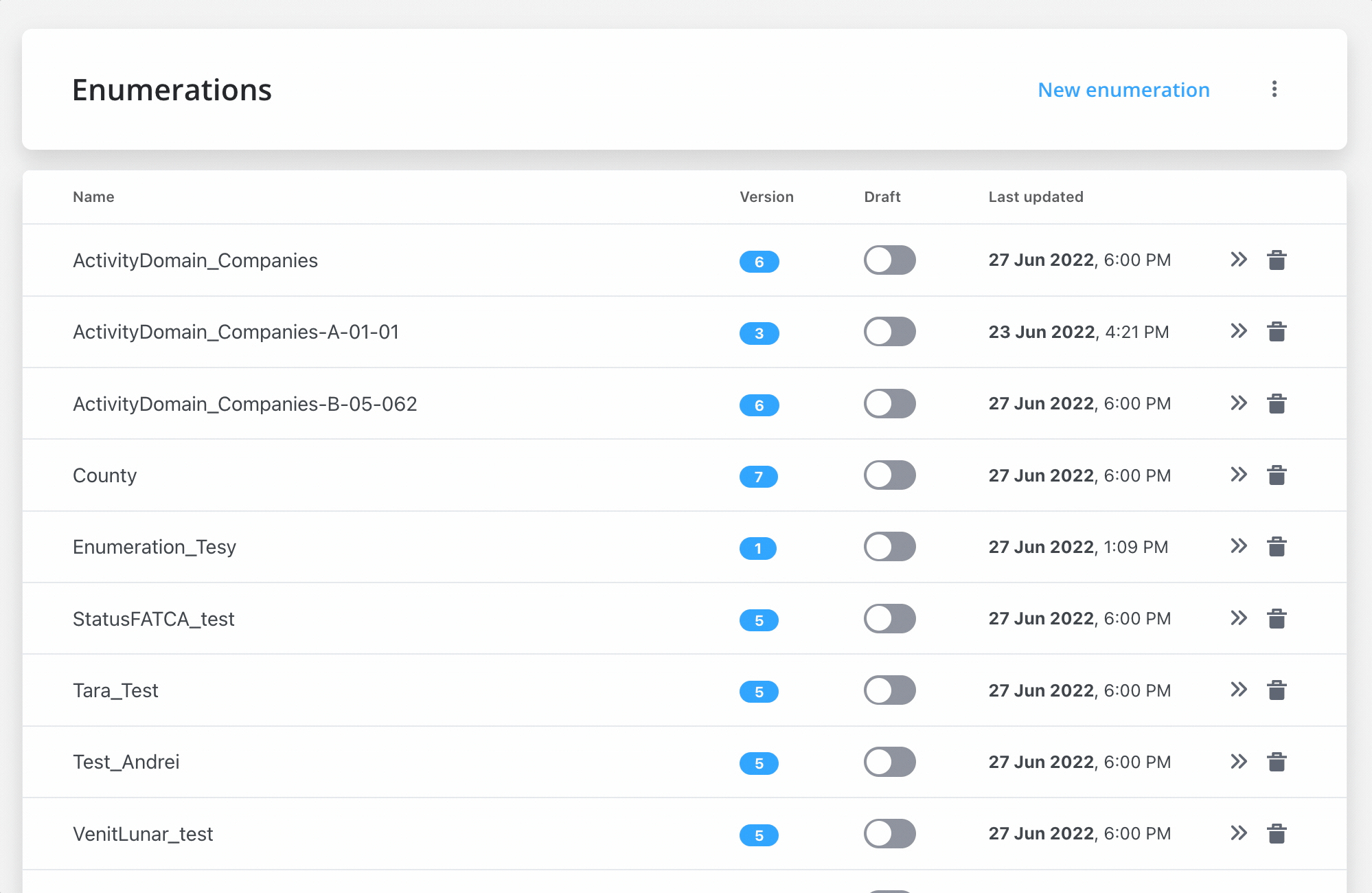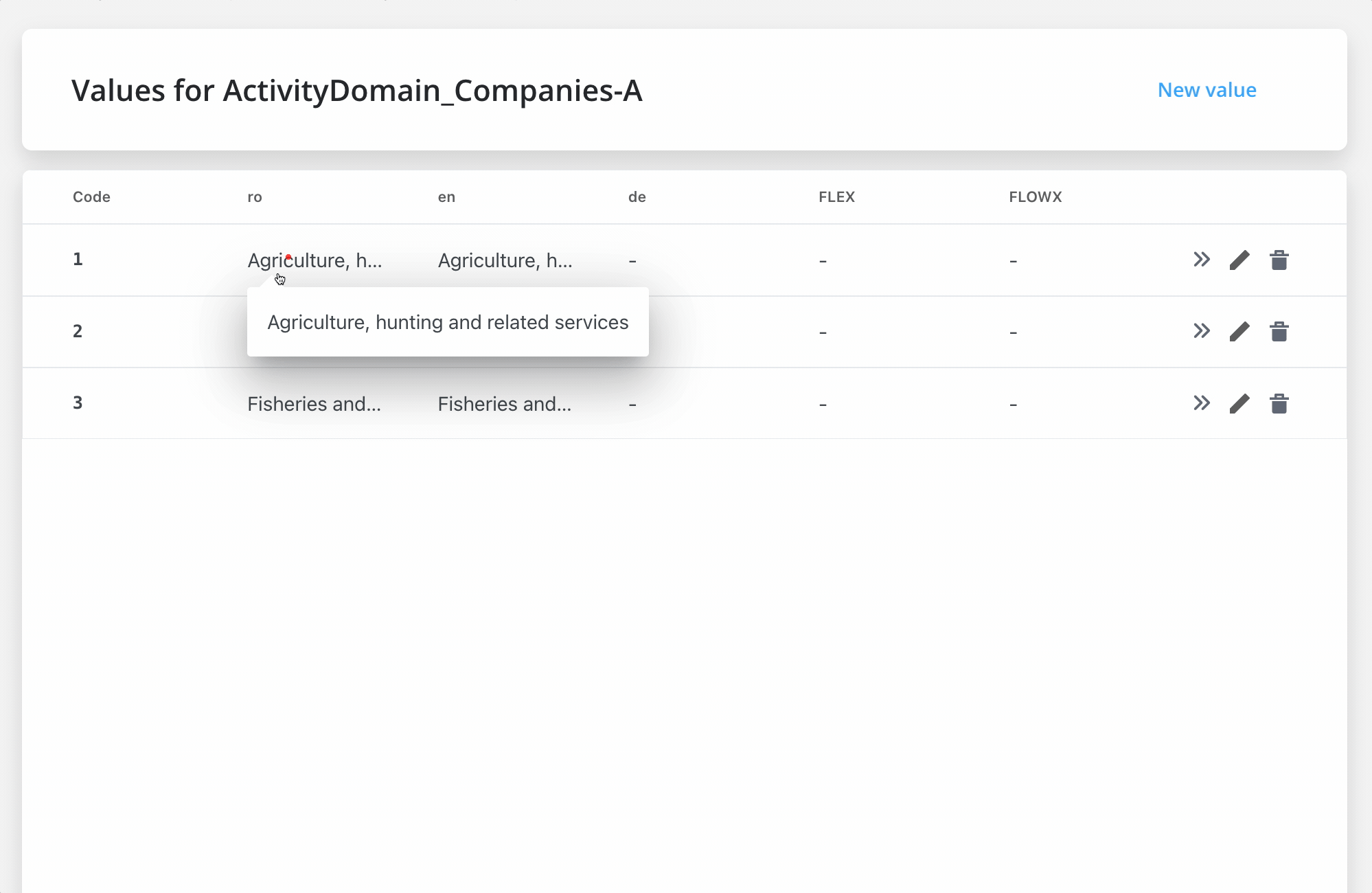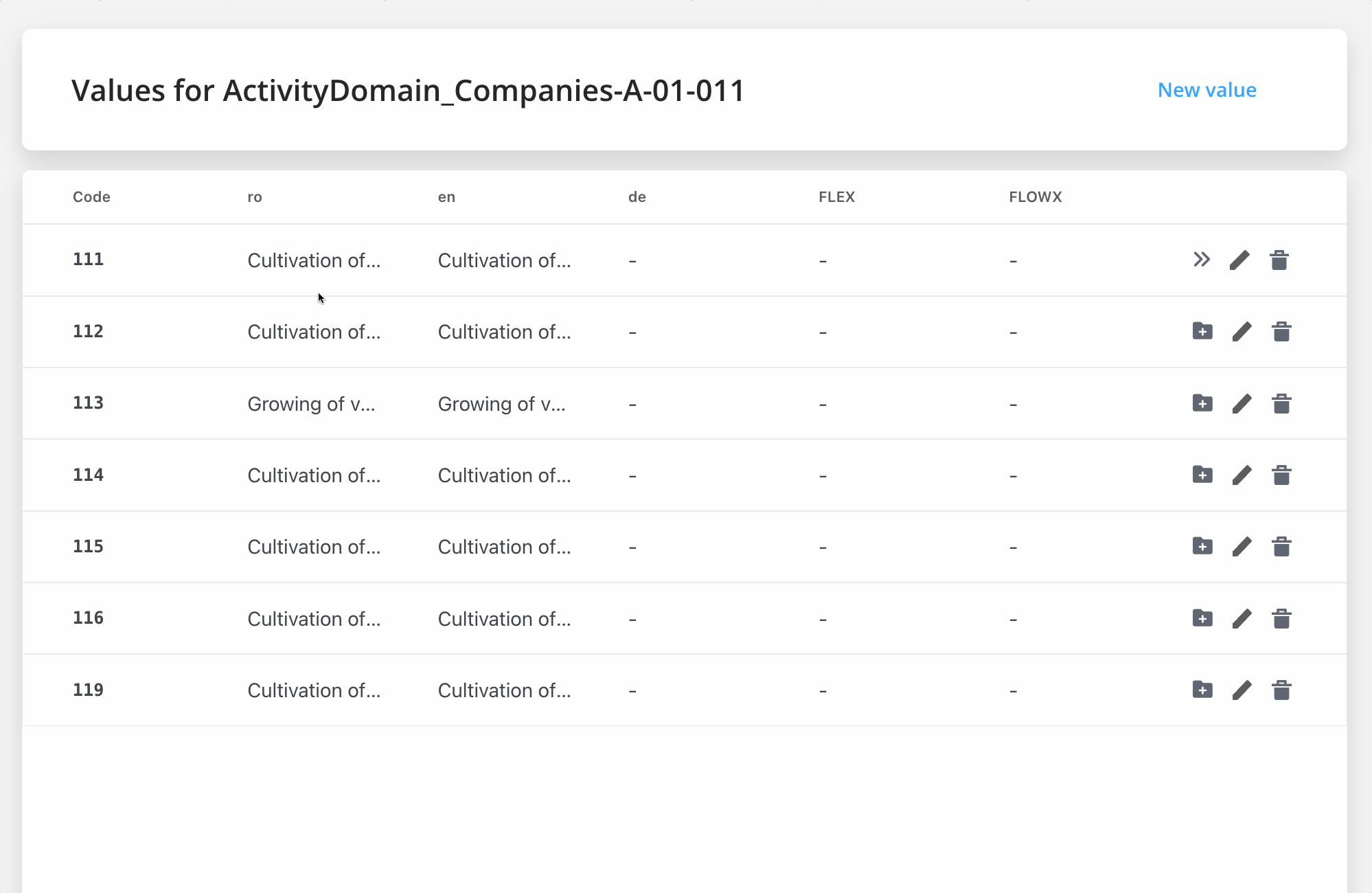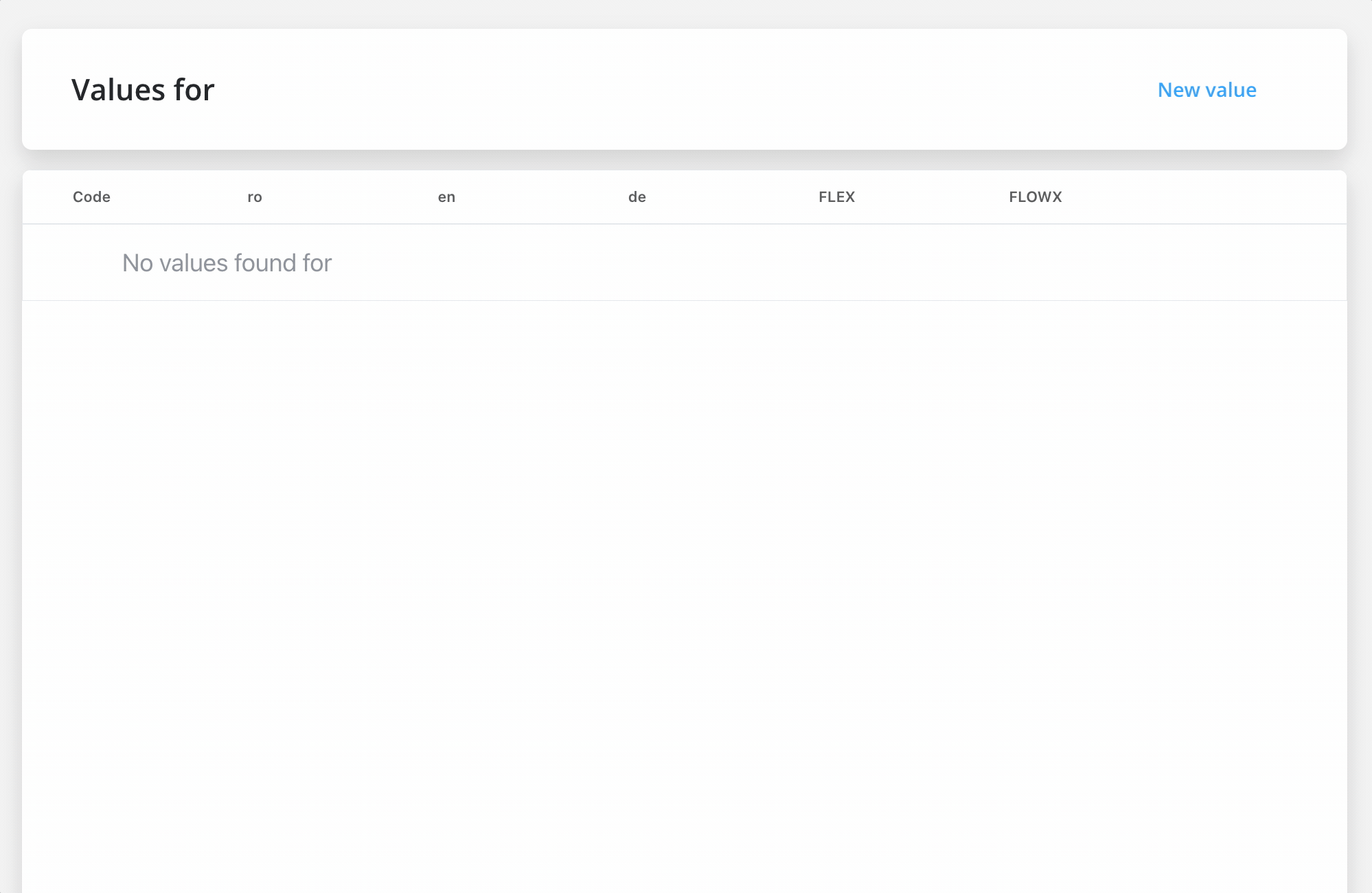
 On the main screen inside Enumerations, you have the following elements:
On the main screen inside Enumerations, you have the following elements:
- Name - the name of the enumeration
- Version - the version of the enumeration
- Draft - switch button used to control the status of an enumeration, could be Draft or Published
- Last Updated - the last time an enumeration has been updated
- Open - button used to access an enumeration to configure it/ add more values, etc.
- Delete - button used to delete an enumeration
- New enumeration - button used to create a new enumeration
- Breadcrumbs - Import/Export
For each entry (when you hit the Open button) inside an enumeration we have to define the following properties:
- Code - not displayed in the end-user interface, but used to assure value uniqueness
- Labels - strings that are displayed in the end-user interface, according to the language set for the generated solution
- External source systems codes - values that are set for each external system that might consume data from the process; these codes are further used by connectors, in other to send to an external system a value that it can validate

Adding a new enumeration
To add a new enumeration, follow the next steps:
- Go to FLOWX Designer and select the Content Management tab.
- Select Enumerations from the list.
- Add a suggestive name for your enumeration and then click Add.

Configuring an enumeration
After creating an enumeration, you can add values to it.
To configure an enumeration value, follow the next steps:
- Go to FLOWX.AI Designer and select the Content Management tab.
- Select Enumerations from the list and open an enumeration.
- Click New value and fill in the necessary details:
- Code - as mentioned above, this is not displayed in the end-user interface but is used to assure value uniqueness
- Labels - set the value of the string for each language you would like to use
- Source Systems - values that are set for each external system that might consume data from the process

Creating a child collection
Enumerations can also be defined as a hierarchy - for each entry, we can define a list of children values (for example, name of the countries defined under the continents’ enumeration values); hierarchies further enable cascading values in the end-user interface (for example, after selecting a continent in the first select UI component, the second select component will contain only the children of this continent).

Importing/exporting an enumeration
You can use the import/export feature to import or export enumerations using the following formats:

Enumerations example
Enumerations, for instance, can be used to build elaborate lists of values (with children). Assuming you wish to add enumerations for Activity Domain Companies, you can create children collections by grouping lists and other related domains and activities.
We have the following example for Activity Domain Companies:
Activity Domain Companies → Agriculture forestry and fishing:
- Agriculture, hunting, and related services →
- Fisheries and aquaculture →
This is the output after adding all the lists/collections from above:
Last modified on January 26, 2026
 On the main screen inside Enumerations, you have the following elements:
On the main screen inside Enumerations, you have the following elements:







