned based on a specific role: execute and self-assign. Other permissions can be added manually, depending on the needs of the user.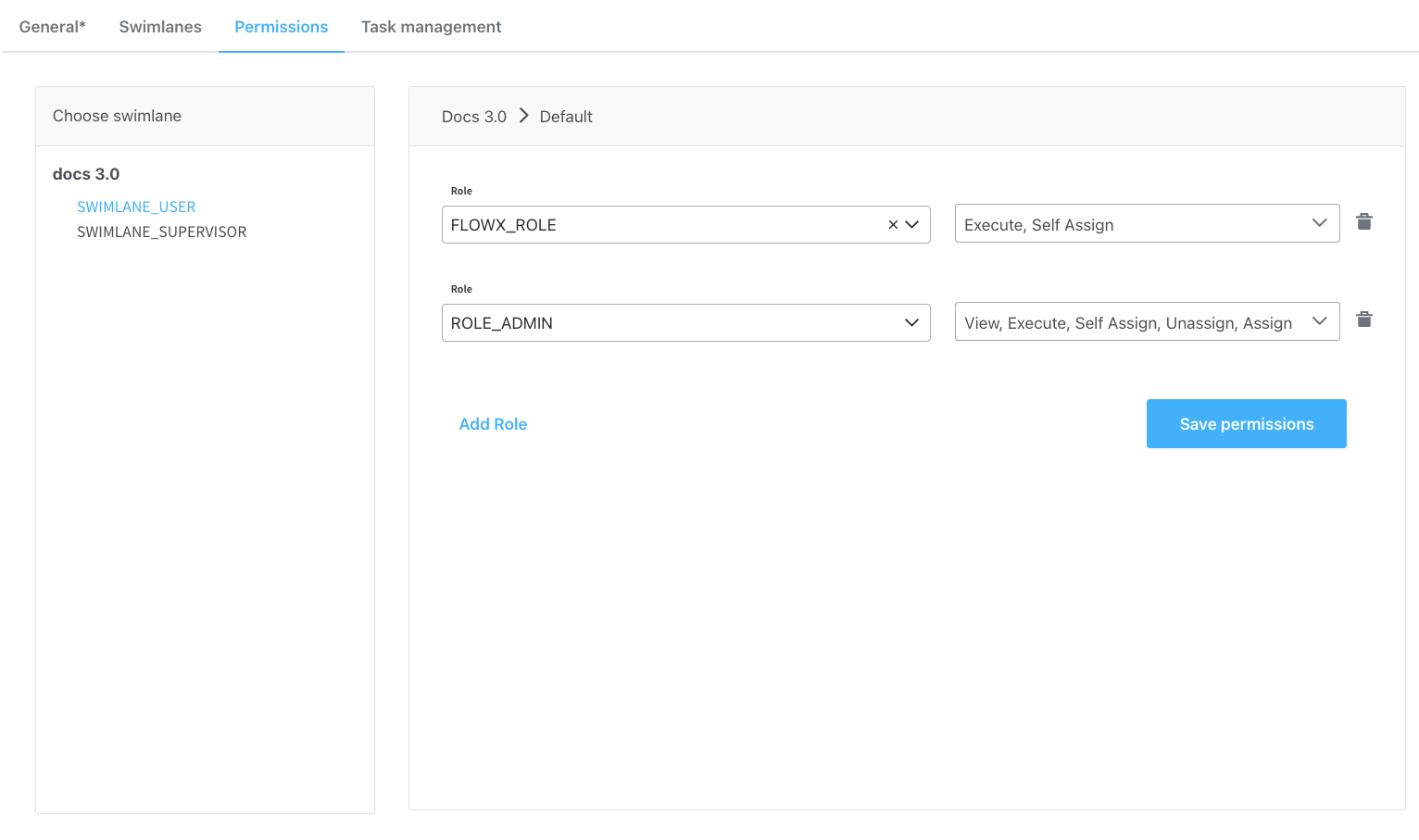
Configuring access rights for processes
Task management
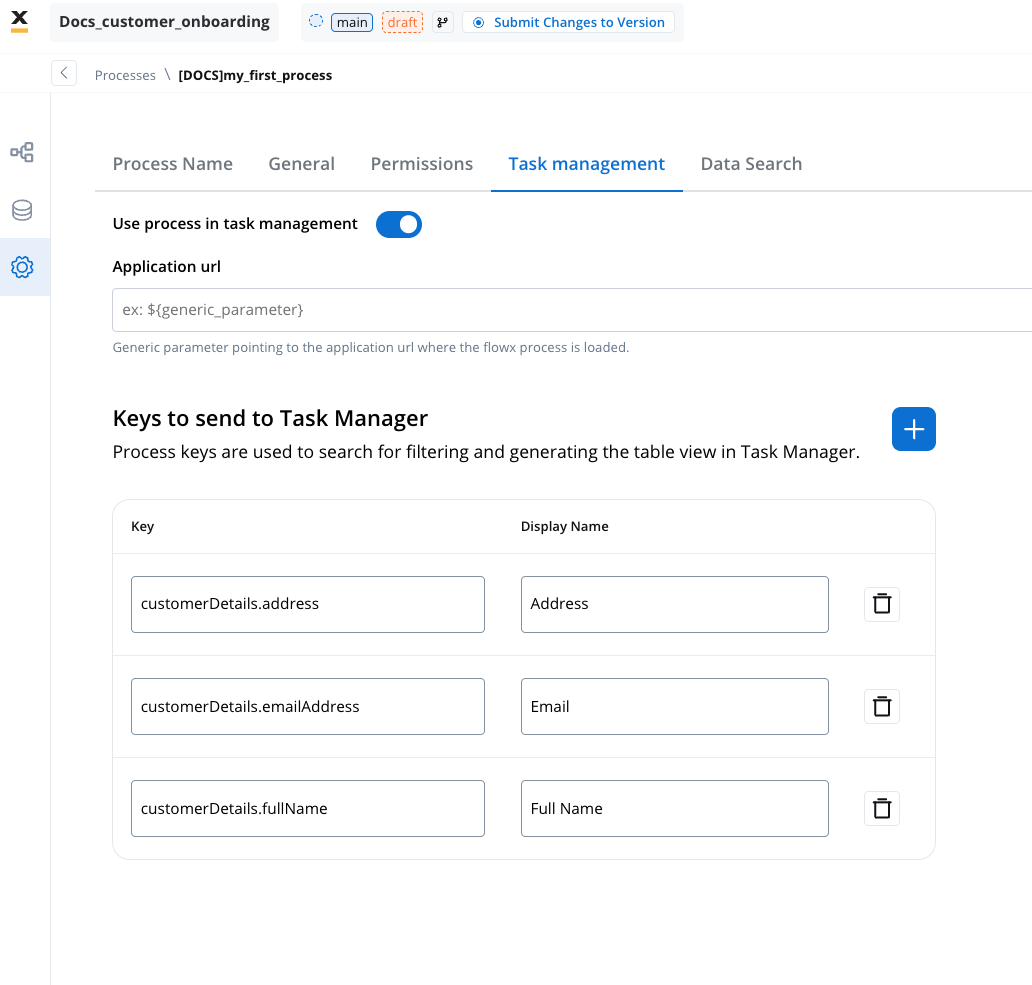
- Use process in task management
- The Use Process in Task Management option enables the integration of a process definition with the Task Manager system.
- By activating this feature, the process becomes available for managing tasks within Task Management, allowing data, tasks, and status updates to flow between the process and the Task Manager.
- Application url
- The Application URL is the endpoint or link that directs users to the specific application instance where a process is executed. It serves as a reference point for accessing and managing tasks associated with a process directly from the Task Manager.
