The script can read and write the data available on the process at the moment the script is executed. For this reason, it is very important to understand what data is available on the process when the script is executed.
Business rules can be attached to a node by using actions with action rules on them. These can be specified using DMN rules, MVEL expressions, or scripts written in JavaScript, Python, or Groovy.
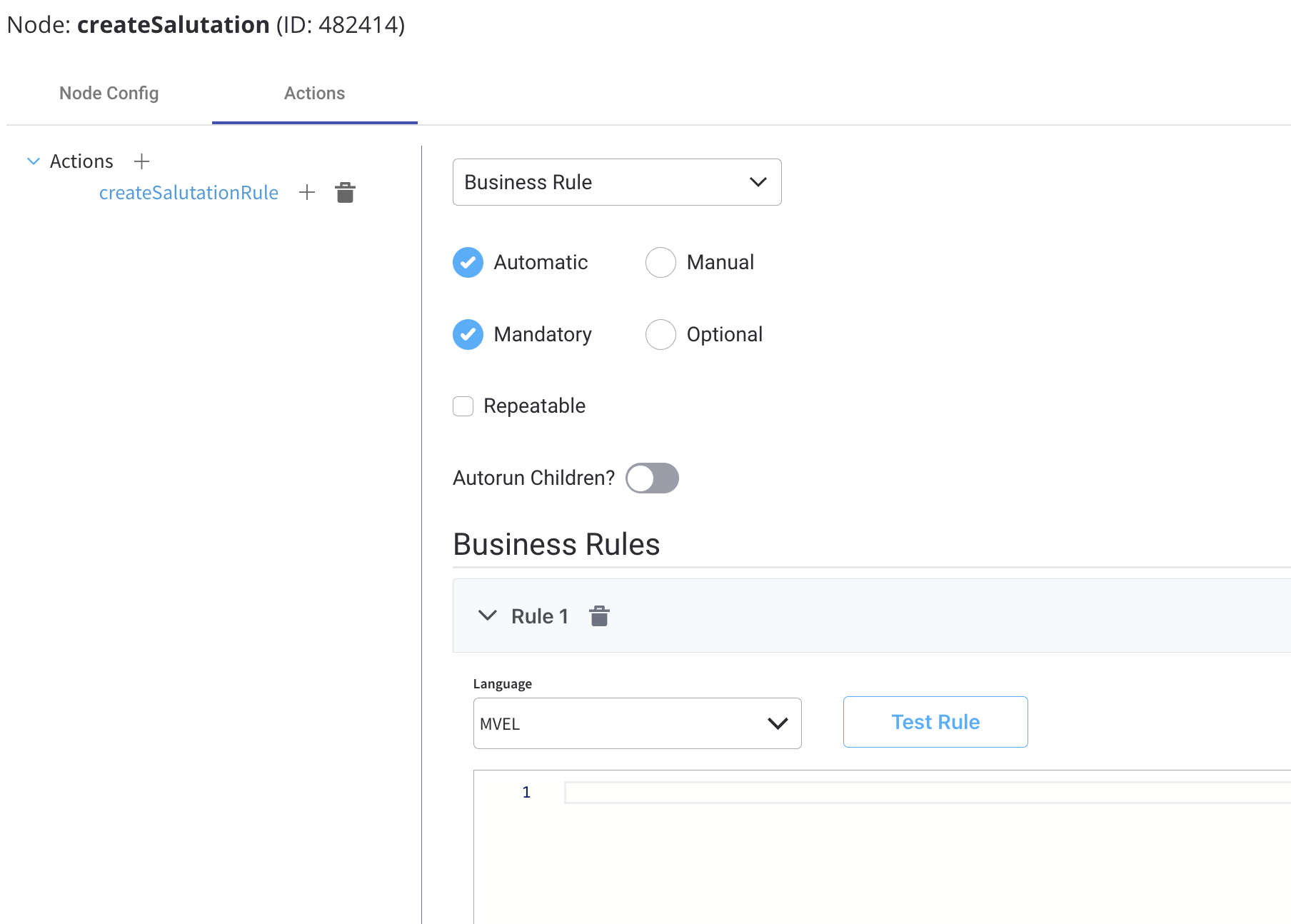 For more information about supported scripting languages, see the next section:
You can also test your rules by using the Test Rule function.
