Infrastructure prerequisites
The Integration Designer service requires the following components to be set up before it can be started:- PostgreSQL - version 13 or higher for managing advancing data source
- MongoDB - version 4.4 or higher for managing integration and runtime data
- Kafka - version 2.8 or higher for event-driven communication between services
- OAuth2 Authentication - Ensure a Keycloak server or compatible OAuth2 authorization server is configured
Dependencies
Configuration
Config profile
CONFIG_PROFILE- This environment variable must be set explicitly and exactly to ensure that no unintended profiles are loaded by mistake. The value of this variable should represent a minimal configuration state, relying only on defaults specified in theapplication.propertiesfile of the application.
Database configuration
Integration Designer uses both PostgreSQL and MongoDB for managing advancing data and integration information. Configure these database connections with the following environment variables:PostgreSQL (Advancing data source)
ADVANCING_DATASOURCE_URL- Database URL for the advancing data source in PostgreSQLADVANCING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME- Username for the advancing data source in PostgreSQLADVANCING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD- The password for the advancing data source in PostgreSQL.- Details: Must match the credentials configured in the PostgreSQL database.
ADVANCING_DATASOURCE_DRIVER_CLASS_NAME- The database driver class name for the advancing data source- Details: Required to ensure proper database connectivity. This value can be overridden for other databases, such as Oracle.
- For PostgreSQL:
org.postgresql.Driver - For Oracle:
oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
- For PostgreSQL:
- Details: Required to ensure proper database connectivity. This value can be overridden for other databases, such as Oracle.
MongoDB (Integration data and runtime data)
Integration Designer requires two MongoDB databases for managing integration-specific data and runtime data. Theintegration-designer database is dedicated to Integration Designer, while the shared app-runtime database supports multiple services.
- Integration Designer Database (
integration-designer): Stores data specific to Integration Designer, such as integration configurations, metadata, and other operational data. - Shared Runtime Database (
app-runtime): Shared across multiple services, this database manages runtime data essential for integration and data flow execution.
SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_URI- URI for connecting to the Integration Designer MongoDB instance- Format:
mongodb://${DB_USERNAME}:${DB_PASSWORD}@<host1>,<host2>,<arbiter-host>:<port>/${DB_NAME}?retryWrites=false
- Format:
DB_USERNAME:integration-designerDB_NAME:integration-designerDB_PASSWORD: DB password.SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_STORAGE- Specifies the storage type used for the Runtime MongoDB instance (Azure environments only)- Possible Values:
mongodb,cosmosdb - Default Value:
mongodb
- Possible Values:
Integration Designer requires a runtime connection to function correctly. Starting the service without a configured and active runtime MongoDB connection is not supported.
SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_RUNTIME_URI- URI for connecting to MongoDB for Runtime MongoDB (app-runtime)- Format:
SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_RUNTIME_URI:mongodb://${RUNTIME_DB_USERNAME}:${RUNTIME_DB_PASSWORD}@<host1>,<host2>,<arbiter-host>:<port>/${RUNTIME_DB_NAME}?retryWrites=false
- Format:
RUNTIME_DB_USERNAME:app-runtimeRUNTIME_DB_NAME:app-runtimeRUNTIME_DB_PASSWORD: DB password.
Dynamic configuration parameters retrieval
The Integration Designer supports dynamic retrieval of configuration parameters from Kubernetes secrets and ConfigMaps. This feature enables secure management of environment variables and sensitive configuration data without hardcoding values in the application.| Environment variable | Description | Default value | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_VARS_PROVIDER_TYPE | Provider type for environment variables | k8s | k8s |
FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_SECRETS_PROVIDER_TYPE | Provider type for secrets | k8s | k8s |
FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_K8S_SECRETS_0 | First Kubernetes secret name | flowx-rt | Any valid Kubernetes secret name |
FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_K8S_CONFIGMAPS_0 | First Kubernetes ConfigMap name | flowx-rt | Any valid Kubernetes ConfigMap name |
You can configure multiple secrets and ConfigMaps by incrementing the index number (e.g.,
FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_K8S_SECRETS_1, FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_K8S_CONFIGMAPS_1). Values are overridden based on the order in which the maps are defined.Kubernetes resources setup
To use this configuration, create the following resources in the cluster namespace where the platform operates:- Secret: Name specified in
FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_K8S_SECRETS_0(default:flowx-rt) - ConfigMap: Name specified in
FLOWX_CONFIG_PARAMS_K8S_CONFIGMAPS_0(default:flowx-rt)
Configuring Kafka
To configure Kafka for Integration Designer, set the following environment variables. This configuration includes naming patterns, consumer group settings, and retry intervals for authentication exceptions.General Kafka configuration
SPRING_KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS- Address of the Kafka server in the formathost:portKAFKA_TOPIC_NAMING_ENVIRONMENT- Environment-specific suffix for Kafka topicsFLOWX_WORKFLOW_CREATETOPICS- To automatically create kafka topics for development environments- When set to true: In development environments, where Kafka topics may need to be created automatically, this configuration can be enabled (flowx.workflow.createTopics: true). This allows for the automatic creation of “in” and “out” topics when workflows are created, eliminating the need to wait for topic creation at runtime.
- Default setting (false): In production or controlled environments, where automated topic creation is not desired, this setting remains false to prevent unintended Kafka topic creation.
Kafka consumer settings
-
KAFKA_CONSUMER_GROUP_ID_START_WORKFLOWS- Consumer group ID for starting workflows- Default Value:
start-workflows-group
- Default Value:
-
KAFKA_CONSUMER_THREADS_START_WORKFLOWS- Number of Kafka consumer threads for starting workflows- Default Value:
3
- Default Value:
-
KAFKA_AUTH_EXCEPTION_RETRY_INTERVAL- Interval (in seconds) between retries after anAuthorizationException- Default Value:
10
- Default Value:
Kafka topic naming structure
The Kafka topics for Integration Designer use a structured naming convention with dynamic components, allowing for easy integration across environments. This setup defines separators, environment identifiers, and specific naming patterns for both engine and integration-related messages.Topic naming components
| Component | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
package | Package identifier for namespace | ai.flowx. |
environment | Environment identifier | dev. |
version | Version identifier for topic compatibility | .v1 |
separator | Primary separator for components | . |
separator2 | Secondary separator for additional distinction | - |
prefix | Combines package and environment as a topic prefix | ${kafka.topic.naming.package}${kafka.topic.naming.environment} |
suffix | Appends version to the end of the topic name | ${kafka.topic.naming.version} |
Predefined patterns for services
-
Engine Receive Pattern -
kafka.topic.naming.engineReceivePattern- Pattern:
engine${dot}receive${dot} - Example Topic Prefix:
ai.flowx.dev.engine.receive.
- Pattern:
-
Integration Receive Pattern -
kafka.topic.naming.integrationReceivePattern- Pattern:
integration${dot}receive${dot} - Example Topic Prefix:
ai.flowx.dev.integration.receive.
- Pattern:
Kafka topics
- Events Gateway - Outgoing Messages
- Topic:
${kafka.topic.naming.prefix}eventsgateway${dot}receive${dot}workflowinstances${kafka.topic.naming.suffix} - Purpose: Topic for outgoing workflow instance messages from the events gateway
- Example Value:
ai.flowx.dev.eventsgateway.receive.workflowinstances.v1
- Topic:
Note: The 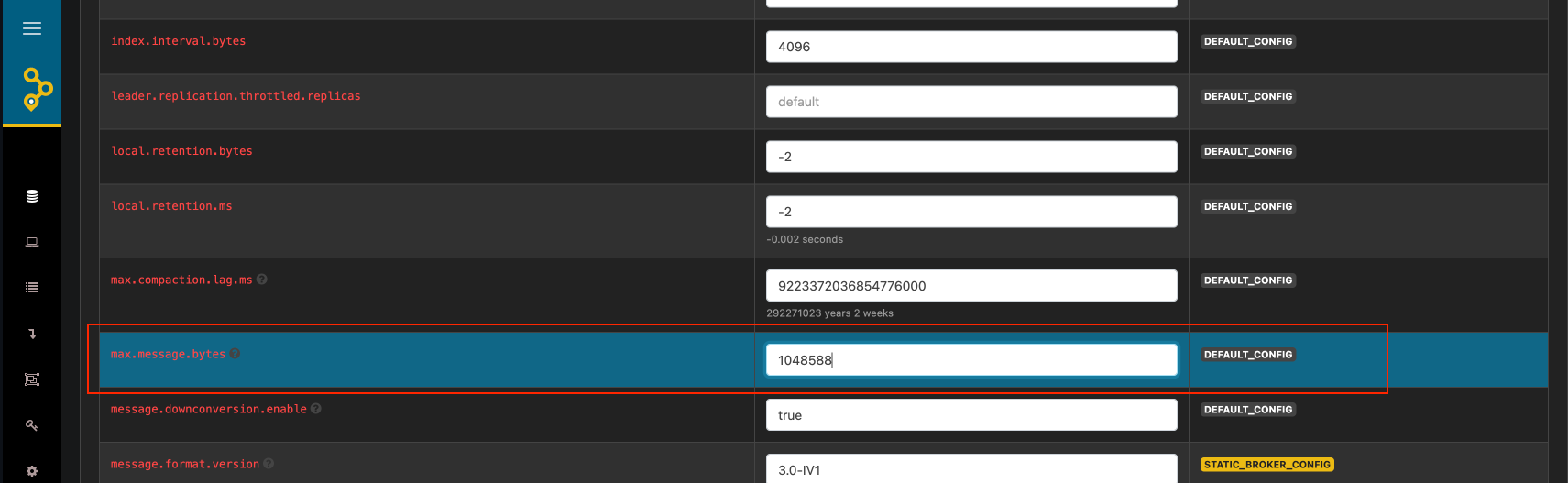 You can do that by using the following procedure:
You can do that by using the following procedure:
Alternative Method: Using Kafka CLIIf AKHQ is not available, you can update the topic configuration via the Kafka CLI:
max.message.bytes configuration should be updated for this topic to ensure compatibility with Integration Designer message sizes.
How to Update `max.message.bytes` Using AKHQ
How to Update `max.message.bytes` Using AKHQ
-
Access AKHQ:
- Open the AKHQ web interface in your browser.
- Log in if authentication is required.
-
Navigate to the Topic:
- Go to the “Topics” section.
- Search for the topic:
ai.flowx.dev.eventsgateway.receive.workflowinstances.v1.
-
Edit Topic Configuration:
- Click on the topic name to view its details.
- Go to the “Configuration” tab or section.
- Locate the
max.message.bytessetting. If it’s not present, add it.
-
Update the Setting:
- Enter the desired value for
max.message.bytes(e.g.,10485760for 10 MB). - Save the changes.
- Enter the desired value for
-
Validation:
- Confirm that the configuration has been successfully updated.
- Optionally, restart any relevant producers or consumers if required (though Kafka applies this setting dynamically in most cases).
Alternative Method: Using Kafka CLIIf AKHQ is not available, you can update the topic configuration via the Kafka CLI:
-
Engine Pattern
- Pattern:
${kafka.topic.naming.prefix}${kafka.topic.naming.engineReceivePattern} - Purpose: Topic pattern for receiving messages by the engine service
- Example Value:
ai.flowx.dev.engine.receive.*
- Pattern:
-
Integration Pattern
- Pattern:
${kafka.topic.naming.prefix}${kafka.topic.naming.integrationReceivePattern}* - Purpose: Topic pattern for receiving messages by the integration service
- Example Value:
ai.flowx.dev.integration.receive.*
- Pattern:
Replace placeholders with appropriate values for your environment before starting the service.
Configuring WebClient buffer size
Integration Designer interacts with various APIs, some of which return large responses. To handle such cases efficiently, the FlowX WebClient buffer size must be configured to accommodate larger payloads, especially when working with legacy APIs that do not support pagination.FLOWX_WEBCLIENT_BUFFERSIZE- Specifies the buffer size (in bytes) for the FlowX WebClient. Default value1048576 (1MB)
If you encounter truncated API responses or unexpected errors when fetching large payloads, consider increasing the buffer size to at least 10MB by setting
FLOWX_WEBCLIENT_BUFFERSIZE=10485760. This ensures smooth handling of large API responses, particularly for legacy APIs without pagination support.Configuring authentication and access roles
Integration Designer uses OAuth2 for secure access control. Set up OAuth2 configurations with these environment variables:SECURITY_OAUTH2_BASE_SERVER_URL- Base URL for the OAuth 2.0 Authorization ServerSECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_CLIENT_ID- Unique identifier for the client application registered with the OAuth 2.0 serverSECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_CLIENT_SECRET- Secret key for authenticating requests made by the authorization clientSECURITY_OAUTH2_REALM- The realm name for OAuth2 authenticationSECURITY_OAUTH2_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ADMIN_CLIENT_ID- Client ID for the integration designer service accountSECURITY_OAUTH2_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ADMIN_CLIENT_SECRET- Client Secret for the integration designer service account
Access Management
Integration Designer service account
Authentication and access roles
SECURITY_OAUTH2_BASE_SERVER_URL- Base URL for the OAuth2 authorization serverSECURITY_OAUTH2_REALM- Realm for OAuth2 authenticationSECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_CLIENT_ID- Client ID for the Integration Designer OAuth2 clientSECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_CLIENT_SECRET- Client Secret for the Integration Designer OAuth2 clientSECURITY_OAUTH2_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ADMIN_CLIENT_ID- Client ID for the Keycloak admin service accountSECURITY_OAUTH2_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ADMIN_CLIENT_SECRET- Client Secret for the Keycloak admin service account
Configuring loogging
To control the log levels for Integration Designer, set the following environment variables:LOGGING_LEVEL_ROOT- The log level for root Spring Boot microservice logsLOGGING_LEVEL_APP- The log level for application-level logs
Configuring admin ingress
Integration Designer provides an admin ingress route, which can be enabled and customized with additional annotations for SSL certificates or routing preferences.- Enabled: Set to
trueto enable the admin ingress route. - Hostname: Define the hostname for admin access.
Monitoring and maintenance
To monitor the performance and health of the Application Manager, use tools like Prometheus or Grafana. Configure Prometheus metrics with the following environment variable:MANAGEMENT_PROMETHEUS_METRICS_EXPORT_ENABLED- Enables or disables Prometheus metrics export (default: false).
RBAC configuration
Integration Designer requires specific RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) permissions to access Kubernetes ConfigMaps and Secrets, which store necessary configurations and credentials. Set up these permissions by enabling RBAC and defining the required rules.rbac.create: Set to true to create RBAC resources.rbac.rules: Define custom RBAC rules as follows:
get, list, watch) to ConfigMaps, Secrets, and Pods, which is essential for retrieving application settings and credentials required by Integration Designer.