- Follows a standard format, e.g.,
{baseURL}/appId/buildId/processes/resourceId/instance. - Can be dynamically defined using configuration parameters (e.g.,
${genericParameter}) or set at the process data level using business rules.
- Keys to send to Task Manager
- The Keys to Send to Task Manager configuration specifies the data fields (keys) from a process definition that are sent to the Task Manager for indexing and display.
- These keys are used to customize task-related views, filters, and parameters, making them accessible for tracking, filtering, and managing tasks effectively.
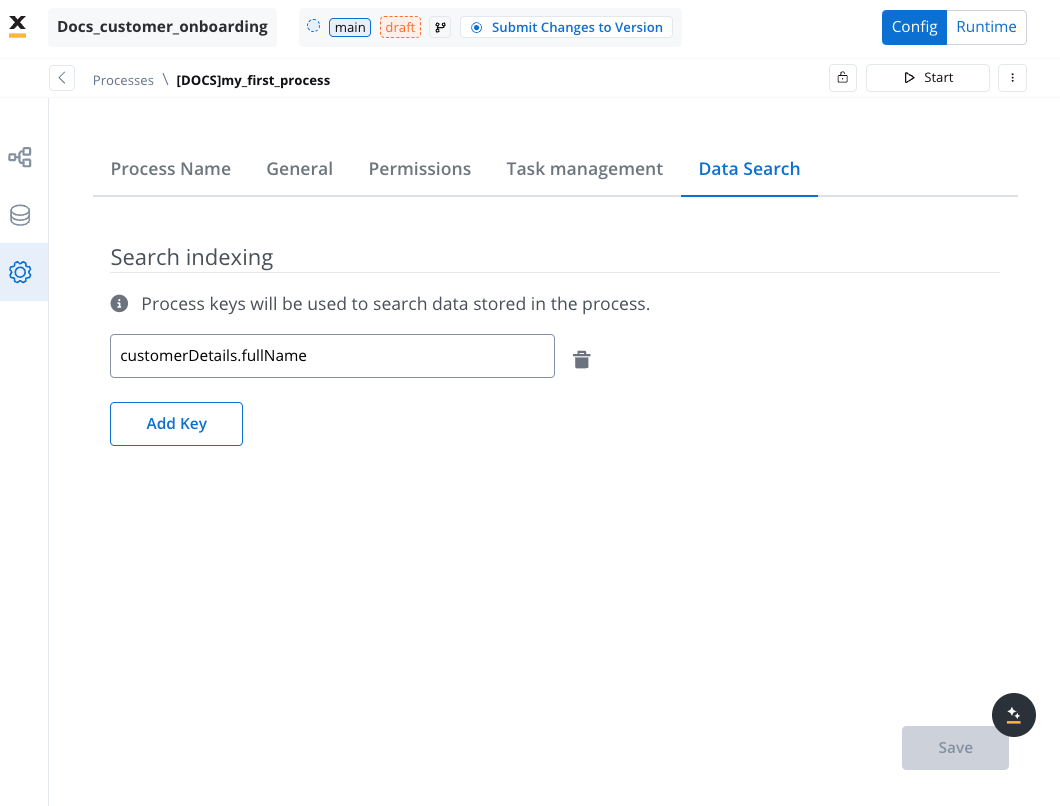
Data Search
The Search indexing tab allows you to configure process data keys used for indexing data stored in a process. These keys facilitate efficient searching and filtering of process instances based on the indexed data.