For more information about supported scripting languages, see the next section:
You can also test your rules by using the Test Rule function.
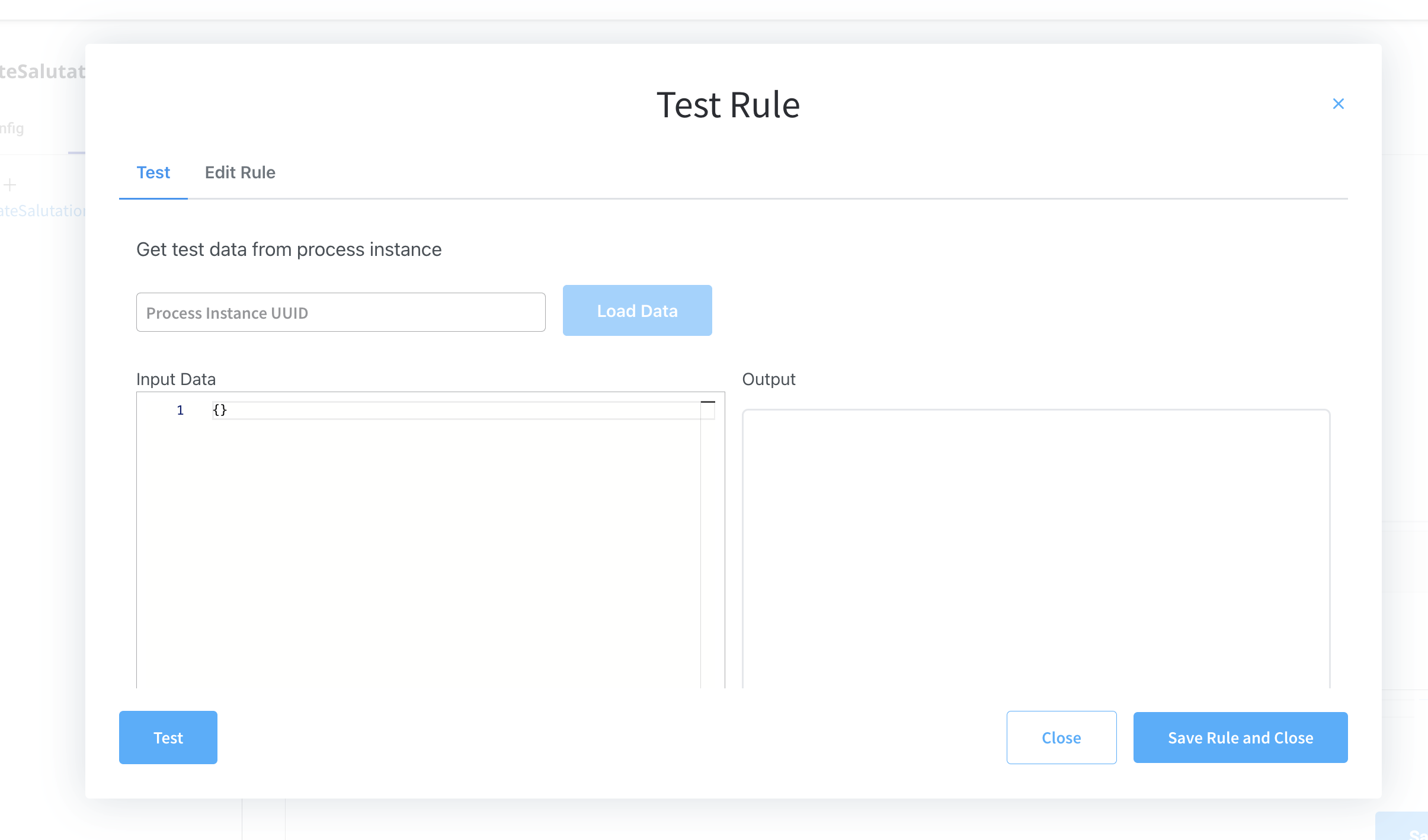
Configuration
To use a Business Rules Action, follow these steps:
- Select a BPMN Task Node: Choose the BPMN task node to which you want to attach the Business Rules Action. This could be a Service Task, User Task, or another task type that supports actions.
- Define the Action: In the task node properties, configure the “Business Rules Action” field and select the desired language (MVEL, Java, JavaScript or Python).
- Write the Business Rule: In the selected language, write the business rule or decision logic. This rule should take input data, process it, and possibly generate an output or result.
- Input and Output Variables: Ensure that the task node can access the necessary input variables from the BPMN process context and store any output or result variables as needed.
- Execution: When the BPMN process reaches the task node, the attached Business Rules Action is executed, and the defined business rule is evaluated.
- Result: The result of the business rule execution may affect the flow of the BPMN process, update process variables, or trigger other actions based on the logic defined in the rule.
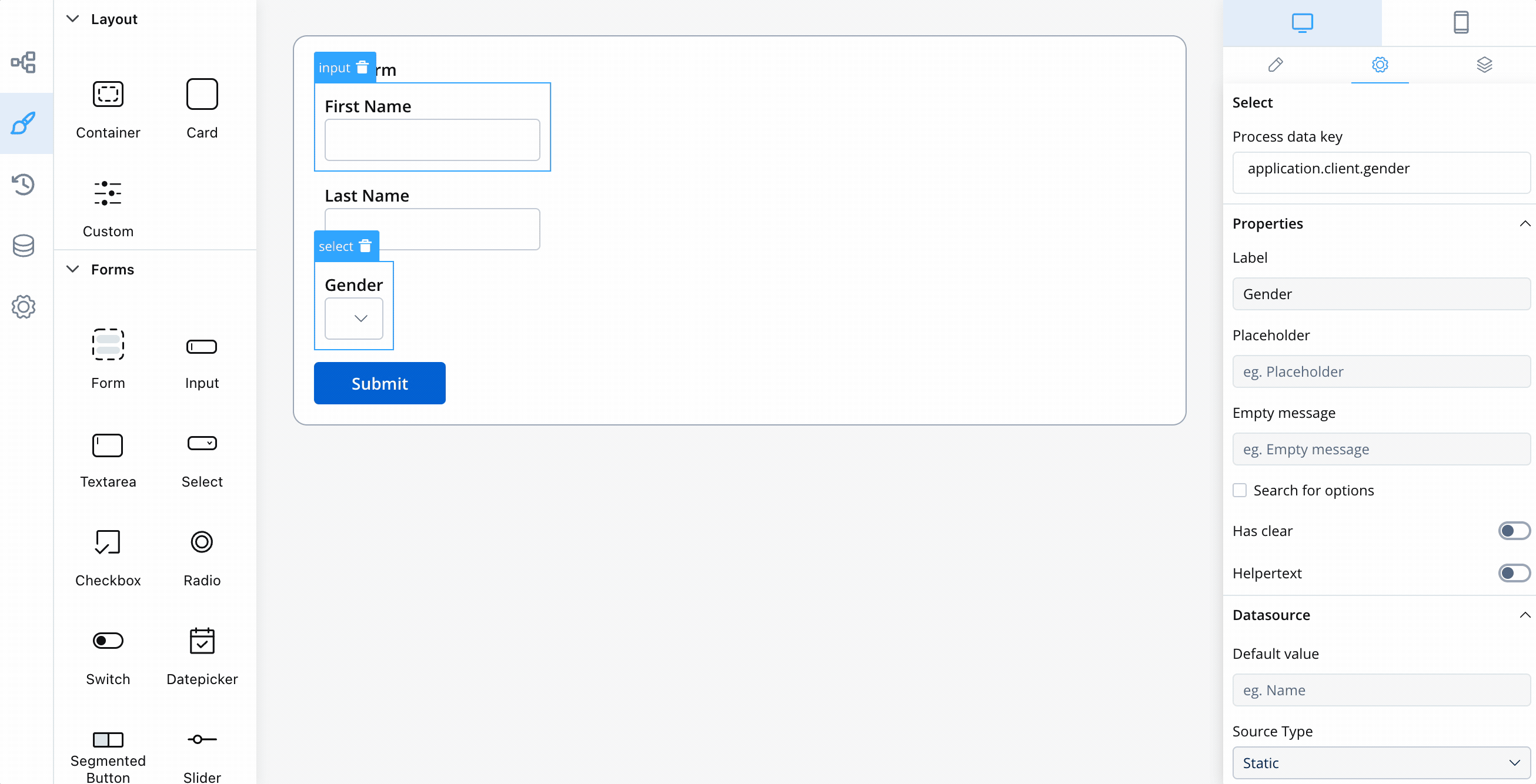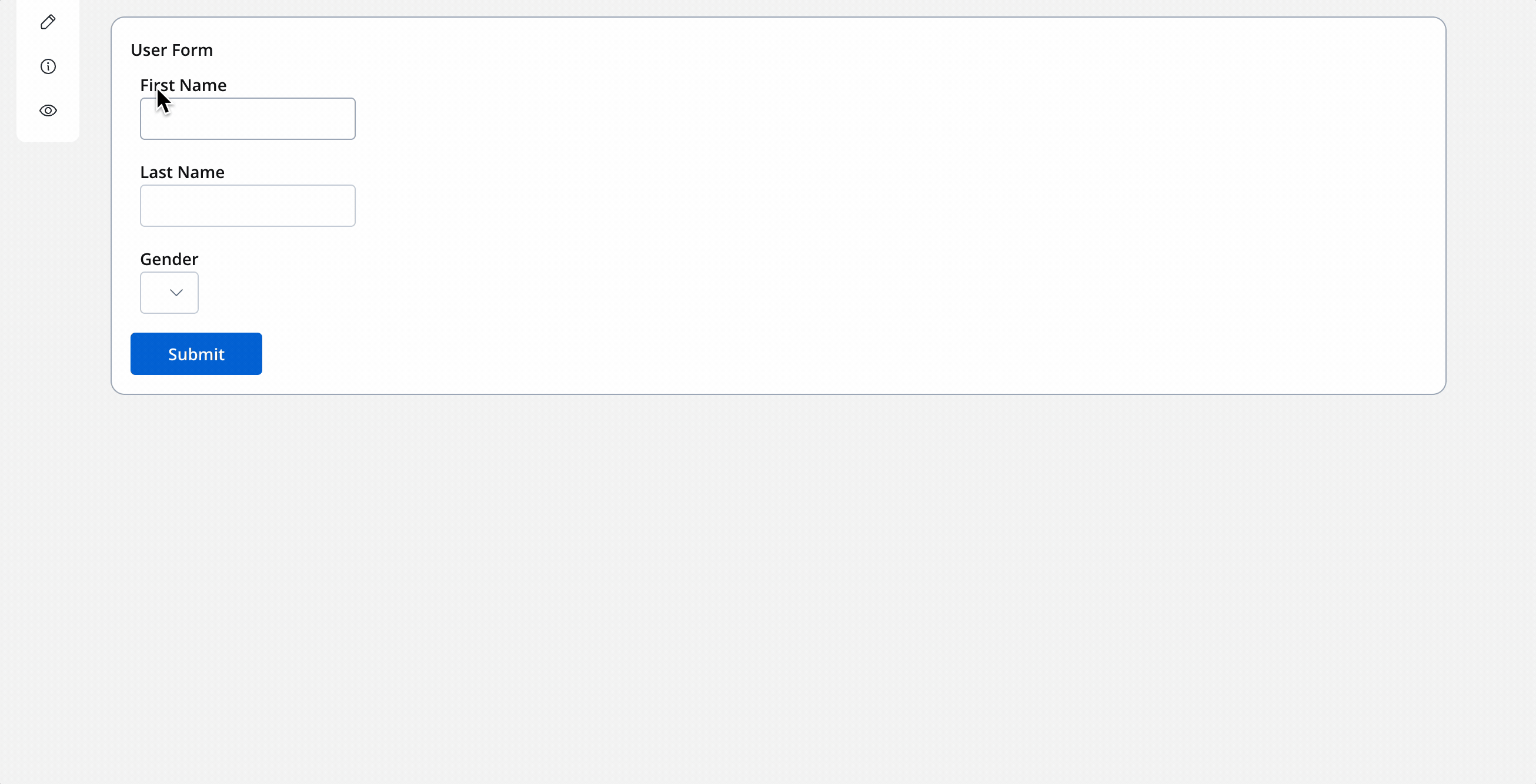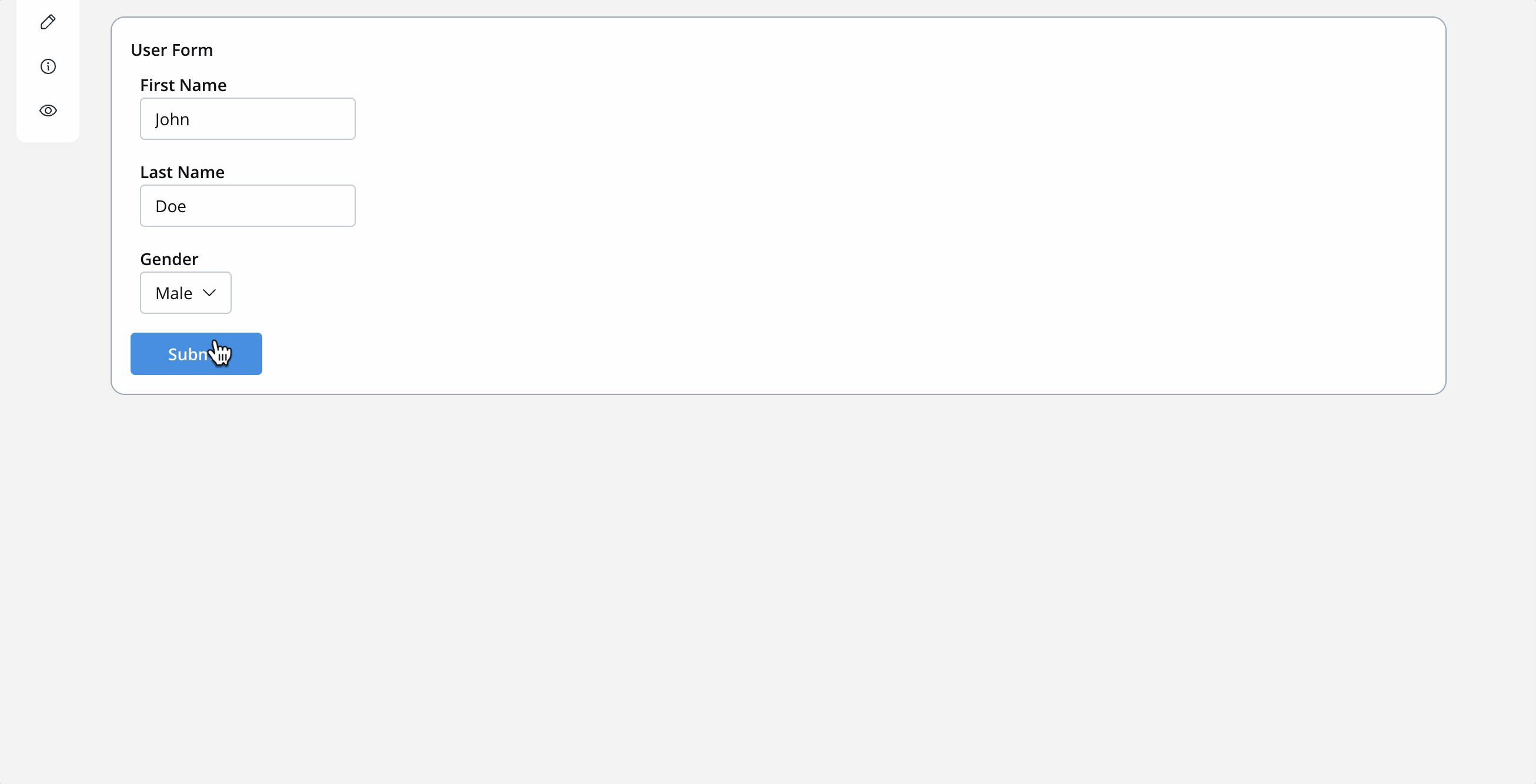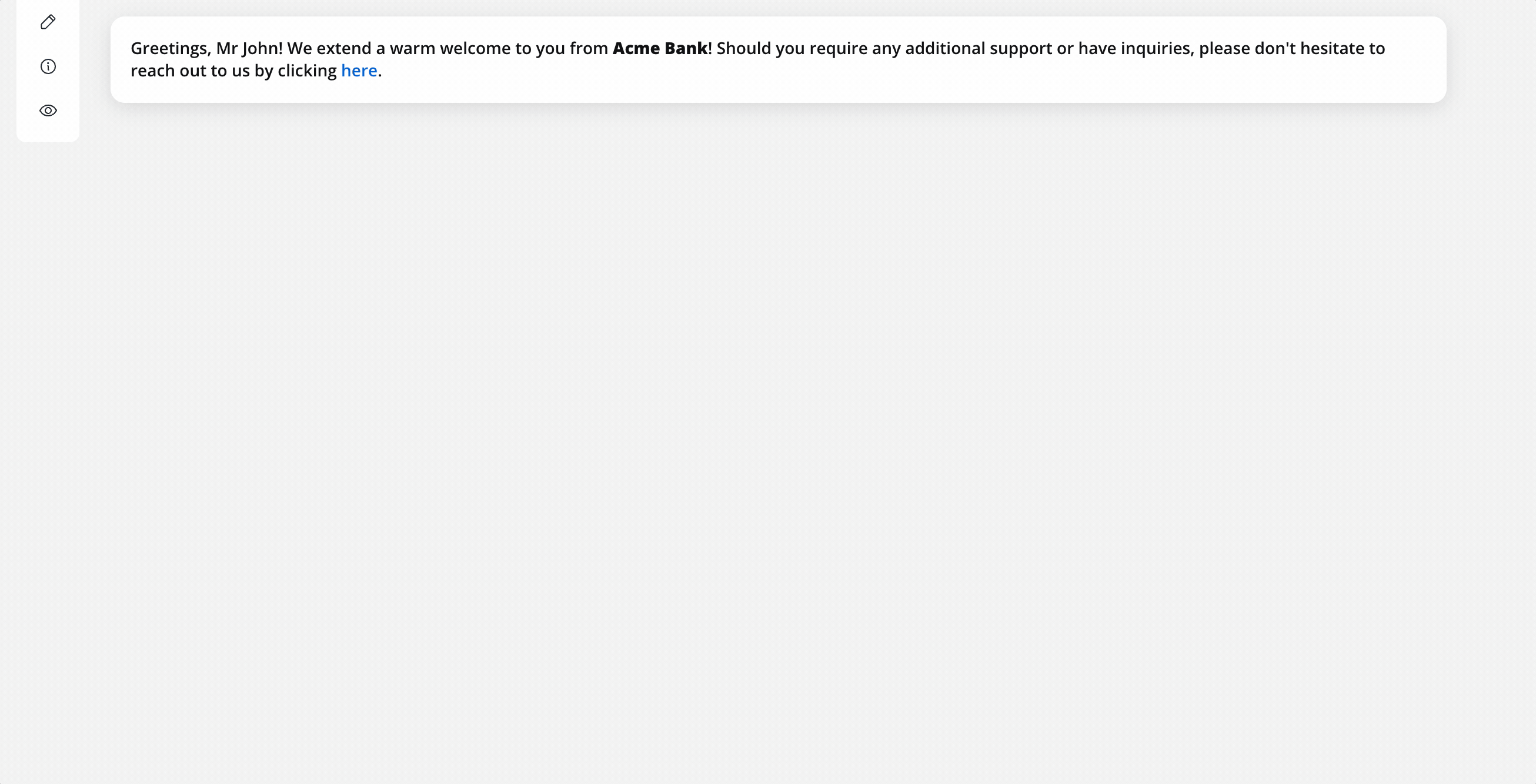
Let’s take look at the following example. We have some data about the gender of a user and we need to create a business rule that computes the formal title based on the gender:
-
This is how the process instance data looks like before it reaches the business rule:
{
"application" : {
"client" :
{
"firstName" : "David",
"surName" : "James",
"gender" : "M",
}
}
}
-
When the token reaches this node the following script (defined for the business rule) is executed. The language used here for scripting is MVEL.
if (input.application.client.gender == 'F') {
output.put("application", {
"client": {
"salutation": "Ms"
}
});
} else if (input.application.client.gender == 'M') {
output.put("application", {
"client": {
"salutation": "Mr"
}
});
} else {
output.put("application", {
"client": {
"salutation": "Mx"
}
});
}
- After the script is executed, the process instance data will look like this:
{
"application": {
"client": {
"firstName": "David",
"surName": "James",
"gender": "M",
"salutation": "Mr"
}
}
}
Flattened vs unflattened keys
With version 2.5.0 we introduced unflattened keys inside business rules. Flattened keys are now obsolete. You are notified when you need to delete and recreate a business rule so it contains an unflattened key. 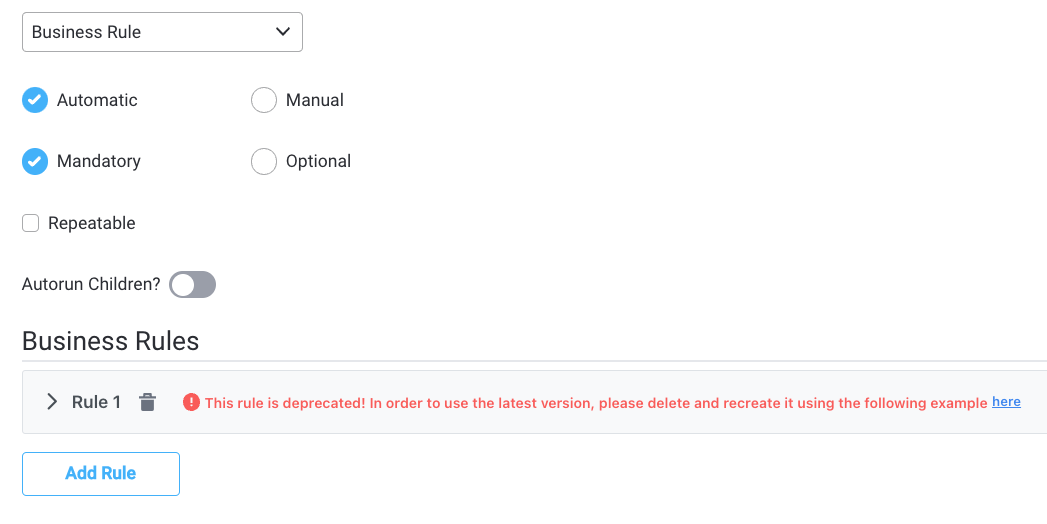
Business rules examples
Examples available for v2.5.0 version and higher if (input.application.client.gender == 'F') {
output.put("application", {
"client": {
"salutation": "Ms"
}
});
} else if (input.application.client.gender == 'M') {
output.put("application", {
"client": {
"salutation": "Mr"
}
});
} else {
output.put("application", {
"client": {
"salutation": "Mx"
}
});
}
if input.get("application").get("client").get("gender") == "F":
output.put("application", {
"client" : {
"salutation" : "Ms"
}
})
elif input.get("application").get("client").get("gender") == "M":
output.put("application", {
"client" : {
"salutation" : "Mr"
}
})
else:
output.put("application", {
"client" : {
"salutation" : "Mx"
}
})
if (input.application.client.gender === 'F') {
output.application = {
client: {
salutation: 'Ms'
}
};
} else if (input.application.client.gender === 'M') {
output.application = {
client: {
salutation: 'Mr'
}
};
} else {
output.application = {
client: {
salutation: 'Mx'
}
};
}
if (input.application.client.gender === 'F') {
def gender = input.application.client.gender
switch (gender) {
case 'F':
output.application = [client: [salutation: 'Ms']]
break
case 'M':
output.application = [client: [salutation: 'Mr']]
break
default:
output.application = [client: [salutation: 'Mx']]
}
Last modified on January 26, 2026
 For more information about supported scripting languages, see the next section:
For more information about supported scripting languages, see the next section:




