Overview
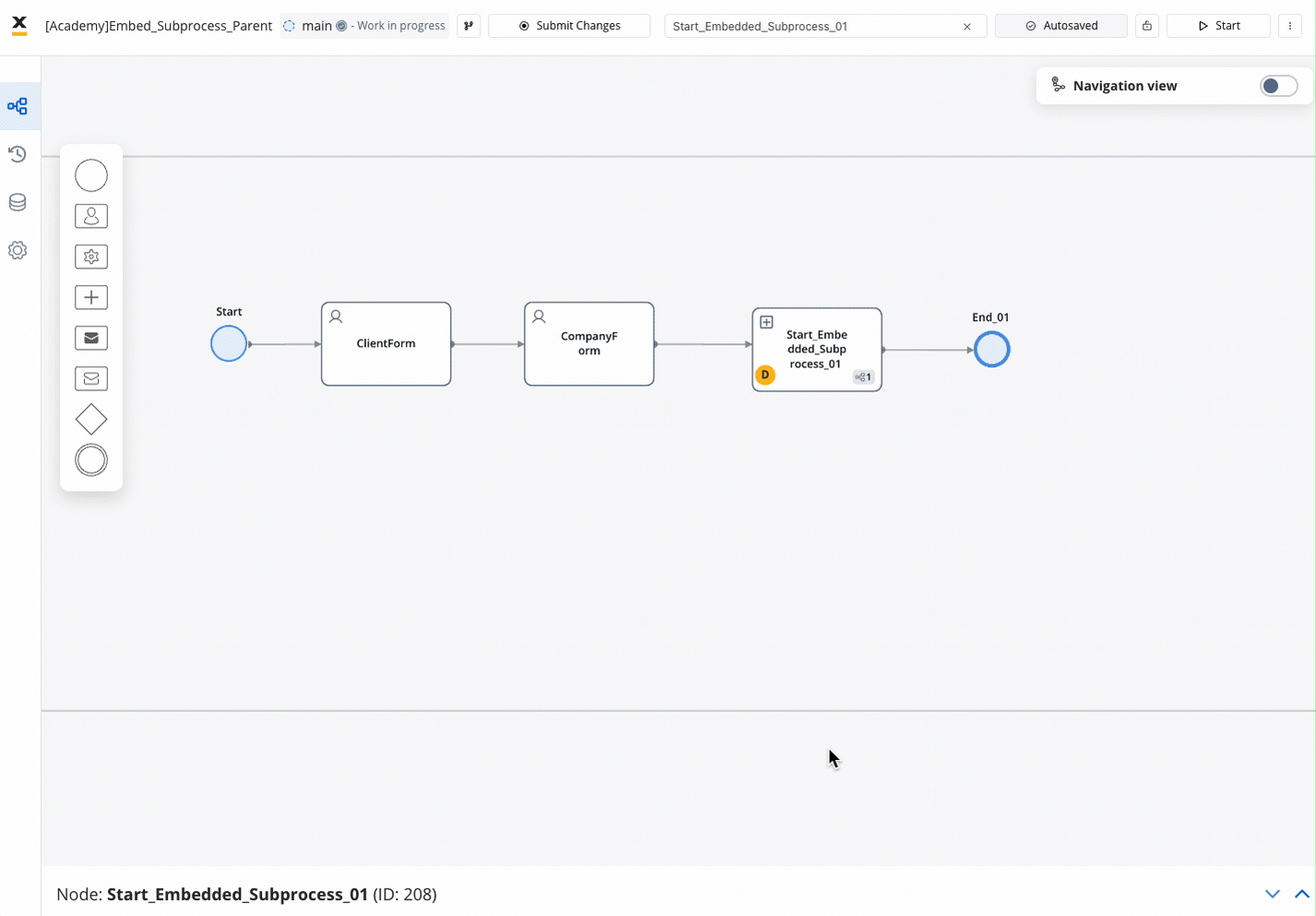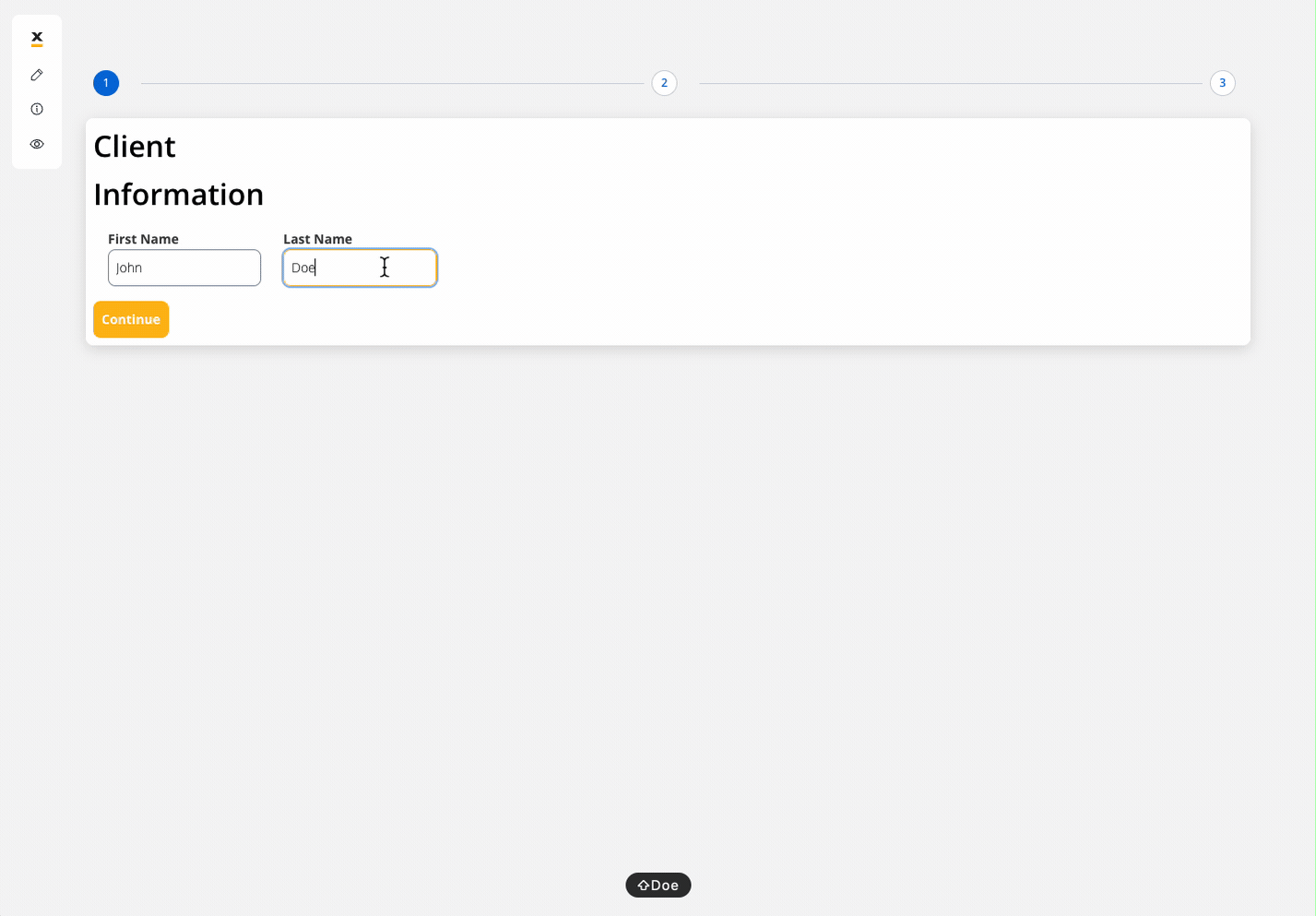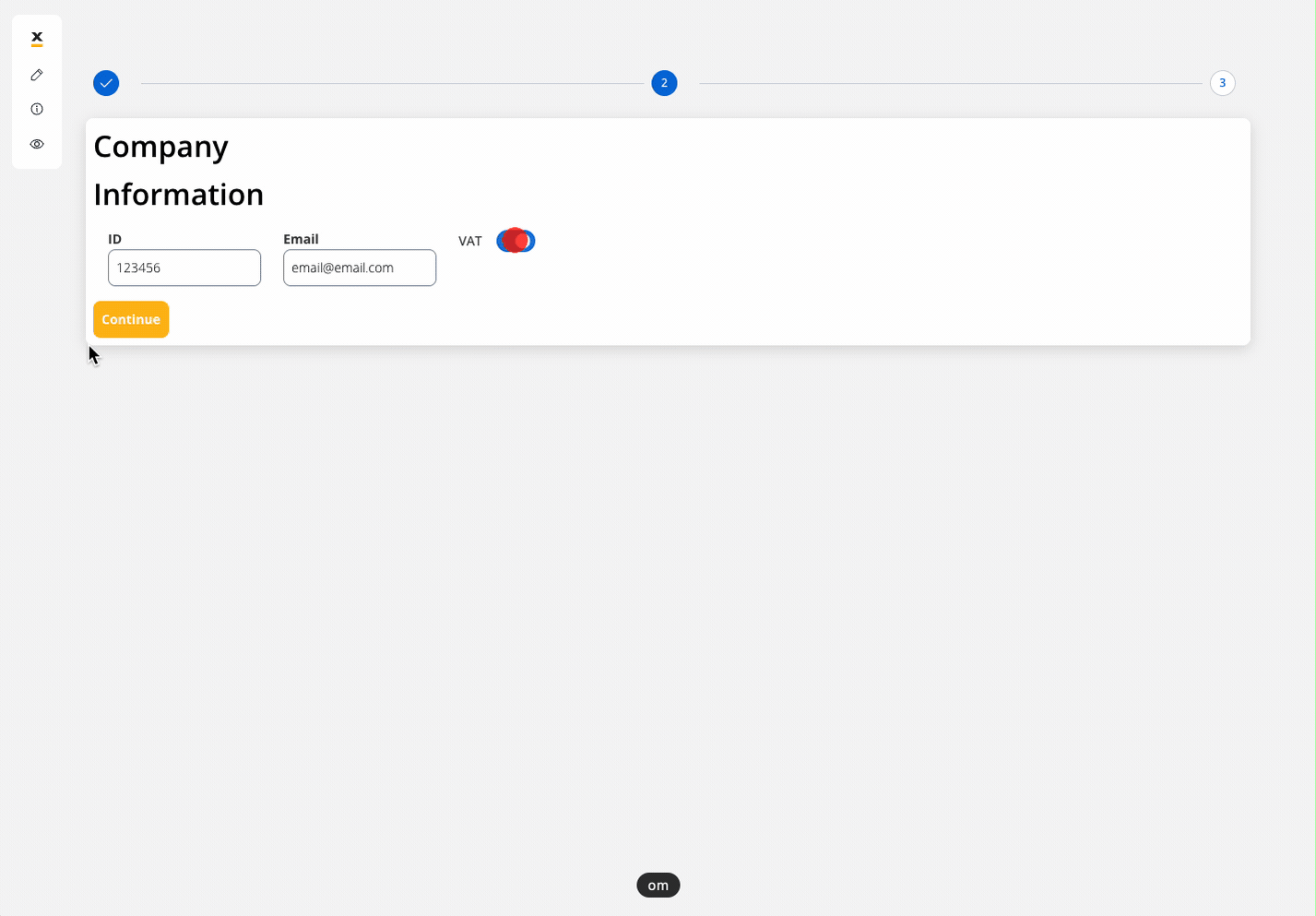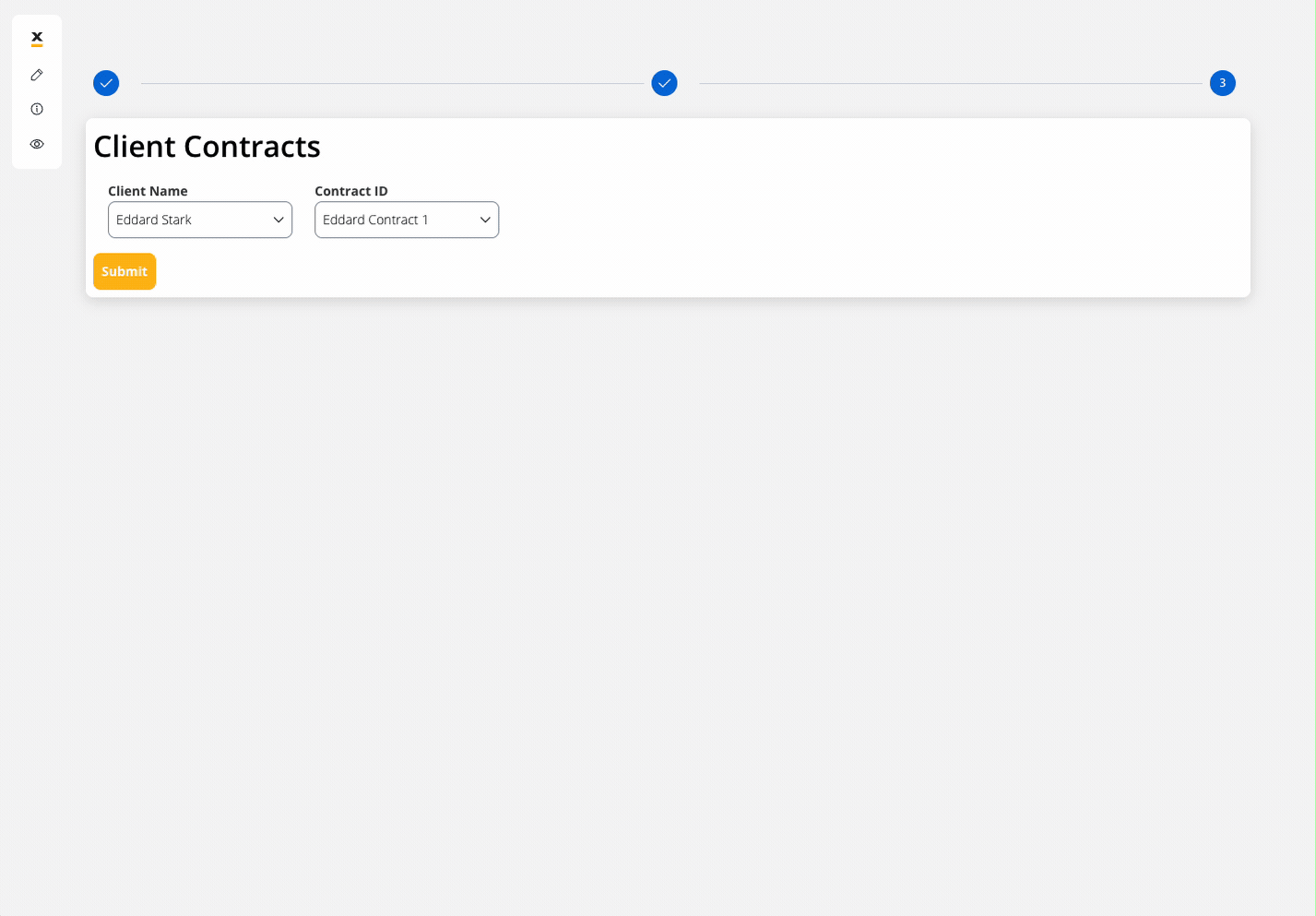
The Start Embedded Subprocess node enables the initiation of subprocesses within a parent process, offering a range of features and options for enhanced functionality.
Usage Considerations
Data Management
Embedded subprocesses offer advantages such as:- Segregated sections from a subprocess can be utilized without rendering them over the parent process.
- Data is stored within the parent process instance, eliminating the need for data transfer.
- Embedded subprocesses are visible in the navigation view.
Runtime Considerations
Important runtime considerations for embedded subprocesses include:- The child process must have only one swimlane.
- Runtime swimlane permissions are inherited from the parent.
- Certain boundary events are supported on Start Embedded Subprocess node, except for Timer events (currently not implemented).
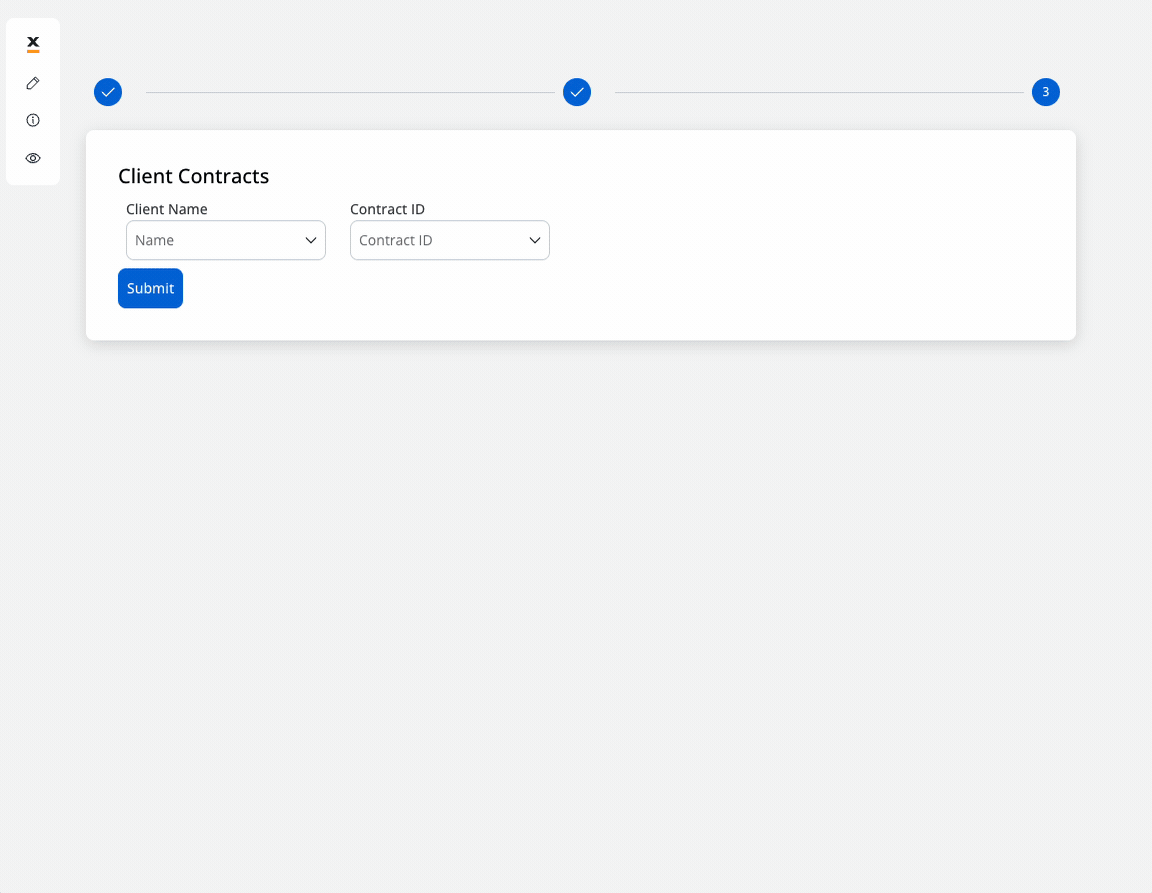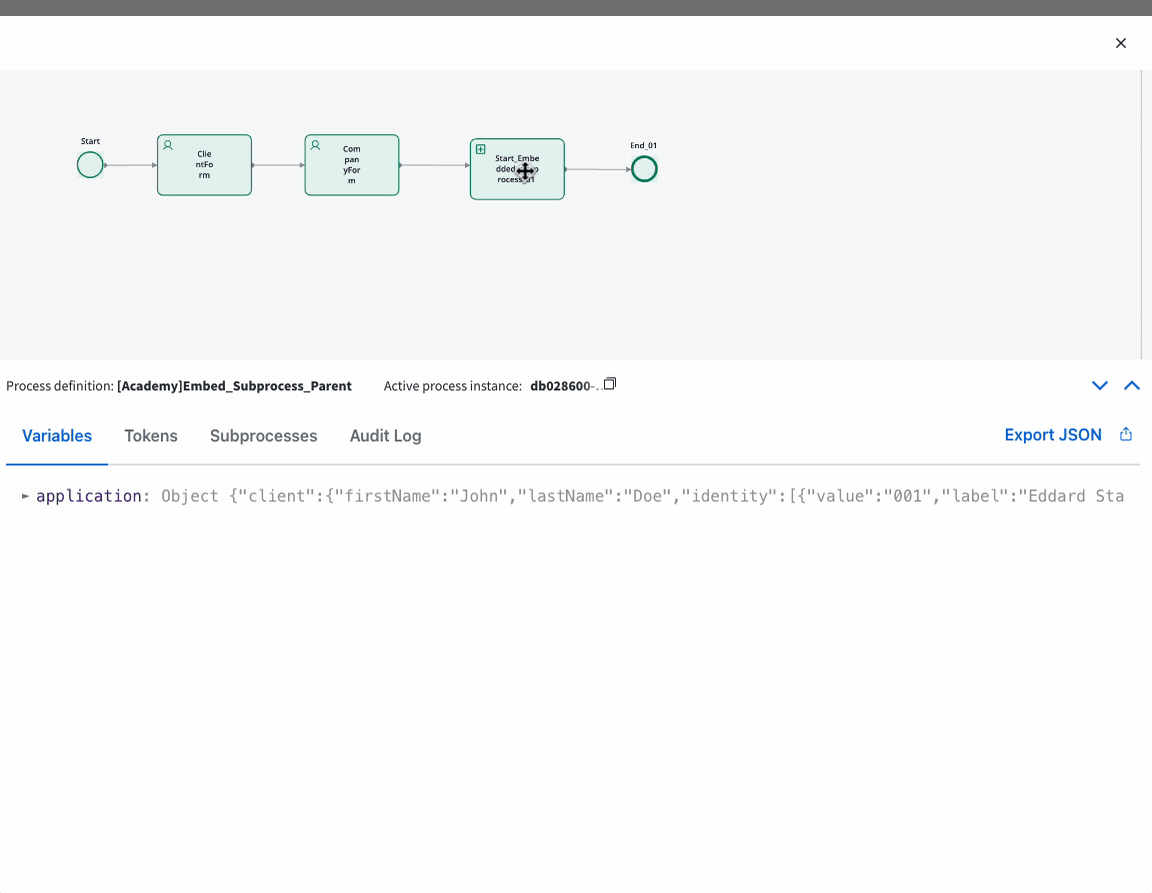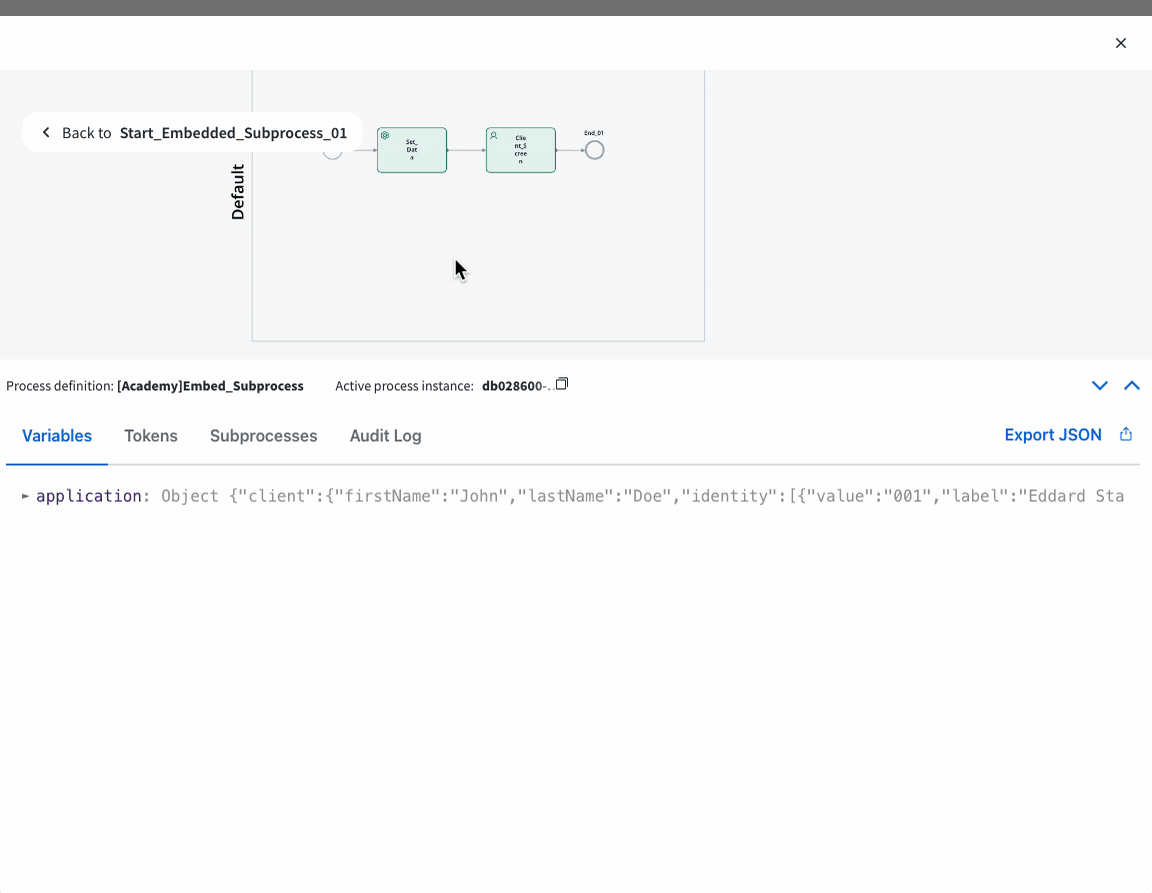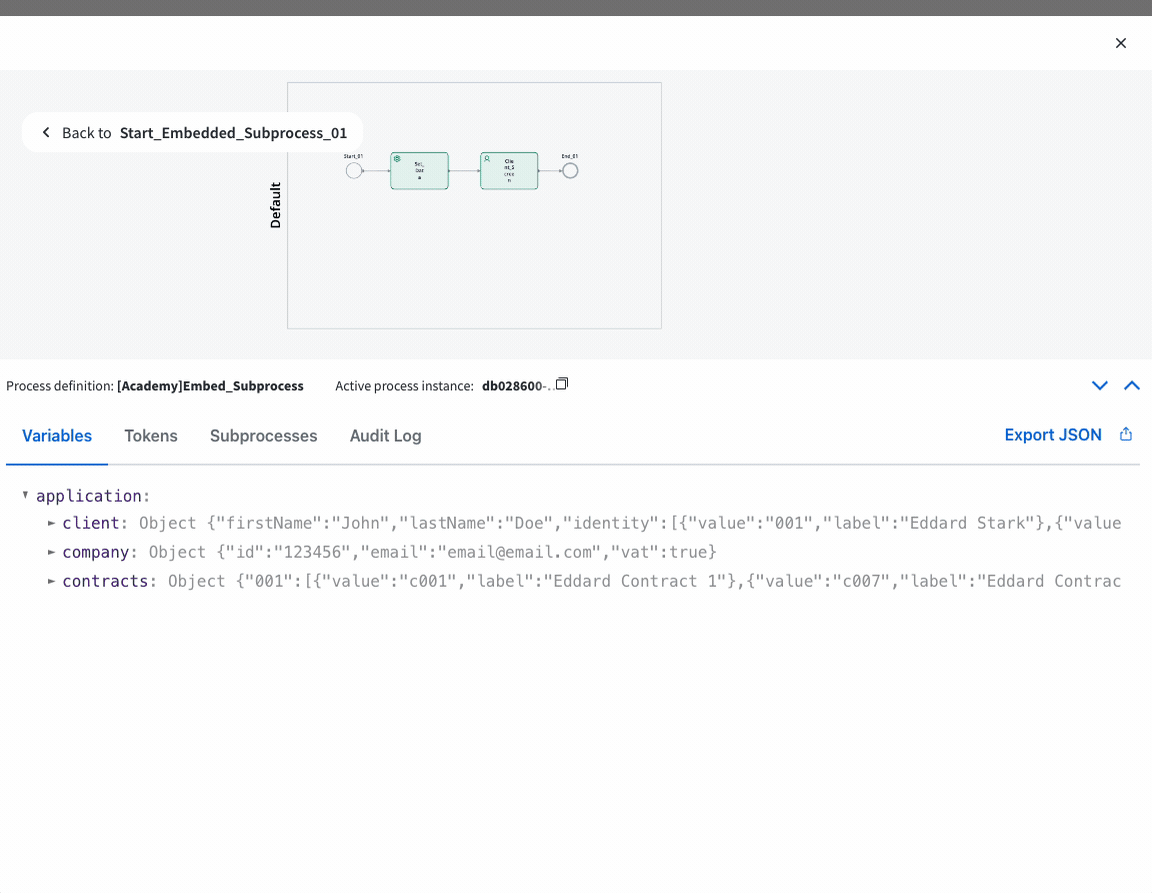
Example
Let’s explore this scenario: Imagine you’re creating a process that involves a series of steps, each akin to a sequential movement of a stepper. Now, among these steps, rather than configuring one step from scratch, you can seamlessly integrate a pre-existing process, treating it as a self-contained unit within the overarching process.Step 1: Design the Embedded Subprocess
Create a New Process
Start by creating a new process or selecting an existing process where you want to embed the subprocess.
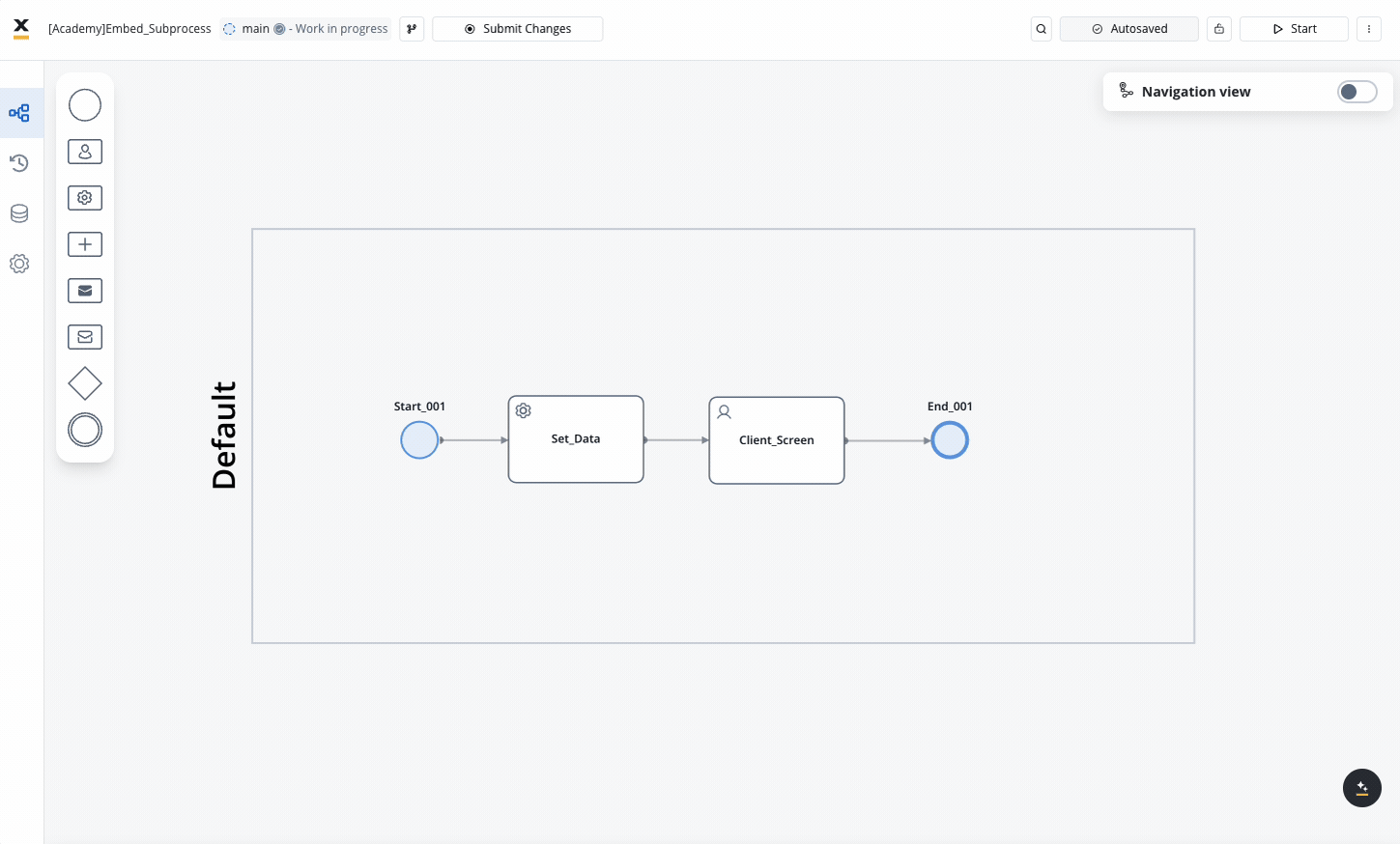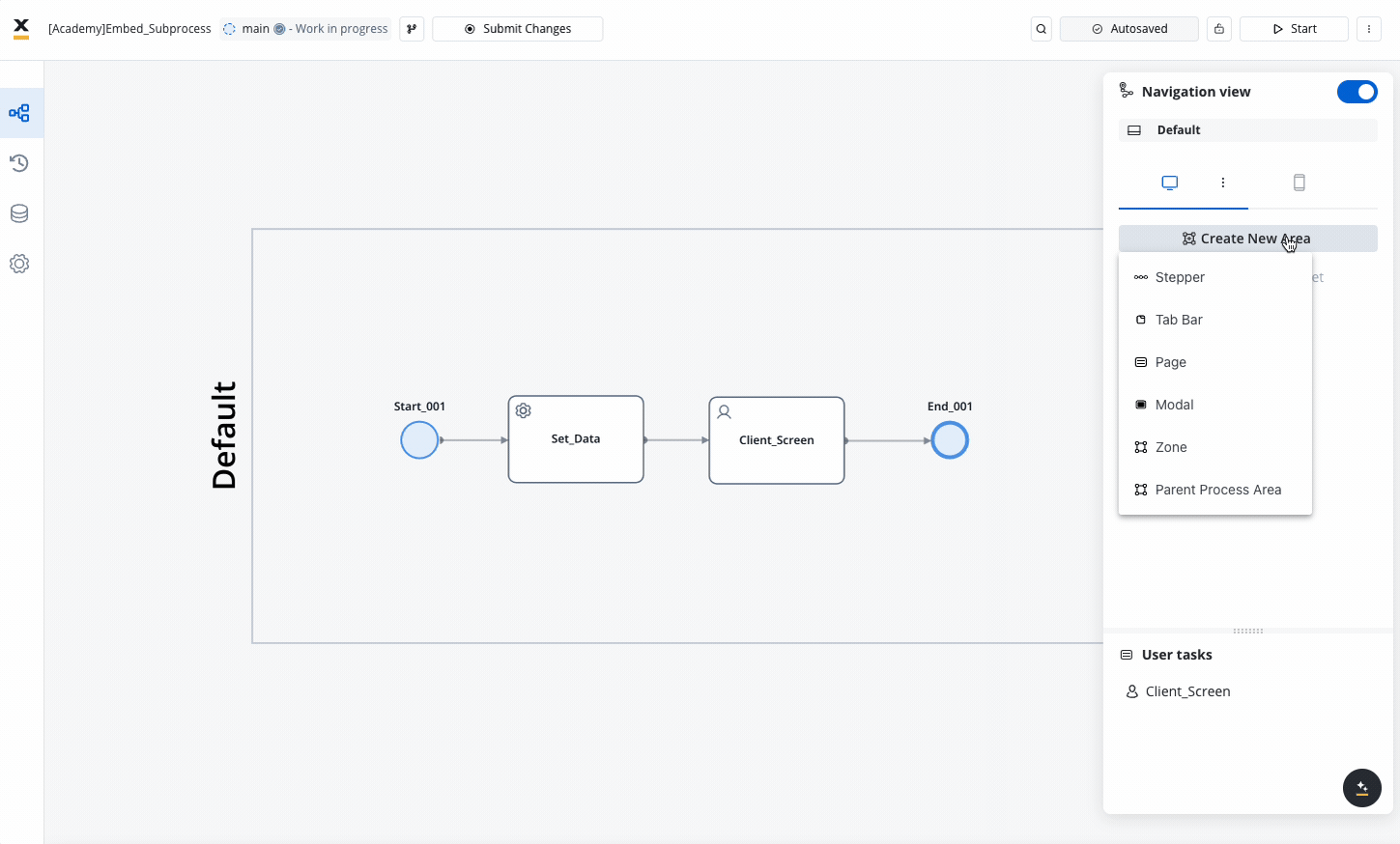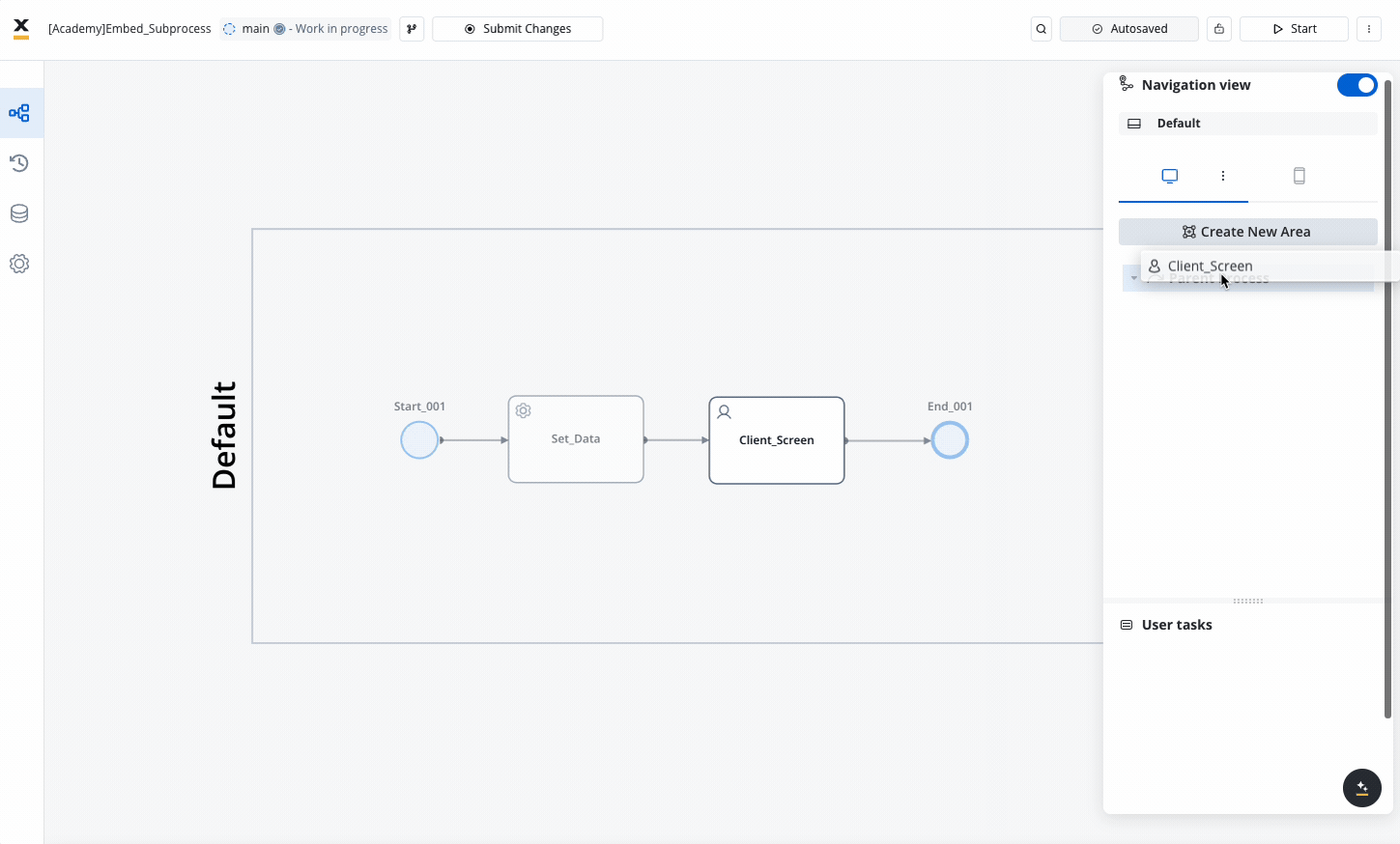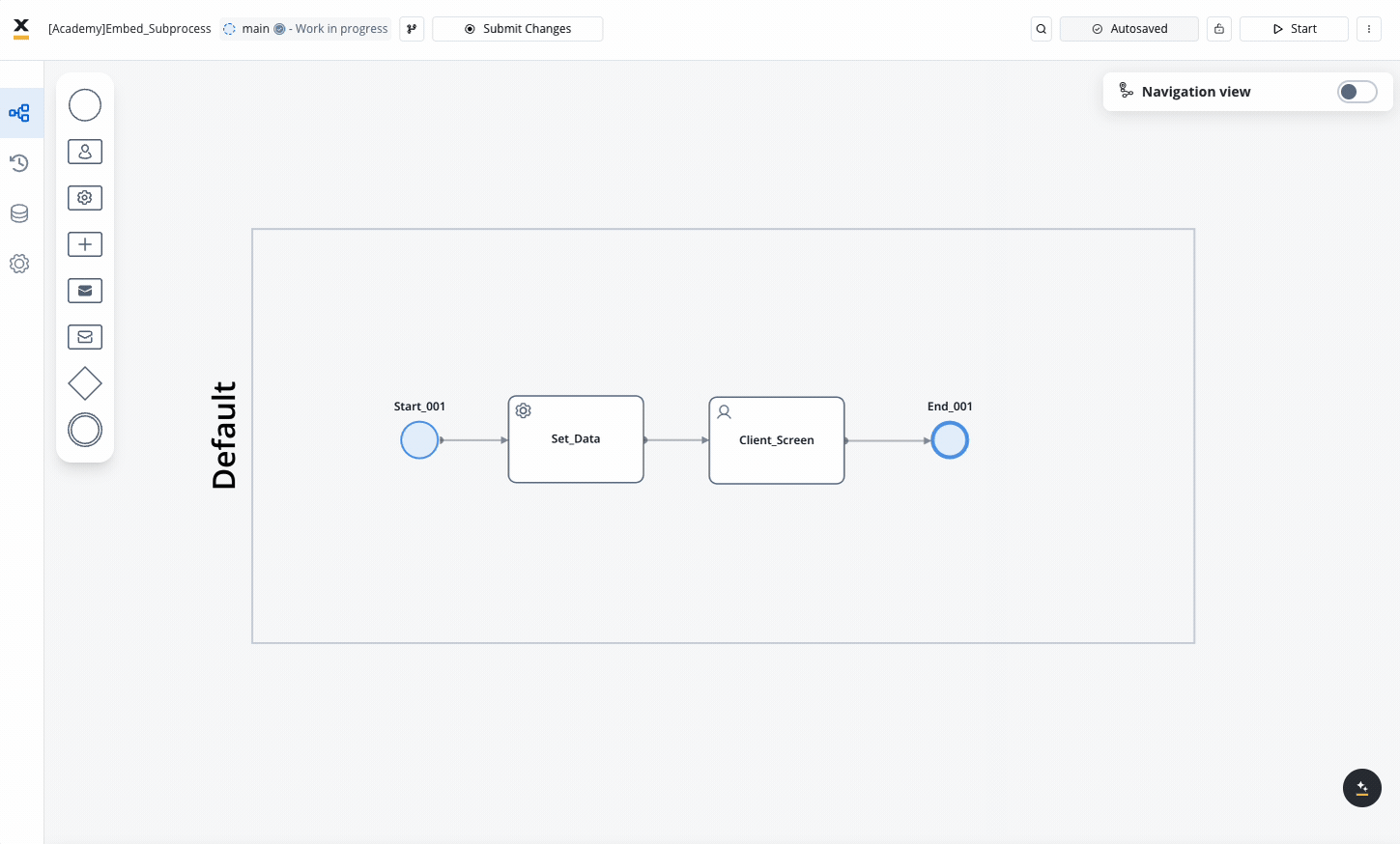
Navigation Areas
Design your navigation areas to match your needs.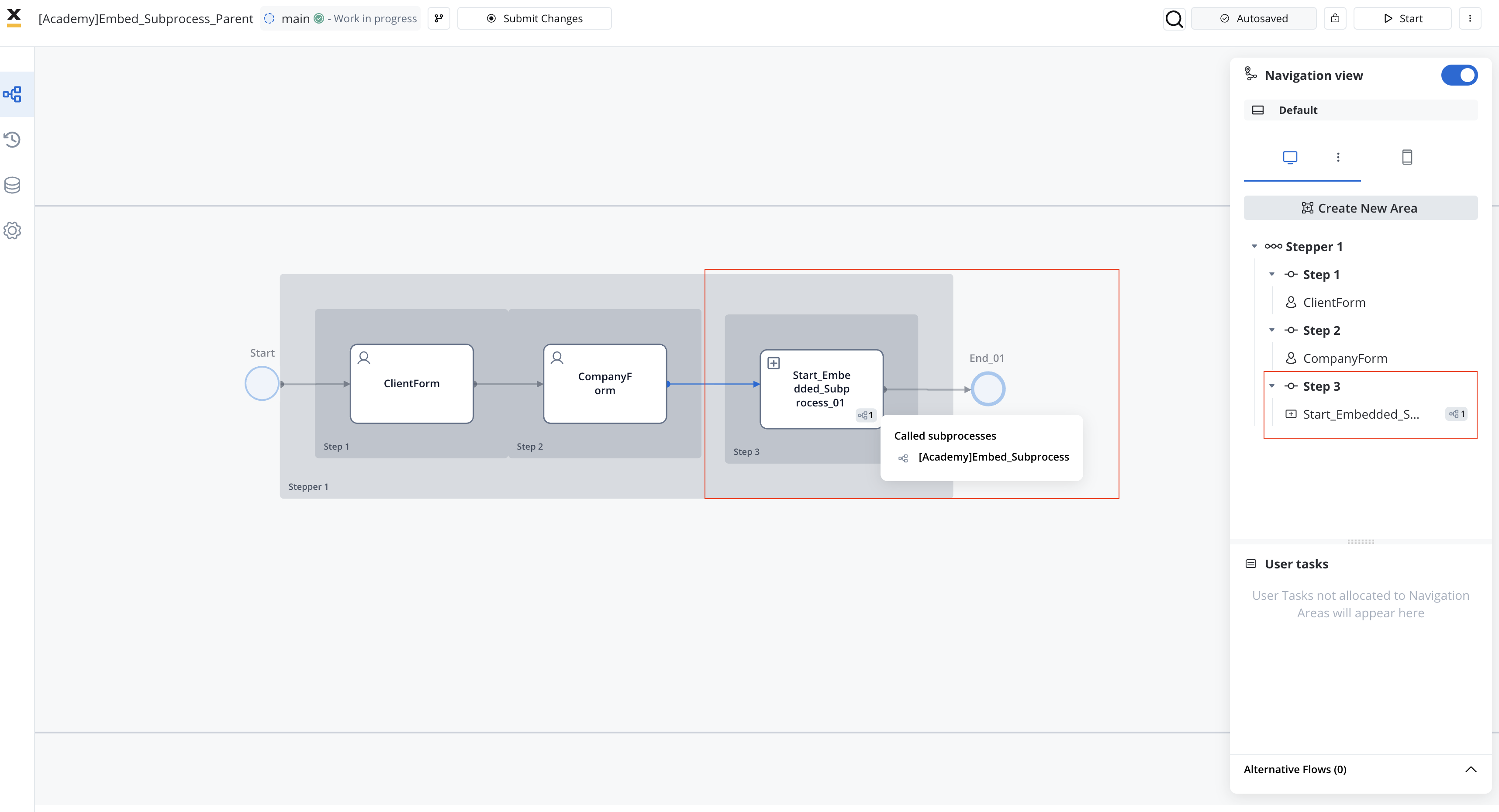

Make sure you allocated all your user tasks into the navigation area accordingly.
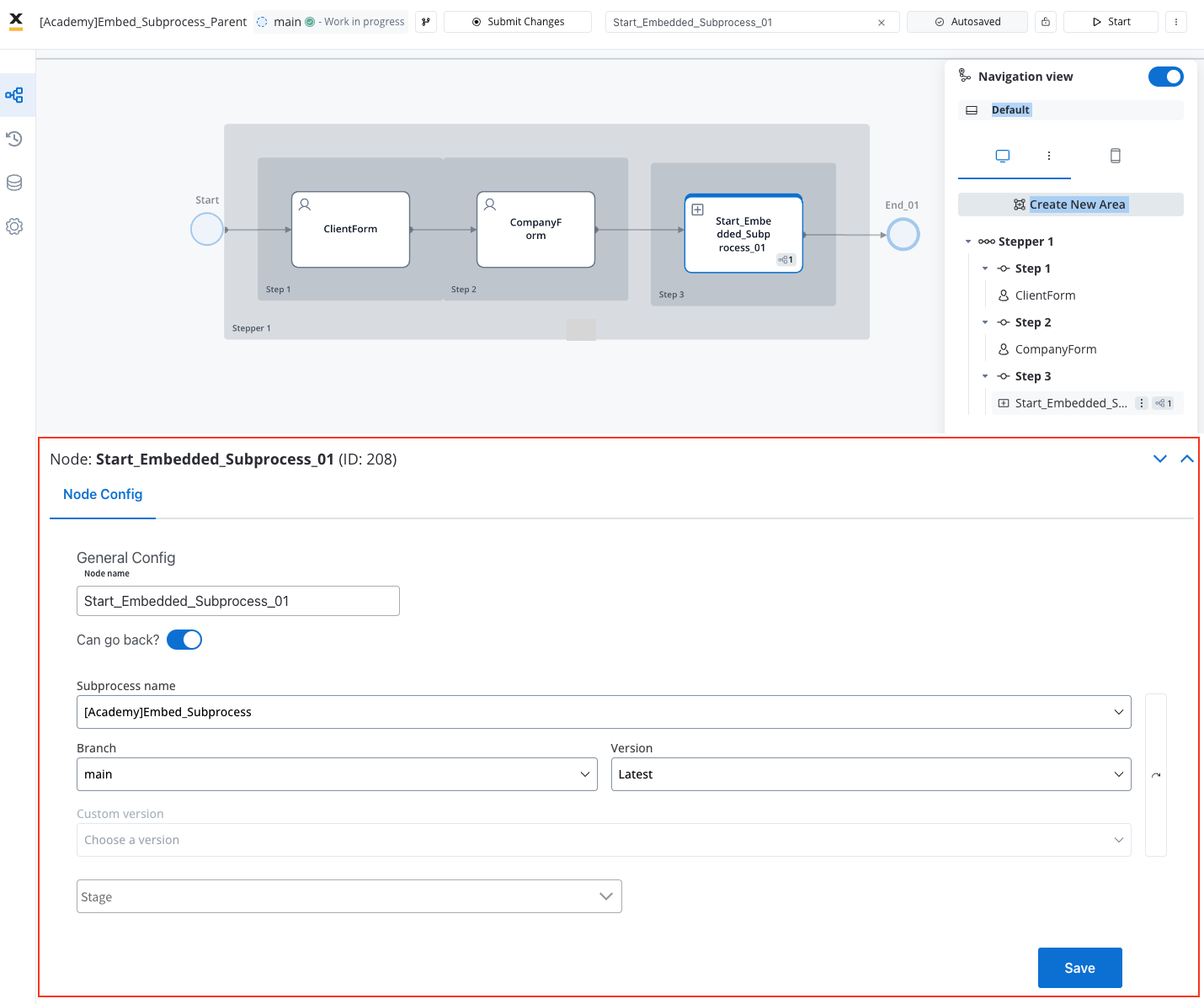
Step 2: Configure Start Embedded Subprocess Node
Add Start Embedded Subprocess Node
Within the parent process, add a Start Embedded Subprocess Node from the node palette to initiate the embedded subprocess.

Step 3: Customize Subprocess Behavior
Alternative flows configured in the main process will also be applied to embedded subprocesses if they share the same name.
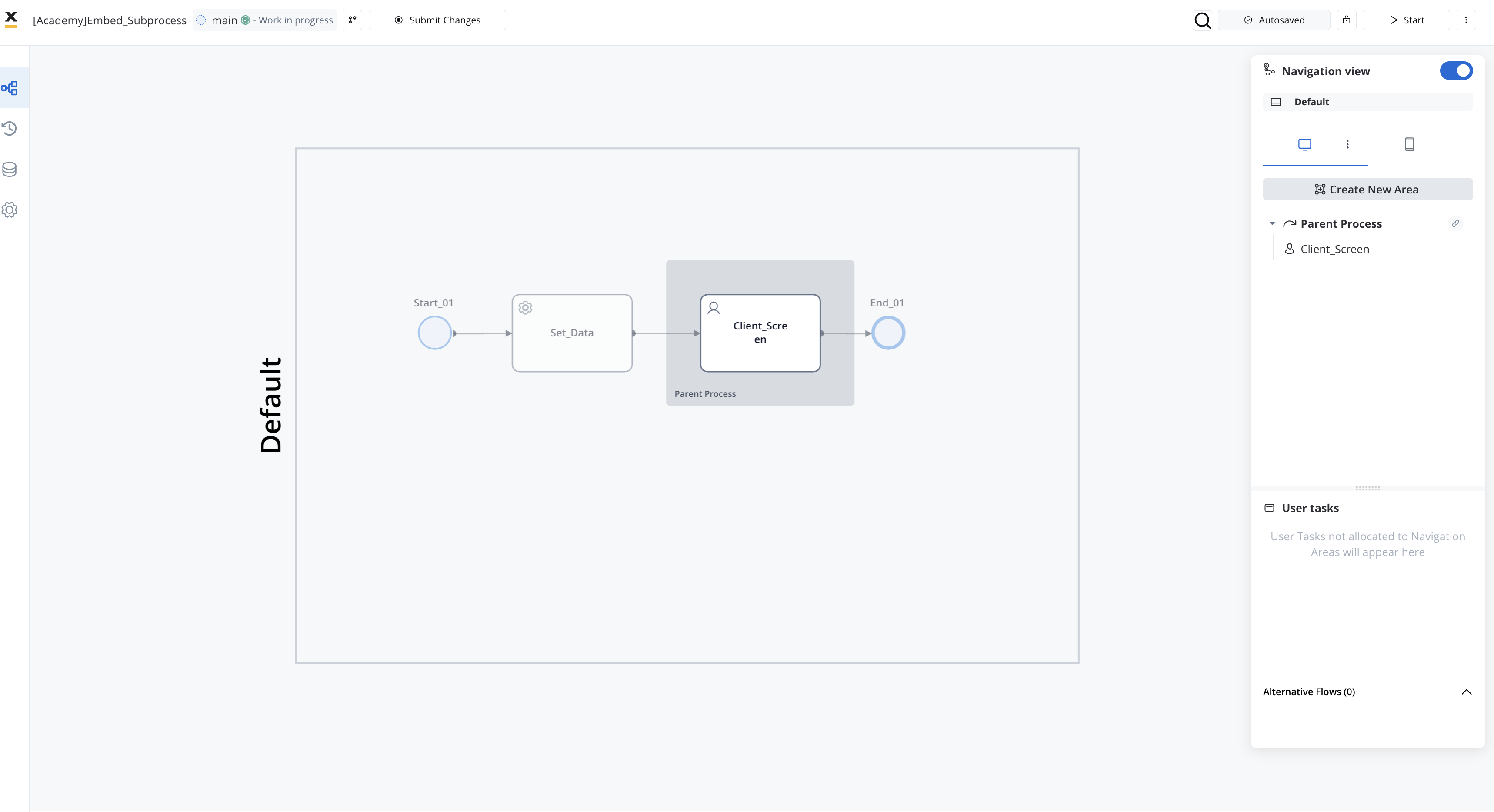
Customize Data Handling
Within the subprocess, handle data as needed. Remember that data is stored within the parent process instance when using embedded subprocesses.
Step 4: Test Integration
Test Functionality
Test the integration of the embedded subprocess within the parent process. Ensure that the subprocess initiates correctly and interacts with the parent process as expected.